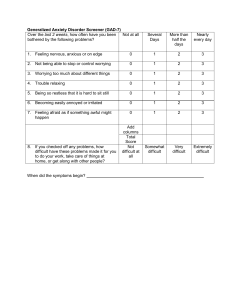
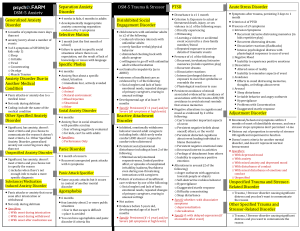
Potential Complications - Low self-esteem - Issues with being assertive - Negative self-talk - Hypersensitive to criticism - Poor social skills - Substance abuse - Suicide or suicide attempts - Isolation and difficult social relationships - Low academic and employment achievement Social Anxiety Disorder “Marked fear of one or more social or performance situations in which the person is exposed to the possible scrutiny of others and fears he will act in a way that will be humiliating.” – Amanda’s ppt Treatment/Medications - Social skills training - Behavior therapy - Cognitive therapy - SSRIs (ex. Zoloft) - SNRIs (ex. Effexor) - MAOIs (ex. Eldepryl) - Benzodiazepines (ex. Valium) Anxiety is out of proportion to actual threat posed by situation. Anxiety lasts > 6 months and significantly interferes with their daily life. Will avoid common social situations, such as… - Interacting with strangers - Attending social gatherings - Going to work or school - Dating - Shopping - Starting conversations - Making eye contact Studies have found “hyperactivity of the amygdala even with a weak form of symptoms provocation” in people with social anxiety disorder. Coping Skills/Prevention - Getting help early - Journaling - Relaxation exercises - Avoid unhealthy substance use - Diet, exercise, sleep Nursing Interventions - Maintain a calm environment and manner - Remain with client when anxiety levels are high - Establish a trusting/therapeutic relationship (i.e., be warm, available, respectful, etc.) - Provide reassurance and comfort measures - Avoid asking or forcing the client to make choices Teaching/Education - Educate patient about their disorder, treatment plan, and medications. - Teach signs/symptoms of anxiety and ways to interrupt its progression (e.g., deep breathing, meditation, relaxing walk, etc.) - Encourage client to express their emotions and to work through their feelings