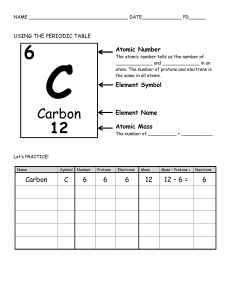
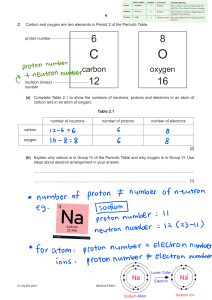
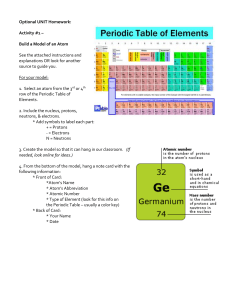
U1L1: The Nature of Atoms and the Atomic Structure Worksheet 1. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate information. Use your periodic table to determine what element it is (Assume that the atoms of each element are neutral) Element Ag Silver As Arsenic Br Bromine Au Gold Sn Tin Atomic # 47 Mass # 108 # of protons 47 # of electrons # of neutrons 47 61 33 75 33 33 42 35 80 35 35 45 79 179 79 79 100 50 119 50 50 69 THE ATOMIC NATURE OF MATTER MODEL 1: Atoms (Adapted from PhET Simulations) Open the Atomic Nature simulation https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/build-an-atom Explore the Atom part of the simulation. You can drag as many neutrons, protons and electrons into the center of the atom model. 1. Click on the + sign for each of the yellow boxes (element name, net charge and mass number) to view changes as you change the number of particles in the atom. 2. What particle(s) are found in the center of the atom? Protons and neutrons 3. What is the name of the following atoms? a. An atom with 2 protons and 3 neutrons: _______Helium______ b. An atom with 2 protons and 7 neutrons: _______Helium______ c. An atom with 4 protons and 4 neutrons: _______Beryllium______ 4. We will be learning about charge of an atom or ion in our next lesson. To get you started, play with the simulation to discover which particles affect the charge of an atom or ion: ___the number of electrons affects the charge of an atom or ion__________ 5. Fill in the blanks below to show your results: a. Neutral atoms have the same number of protons and electrons. b. Positive ions have ____more number of_____ protons than electrons. c. Negative ions have _____less number of____ protons than electrons. 6. Play with the simulation to discover what affects the mass number of your atom or ion. ___________the number of protons and neutrons affect the mass number.____________ a. What is a rule for determining the mass number of an atom or ion? The mass number = the number of protons + the number of neutrons MODEL 2: Symbol (Adapted from PhET Simulations) 1. Using the Symbol readout box, figure out which subatomic particles affect each component of the atomic symbol and how the value of the numbers is determined. d c b a Position in symbol box Term to describe this information Particle used to determine this How the value is determined a Element symbol protons # of p will identify the element b Charge Protons, electrons p+ + e- c Atomic number protons # of p d Mass number Protons, neutrons # of p + # of n 2. Create a definition (using a complete sentence) for each of these items based on your labels from the atomic symbol above. a. Element Symbol 1. The symbol that represents the element in a periodic table b. Charge The number of protons + the number of electrons that characterize element’s positive or negative electric force. c. Atomic Number The number of protons in an atom d. Mass Number The number of protons + the number of neutrons in an atom 3. In addition to atomic symbol, we can represent atoms by name and mass number. Complete the table below: Symbol Name C+1 Carbon-12 18 9 F Fluorine-18 11 5 B Boron-11 12 6 1. How will you use your periodic table to find the number of neutrons? The number of neutrons and the mass number are shown in the periodic table. Then, I can find the number of neutrons by subtracting the number of protons from the mass number. 2. How can you use your periodic table to find the number of electrons in a neutral element? The number of protons is the same as the number of electrons in a neutral element. So, I can find the number of electrons in a periodic table by seeing the number of protons.