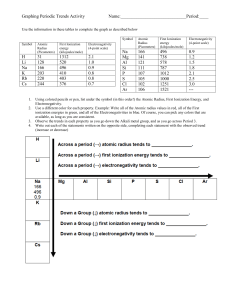
Chemistry Review Questions: Periodic Trends & Oxides
advertisement
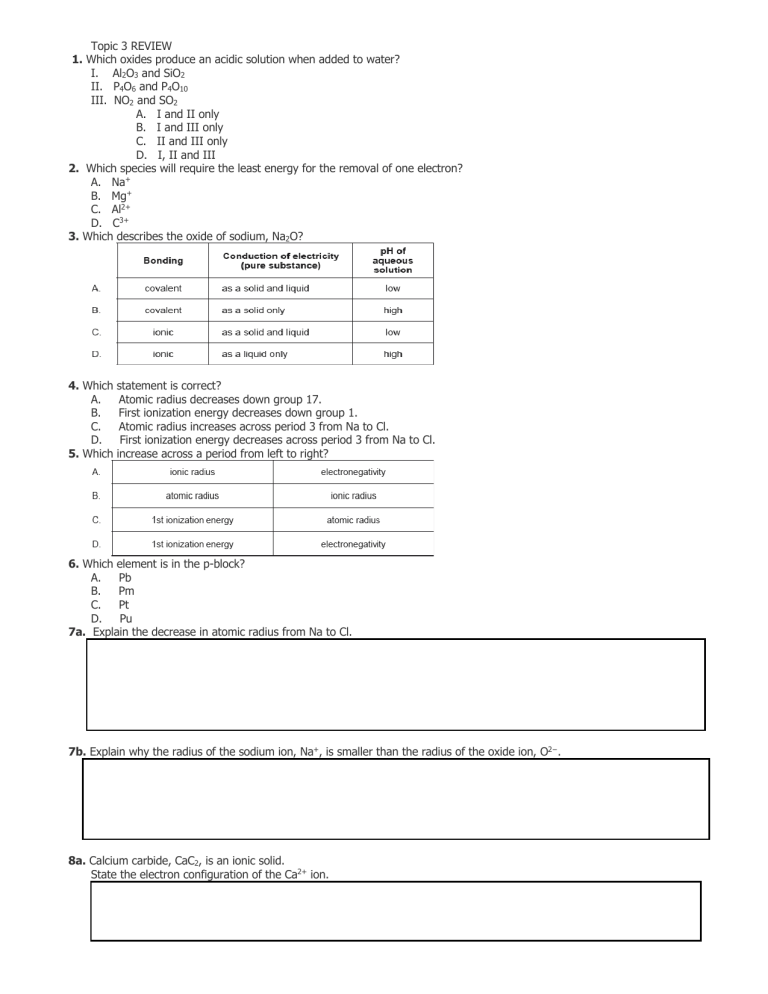
Topic 3 REVIEW 1. Which oxides produce an acidic solution when added to water? I. Al2O3 and SiO2 II. P4O6 and P4O10 III. NO2 and SO2 A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 2. Which species will require the least energy for the removal of one electron? A. Na+ B. Mg+ C. Al2+ D. C3+ 3. Which describes the oxide of sodium, Na2O? 4. Which statement is correct? A. Atomic radius decreases down group 17. B. First ionization energy decreases down group 1. C. Atomic radius increases across period 3 from Na to Cl. D. First ionization energy decreases across period 3 from Na to Cl. 5. Which increase across a period from left to right? 6. Which element is in the p-block? A. Pb B. Pm C. Pt D. Pu 7a. Explain the decrease in atomic radius from Na to Cl. 7b. Explain why the radius of the sodium ion, Na+, is smaller than the radius of the oxide ion, O2−. 8a. Calcium carbide, CaC2, is an ionic solid. State the electron configuration of the Ca2+ ion. 8c. Outline why solid calcium is a good conductor of electricity. 9b. Outline why the ionic radius of K+ is smaller than that of Cl−. 11. Calcium carbide, CaC2, is an ionic solid. Sketch a graph of the first six ionization energies of calcium. 12. Which trends are correct across period 3 (from Na to Cl)? I. Atomic radius decreases II. Melting point increases III. First ionization energy increases A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 13. Which oxide dissolves in water to give a solution with a pH below 7? A. MgO B. Li2O C. CaO D. P4O10 15. Which metal has the strongest metallic bond? A. Li B. Na C. K D. Rb 16. Which property increases down Group 1, the alkali metals? A. Atomic radius B. Electronegativity C. First ionization energy D. Melting point 17. Which element is a lanthanide? A. Hf B. Tb C. U D. Y 18. Which electron configuration is that of a transition metal atom in the ground state? A. [Ne]3s23p64s1 B. [Ar]3d9 C. 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p2 D. [Ar]4s13d5 19. What is the order of decreasing ionic radius? A. S2− > Cl− > Al3+ > Mg2+ B. Cl− > S2− > Al3+ > Mg2+ C. S2− > Cl− > Mg2+ > Al3+ D. Mg2+ > Al3+ > Cl− > S2− 20. X, Y and Z represent the successive elements, Ne, Na and Mg, but not necessarily in that order. What is the order of increasing atomic number? A. X<Y<Z B. X<Z<Y C. Y<Z<X D. Y<X<Z 21a. Trends in physical and chemical properties are useful to chemists. Explain the general increasing trend in the first ionization energies of the period 3 elements, Na to Ar. 21c. State an equation for the reaction of phosphorus (V) oxide, P4O10 (s), with water. 22. Titanium is a transition metal. State the full electron configuration of the 2+ ion. 23. Which properties decrease down group 1? I. Melting point II. Atomic radius III. First ionization energy A. B. C. D. I and II only I and III only II and III only I, II and III 24. Which pair of elements shows the greatest difference in electronegativity? A. Mg and O B. Li and F C. K and F 25. Which statements are correct for the oxides of period 3 going from Na to Cl? I. The oxides become increasingly acidic. II. The bonding of the oxides changes from ionic to covalent. III. All the oxides dissolve readily in water. A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III D. Li and I 26. The elements argon, potassium, and calcium are consecutive in the periodic table. Which gives the correct order of increasing first ionization energies? A. B. C. D. 27. Which statements about reactivity are correct? I. Potassium reacts more vigorously than sodium with chlorine. II. Lithium reacts more vigorously than potassium with water. III. Fluorine reacts more vigorously than bromine with a potassium iodide solution. A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 28. State an equation for the reaction of magnesium oxide with water. 29a. Periodic trends enable chemists to predict the behavior of related compounds. (i) State the equation for the reaction of sodium metal with water. (ii) Describe two changes that could be observed during the reaction. (iii) Predict the relative reaction rates of lithium, sodium and potassium with water. 29b. Chlorine gas, (i) , is bubbled through separate solutions of aqueous bromine, . Predict any changes that may be observed in each case. : : , and potassium bromide, 29d. Explain why the ionic radius of a chloride ion is greater than the atomic radius of a chlorine atom. 29f. State the acid-base natures of 29g. State equations for the reactions of and . and with water. 32a. The oxides and chlorides of period 3 elements exhibit periodicity. State the changes in the acid-base nature of the oxides across period 3 (from for the reactions of and with water. 32d. State the full electron configurations of Cr and Cr: : 33. (i) (ii) to ), including equations . Describe the colour change that occurs when aqueous chlorine is added to aqueous sodium bromide. Outline, with the help of a chemical equation, why this reaction occurs. Part 2 1. Which series is arranged in order of increasing radius? A. B. C. D. 2. Which oxides form acidic solutions when added to water? A. and B. C. D. and and and 3. Which species has the electron configuration of A. Ni B. C. Fe D. 6. Which statements are correct for the alkali metals Li to Cs? I. Melting point increases II. First ionization energy decreases III. Ionic radius increases A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III ? 8a. Chlorine occurs in Group 7, the halogens. Chlorine has an electronegativity value of 3.2 on the Pauling scale. Define the term electronegativity. 8b. Using the Data Booklet, explain the trends in electronegativity values of the Group 7 elements from F to I. 10a. Bromine is a member of group 7, the halogens. Explain the trend in reactivity of the halogens. 10b. Deduce, using equations where appropriate, if bromine reacts with sodium chloride solution and with sodium iodide solution. 10c. Iron is a transition metal. Describe the bonding in metals and explain their malleability. 11. Which statements about atomic structure and the periodic table are correct? I. An element in group 2 has 2 electrons in its valence (outer) energy level. II. An element in period 3 has electrons in 3 energy levels. III. The element in group 2 and period 3 has an atomic number of 12. A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 12. Which combination is correct for the properties of the alkali metals from Li to Cs? 13. Which oxides are acidic? I. II. III. A. B. C. D. I and II only I and III only II and III only I, II and III 14. Which series is correctly arranged in order of decreasing radius? A. B. C. D. 16a. State the equation for the reaction between sodium and water. 16b. State and explain one difference between the reactions of sodium and potassium with water. 17. Which physical property of elements is represented by y on the graph below? A. B. C. D. First ionization energy Ionic radius Atomic radius Electronegativity 19. Which property generally decreases across period 3? A. Atomic number B. Electronegativity C. Atomic radius D. First ionization energy 20. Which property increases down group 1? A. First ionization energy B. Melting point C. Reactivity D. Electronegativity 22. Which pair of elements has the greatest difference in electronegativity? A. Cs and F B. Cs and Cl C. Cs and Br D. Cs and I 25. Describe the acid-base character of the oxides of the period 3 elements, Na to Cl. For the compounds sodium oxide and phosphorus(V) oxide, state the balanced chemical equations for the reaction of each oxide with water. 26a. Define the term first ionization energy. 26b. Explain why the first ionization energy of magnesium is higher than that of sodium. 26c. Explain why: calcium has a higher melting point than potassium. 26d. Samples of sodium oxide and sulfur trioxide are added to separate beakers of water. Deduce the equation for each reaction and identify each oxide as acidic, basic or neutral. 28. Which properties of the alkali metals decrease going down group 1? A. First ionization energy and reactivity B. Melting point and atomic radius C. Reactivity and electronegativity D. First ionization energy and melting point 29. Which statements about the periodic table are correct? I. The elements Mg, Ca and Sr have similar chemical properties. II. Elements in the same period have the same number of main energy levels. III. The oxides of Na, Mg and P are basic. A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 30. Which property decreases down group 7 in the periodic table? A. Melting point B. Electronegativity C. Atomic radius D. Ionic radius 31. Which oxides produce an acidic solution when added to water? I. II. MgO III. A. B. C. D. I and II only I and III only II and III only I, II and III 32. The x-axis of the graph below represents the atomic number of the elements in period 3. Which variable could represent the y-axis? A. Melting point B. Electronegativity C. Ionic radius D. Atomic radius 33b. With reference to electronic arrangements, suggest why the reaction between rubidium and water is more vigorous than that between sodium and water. 33c. Describe and explain what you will see if chlorine gas is bubbled through a solution of (i) potassium iodide. (ii) potassium fluoride. 34a. Consider the bonding and structure of the period 3 elements. Explain the increase in the melting point from sodium to aluminium. 34c. [Explain why silicon has the highest melting point and argon has the lowest melting point. 35a. The periodic table shows the relationship between electron arrangement and the properties of elements and is a valuable tool for making predictions in chemistry. (i) Identify the property used to arrange the elements in the periodic table. (ii) 36b. Outline two reasons why electronegativity increases across period 3 in the periodic table and one reason why noble gases are not assigned electronegativity values. (i) State whether aqueous solutions of magnesium oxide and magnesium chloride are acidic, alkaline, or neutral. (ii) State an equation for the reaction between magnesium oxide and water. 37b. (i) Outline two reasons why a sodium ion has a smaller radius than a sodium atom. (ii) Explain why the ionic radius of is greater than the ionic radius of . 37d. (i) Explain why the first ionization energy of aluminium is lower than the first ionization energy of magnesium. (ii) Explain why the first ionization energy of sulfur is lower than the first ionization energy of phosphorus. 41. An element is in group 4 and period 3 of the periodic table. How many electrons are in the highest occupied energy level of an atom of this element? A. 3. B. 4 C. 12 D. 14 42. A. B. C. D. Which statement describes the trends of electronegativity values in the periodic table? Values increase from left to right across a period and increase down a group. Values increase from left to right across a period and decrease down a group. Values decrease from left to right across a period and increase down a group. Values decrease from left to right across a period and decrease down a group. 43. A. B. C. D. Which statement is correct for all elements in the same period? They have the same number of electrons in the highest occupied energy level. They have the same chemical reactivity. They have the same number of occupied energy levels. They have the same number of neutrons. 44. Which species has the largest radius? A. Cl– B. K C. Na+ D. K+ 45. Which equation best represents the first ionization energy of magnesium? A. B. C. D. 46a. Define the term first ionization energy and state what is meant by the term periodicity. 46e. Explain why the melting points of the Group 1 metals points of the Group 7 elements increase down the group. decrease down the group whereas the melting