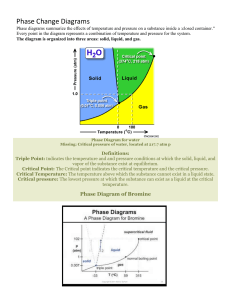
CHM 222 - Industrial Chemical Processes Introduction to Chemical Processes What is a Chemical Process? Chemical processes convert raw material(s) into desired products by changing the chemical and/or physical properties of the materials. Raw materials Utilities Chemical solvents Products By-Product Waste products Raw materials undergo physical and chemical processing to achieve desired finished products. 2 Fundamental sources of raw materials Air: Cheap and readily available. Mostly required in certain reaction and combustion processes Water: Important solvent in many chemical industries Minerals: Solid inorganic elements or compounds. They are major feedstock for the inorganic chemical industries. Fossil fuels: They are mostly hydrocarbon materials and consist of natural gas, crude oil and coal. They serve as raw materials in chemical and petrochemical industries. Agricultural and forest products: major raw material for production of natural rubber, natural fiber, paper and medicines 3 Examples of operations in chemical processes 4 Mixing Distillation Crystallization Drying Screening Crushing Extraction Filtration Chemical reaction Polymerization Absorption Adsorption Evaporation Condensation Reasons for designing, constructing and operating chemical industries. To make products that have specific desired functions e.g. petrochemical and specialty chemical industry To convert waste materials into useful products e.g. farm or household wastes. To convert materials into energy e.g. oil and gas industry To improve the performance of a natural material e.g. pharmaceutical industry 5 Chemical Process Diagrams Block Flow Diagram (BFD) o Chemical processes are represented as a group of connected blocks; o Unit operations are represented by blocks or rectangles; o Straight vertical and horizontal lines are used to represent material flow into and out of the blocks. 6 Chemical Process Diagrams (cont’d) Process Flow Diagram (PFD) o Chemical processes are represented as a connected group of process equipment; o Equipment used to move materials around (e.g pumps), heat and cool (e.g heaters and coolers) material are included in the diagram. 7 Chemical Process Diagrams (cont’d) Process and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID) o This is an extension from early developmental block diagrams and process flow diagrams. o It is sometimes called piping and instrumentation diagram o It shows information on piping, fittings, equipment, instrumentation, and process plant in a representative and sequential arrangement on the basis of product flow paths. 8