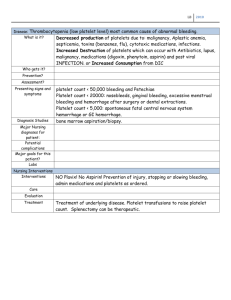
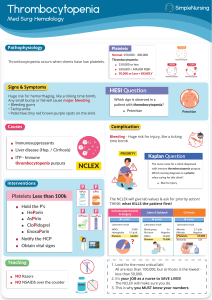
Thrombocytopenia Labs Pathophysiology - Decreased number of platelets Diminished production= infection Increases destruction= medication Idiopathic= pregnancy Causes - Platelets >150,000 100,000= Major Risk <50,000= deadly **Patients who are immunocompromised** Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)= give steroids Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ttp)= rare, mainly female Heparin Induced thrombocytopenic (HIT) Liver disease (Hep. / Cirrhosis) Medications (Immunosuppressants) Signs and Symptoms Complications *Many asymptomatic* ! Bleeding ! ‧ Hemorrhage ‧ Mucosal (nose/gingival) bleeding ‧ Petechiae (red freckles, usually on abdomen) ‧ Purpura (small hemorrhage under skin or Mucus membranes) ‧ Ecchymosis (blood under skin) ‧ Fatigue/dizziness ‧ Tachycardia ‧ Hypotension - Huge Risk for injury, like a ticking time bomb - Priority Nursing diagnosis is Risk for injury Teaching - Notify HCP at any signs of bleeding - No razors - use soft bristle toothbrush - No Nsaids (Asprin) Treatments and Interventions - Notify HCP - Find and treat underlying cause - Corticosteroids (First)= Will decrease platelet destruction *Do not abruptly stop= Addison’s Crisis* - Splenectomy - Transfusion when <20,000 - Monitor Hgb, Hct, Platelets, coag - Increase Fluids and Fiber - Hold P’s= Heparin, aspirin, clopidogrel, enoxaparin