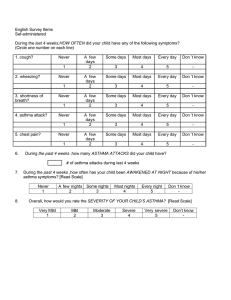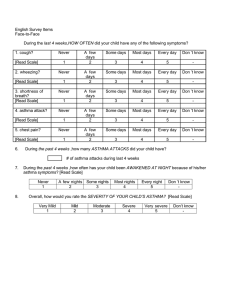
Bronchial asthma PICU OBJECTIVE 1- Definition of asthma 2- pathophysiology of asthma 3- signs and symptoms 4- treatment of asthma 5- nursing intervention Asthma Is a chronic inflammation of the small airway of the lunges that causes them to be obstructed and therefore air passes through them less easily . It is one of the most common respiratory conditions affecting children , causing significant morbidity and mortality Asthma Usually associated with airflow obstruction of variable severity Airflow obstruction is usually reversible , either spontaneously , or with treatment The inflammation associated with asthma causes an increase in the baseline bronchial hyper responsivness to avareity of stimuli ASTHMA TRIGGERS:Dust mites, mold spores, animal dander, cockroaches , pollen, indoor and outdoor pollutants , irritants (smoke, perfumes, cleaning agent) Pharmacological agents (ASA, beta blockers) Physical triggers (exercise, cold air) Physiologic factors (stress, rhinitis, GERD, viral and bacterial URI ( Signs & Symptoms Coughing especially at night Wheezing Shortness of breath Chest tightness , pain or pressure Sneezing Chin or throat itching Running nose Dark circles under eyes Difficulty talking or concentrating Decreased or change lung function What is the Pathophysiology? Trigger Factor Mast cell Mediators : histamine , prostaglandin, leukotrienes , as well as cytokines. Inflammatory cells Sustained Inflammatory response Contraction of airway smooth muscles ( Bronchoconstriction ) Pathophysiology (Cont.) Airway wall swelling (mucosal edema) Airway hyper responsiveness Chronic changes Hypertrophy of the smooth muscles, thickening of the basement membrane Airway remodeling There is good evidence that asthma occurs in families. many cells and cellular elements play a role, in particular, mast cells, eosinophils , T lymphocytes, neutrophils and epithelial cells. When mast cells activate, there is infiltration of inflammatory cells, edema, denudation and disruption of the bronchial epithelium, goblet cell hyperplasia and smooth muscle thickening resulting to asthmatic inflammation. HOW TO DIAGNOSE BRONCHIAL ASTHMA Consultation skill Relevant History -Symptom -history of allergic disease -Family history -Environmental history -Exclusion of other medical condition Diagnosis of B.A ( cont.) `Relevant physical examination Investigation Do you need to do investigation? Why ? Follow up Medical record Role of Peak Flow Meter How to manage and control Bronchial Asthma Educate patients to develop a partnership in asthma care Assess and monitor asthma severity Avoid exposure to trigger factors Establish individual medication plans for long term management in children and adults Medical Management: Use of short acting bronchodilator which is inhaled beta2-agonists as needed for symptoms with MDI spacer/holding chamber Bronchodilators should be given every 4 to 6 hours for 24 hours for patient with asthma and viral infection Rapid reversal of airflow obstruction with repeated or continuous administration of an inhaled beta2-agonist; early adminstration of systemic corticosteroids (eg, oral prednisone or intravenous methylprednisolone) is suggested in children with asthma that fails to respond promptly and completely to inhaled beta2agonists Reduction in the likelihood of recurrence of severe airflow obstruction by intensifying therapy: Often, a short course of systemic corticosteroids is helpful Nursing Management: Regular monitoring and assessment of the symptoms in the past 2 weeks. Assess for exacerbation, proper compliance to medications. Assess for difficulty with feedings, changes in respiratory rate, altered sleep patterns, presence of retractions Teach the parents to control or minimize the exposure to allergens. * Emphasize the need for flu vaccine for patients with no restrictions. Limit the exposure to cigarette smoke Eliminate dust mites Encourage to use air conditioners at home and keep doors and windows closed to minimize the exposure to these triggers. Encourage a regular visit to the physician and evaluate the proper usage of equipment. Provide a written instruction for management plans when at home, at school or care givers. Remind the parents or care givers about the medications, its expiry date as well as having a reserve of it in times of exacerbations. QUESTIONS ????