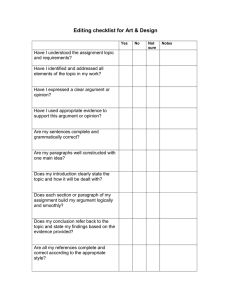
English 1130 - A list of five common fallacies FALLACY Circular reasoning Hasty generalization Slippery slope Straw Man Ad hominem DEFINITION Occurs when the end of an argument comes back to the beginning without having proven itself. (So, X is true because of Y; and Y is true because of X) Jumping to conclusions based on insufficient evidence or biases Arguing that an idea or action will lead to inevitably to unrealistically steeper and steeper consequences. Misrepresenting (or improperly representing) an argument so that you can attack the misrepresentation instead of the actual argument. Literally, “against the man/person.” Attacking the character of a person by providing irrelevant negative information. EXAMPLE You must obey the law, because it’s illegal to break the law. I’m not moving to that neighborhood. When I visited it, there were two people arguing in the street so it must be dangerous. If we legalize marijuana, then other drugs like ecstasy and cocaine will soon follow, and then everyone will be an addict. If you want prison reform, you are basically saying you want to treat criminals like they’re at a resort. We should not be rewarding criminals! How can this woman be the mayor when she can’t even keep her own house tidy? Note that some of these fallacies are derived from Barnet, Sylvan, et. al, eds. From Critical Thinking to Argument: A Portable Guide. Bedford/St. Martin’s, 2020. Pp. 370-3.