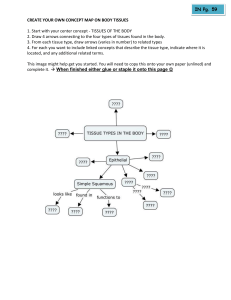
Transverse tubule - Invaginations of the muscle cell membrane that contain dihydropyridine receptors. - When they depolarize they allow the impulse to propagate through the interior of the muscle fiber - Allows for synchronized contraction of myofibrils in each muscle cell Growth hormone - In tissues: increases insulin resistance, fat utilization, protein synthesis - In liver: increases IGF-1 production growth and development - Works via JAK/STAT pathway (non receptor tyrosine kinase) Burns - Superficial burns morphological changes occur due to tissue damage and inflammatory mediators such as Mast cells, which release histamine (dilates capillaries in the skin) - Deeper burns may damage nerve and venules. Can create a blistering due to fluid extravasation through gaps between injured venule endothelial cells Nonseminomatous germ cell tumor - Undiff/ partially differentiated germ cells - Usually make abnormal hormones (AFP, hCG) - Solid mass in testicle Lead poisoning - Microcytic anemia, constipation, mental status changes - Shortness of breath due to decreased oxygen delivery to peripheral tissues - Lead inhibits ALAD, and ferrochelatase - Will see basophilic stippling on Blood smear - Wilson Disease - Autosomal recessive, ATP 7B mutation. Damage from increased copper accumulation, deposition into various tissues - Increased urinary copper excretion, decreased ceruloplasmin. - Kayser-fleischer rings detected on silt lamp examination . - Tx: Chelators like penillamine, trientine,… Zinc Types of muscles fibers - Type 1 = slow twitch o Sustained contractions. Generate energy through aerobic metabolism o High myoglobin and mitochondrial concentrations o i.e. Postural muscules - Type 2 = fast twitch o Derive ATP from anerobic glycogenolysis and glycolysis o Rapid, forceful movements (biceps, deltoid etc.) GIST : Gastrointtestinal stromal tissue - Normally present in the sixth decade as gastric bleeding or obstruction - Spindle shaped cells on histology Echinococcus Granulosus