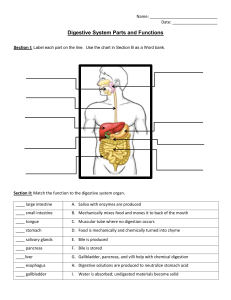
The digestive System Page 530 WHAT HAPPENS TO THE FOOD AFTER IT IS EATEN? No matter what you eat, your food goes through 4 steps: • Ingestion is the act of eating, or putting food in your mouth.(mechanical) • Digestion is the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food into small particles and molecules that your body can absorb and use. • Absorption occurs when the cells of the digestive system take in small molecules of digested food. • Elimination is the removal of undigested food and other wastes from your body. All 4 steps happen in the organs and tissues of the digestive system Before your body can absorb nutrients from food, the food must be broken into small molecules by digestion. There are TWO types of digestion: Mechanical digestion • In mechanical digestion, food is physically broken into smaller pieces. Chemical digestion • In chemical digestion, chemical reactions break down pieces of food into small molecules. • It cannot occur without substances called: Enzymes Chemical digestion •Enzymes are proteins that -help break down larger food molecules into smaller molecules. -speed up, or catalyze, the rate of chemical reactions. Chemical digestion step 1: an enzyme attaches to a food particle step 2: the enzyme speeds up a chemical reaction that breaks down the food particle step 3: the enzyme releases the broken down food particles. Notice that the food molecule breaks apart, but the enzyme does not change. Therefore, the enzyme can immediately be used to break down another food molecule. Properties of enzymes There are many kinds of enzymes. Each one is specialized to help break down a specific molecule at a specific location. • The enzyme AMYLASE helps break down carbohydrates. • The enzymes PEPSIN and PAPAIN help break down proteins. • Fats are broken down with the help of the enzyme LIPASE. Temperature affects the activity of enzymes Answer the following questions •List the different Functions of The Digestive System. •Differentiate between chemical and physical digestion. •Why our body should break down the foods we eat? •Define enzymes and list some examples. •List the three properties of an enzyme. Organs of the digestive system Your Digestive system has TWO parts: - the digestive tract and - different organs connected by tube-like structures. The digestive tract extends from the mouth to the anus These Organs include the tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. h t u o M • Mechanical digestion of food begins in your mouth. - Your teeth and tongue mechanically digest food as you chew. • But even before chewing begins, your salivary glands produce saliva at the thought of food. • Saliva contains - an enzyme that helps break down carbohydrates. They produce more than 1 L of saliva every day. s u g a h p o Es It is a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. Food moves through the esophagus and the rest of the digestive tract by waves of muscle contractions called peristalsis. h c a m o t S • The stomach contains an acidic fluid called gastric juice. . - Gastric juice makes the stomach acidic. Acid helps break down some of the structures that hold plant and animal cells together. - Gastric juice also contains pepsin, which is an enzyme that helps break down the proteins in foods into amino acids. Mechanical & Chemical digestion Food and gastric juices mix as muscles in the stomach contract through peristalsis. As food mixes with gastric juice in the stomach, it forms a thin, watery liquid called CHYME (PH<7) l l a Sm tine s e t n I Most chemical digestion and nutrient absorption take place in the small intestine. • Chemical digestion by receiving pancreatic juice, takes place in the first part of the small intestine, called the duodenum. • The remainder of the small intestine absorbs nutrients from food. The wall of the intestine is folded like the stomach. The folds of the intestine are covered with fingerlike projections called villi. Each villus contains small blood vessels. Nutrients in the small intestine diffuse into the blood through these blood vessels. The pancreas and liver produce substances that enter the small intestine and help with chemical digestion. Liver The liver produces bile. Bile makes it easier to digest fats. The gallbladder stores bile until it is needed in the small intestine. Pancreas The pancreas produces: - the enzyme amylase that helps break down carbohydrates. - a substance that neutralizes stomach acid. e g r a L tine s e t n I • Also called Colon. • More water is absorbed there. e g r a L tine s e t n I Any food that is not absorbed in the small intestine moves by peristalsis into the large intestine. Materials that pass through the large intestine are the waste products of digestion e g r a L tine s e t As these waste products travels n I through the large intestine, even more water is absorbed.so The waste products become more solid. • The rectum, the last section of the large intestine, where undigested food is eliminated & rejected outside. Q z z i uiz