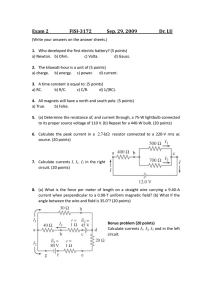
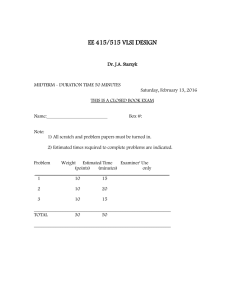
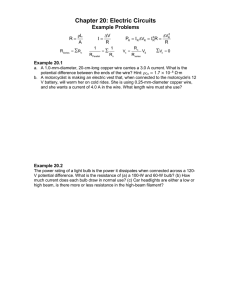
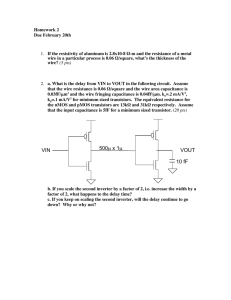
Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Spring 2021 EE115C – Digital Electronic Circuits Homework #7 Due Thursday, May 27, 11:59pm Problem 1 : Pass-Gate Logic (Exam Sample) Figure 1 contains a pass-gate logic network. Assume that the PMOS has weaker driving strength than the NMOS. VDD = 1V. All transistors have drawn length of 100nm. NMOS have width of 430nm. (a) Determine the truth table for the circuit. What logic function does it implement? Which input pattern(s) will result in static energy consumption? (b) Assuming 0 and 1V inputs, size the PMOS transistor to achieve a VOL = 0.2V. (c) If the PMOS were removed, would the circuit still function correctly? Does the PMOS transistor serve any useful purpose? Figure 1 Use following parameters for hand calculations: VDSAT = 0.3V, xd = 10nm for NMOS, and VDSAT = −0.4V, xd = 15nm for PMOS NMOS: VT0 = 0.17V, kn’ = 130A/V2, = 0.1V1/2, = 0.75V-1, 2F = 0.6V PMOS: VT0 = −0.20V, kp’= −100A/V2, = −0.16V1/2, = −0.62V-1, 2F = −0.6V Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Spring 2021 Problem 2 : Flip-flop Design A. The following flipflop is a common design used in a standard cell library. All devices are minimum channel length. Each unit of device size is 0.12um. Analyze the circuit, identify main building blocks, and explain the circuit operation. B. Sweep the data (D) arrival time with respect to the clock (CK) and plot tClk-Q time versus D-CK offset. Find tsetup and thold defined as minimum tD-Q. Use 𝑉𝐷𝐷 = 1 𝑉 . What percentage tClk-Q delay increase from the nominal (D settles long before clk, and it will hold after the clock edge) to these definitions of tsetup and thold? For both 1→0, 0→1 transitions, determine corresponding parameters: tsetup(0), thold(0), tsetup(1), thold(1). CP CP CP QM D Q CP CP CP Clk Block A CPI Block B P1 Block C CP CP C. Consider the flip-flop shown below. Analyze and explain its operation. In particular, explain the functionality of blocks A, B, and C. Hint: The name of this flip-flop is “datatransition look-ahead flip-flop”. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this design as compared to the latch in (a)? Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Spring 2021 Problem 3 : Sizing the logic with wire In the previous homework, the wire capacitance and resistance are neglected while we are sizing the gate circuit for the shortest delay. What would happen if resistance and capacitance induced by wire is not neglected? Consider the circuit below. The wire between inverter x and y is 0.15𝜇𝑚 wide and 0.05𝑚𝑚 long. 100fF A. Assume the sheet resistance of wire is 0.1 Ω⁄□. What is the total resistance of the wire? B. The on resistance of the inverter with input capacitance of 10𝑓𝐹 is 100Ω. The unit capacitance of the wire is 2𝑓𝐹/𝜇𝑚. How large should the x and y be to get the shortest path delay (express the size of inverter in terms of input capacitance)? What is the shortest delay? Assume the wire can be modeled with single segment 𝜋 model as shown in the figure, and 𝐶 𝐶𝑝 𝑔𝑎𝑡𝑒 =1 C. Size the x and y for shortest delay without the wire resistance and capacitance. Compare your result with part B.