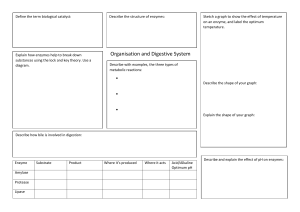
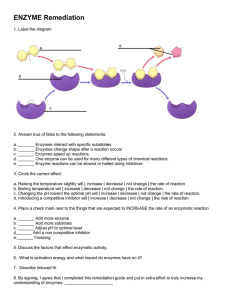
Chemical Reactions & Enzymes BIOLOGY I Chemical Reactions: ● Change one set of chemicals into another. ● Reactants - go into the reaction (left side) ● Products - elements or compounds produced by chemical reaction (right side) Energy in Reactions ● Chemical reactions that release energy often occur spontaneously. ● Chemical reactions that absorb energy require a source of energy. Which reaction can occur spontaneously? Enzymes & Energy Activation Energy:the minimum quantity of energy which the reacting species must possess in order to undergo a specified reaction. Exergonic Reaction - energy is released (products have less chemical energy than reactants) Enzymes & Energy Endergonic Reaction - One in which energy must be supplied for the reaction to occur (products have more chemical energy than reactants) Energy is stored. Enzymes: •Proteins which cells use to speed up biological reactions by lowering activation energy. Enzymes: (AKA Biological Catalyst) Lock & Key Model •Usually globular in shape. •Often have surface depressions called active sites which allow SPECIFIC molecules called substrates bind to them. •Have molecules that fit into active site where chemical change occurs Reaction: Product: Reactants: Induced Fit Model ● Enzymes: ○ are often are flexible. ○ can change shape when an appropriate molecule binds to an active site -- known as Induced Fit Factors Affecting Enzymes: •Temperature:Enzyme activity increases as temperature increases, and in turn increases the rate of the reaction; activity decreases at colder temperatures. All enzymes have a range of temperatures when they are active, but have certain temps they work best. At higher temperatures, proteins (enzymes) can be denatured (destroyed or broken down). (Most human enzymes Effects of pH on Enzymes operate at 95-104 degrees F). •pH: Charged areas of an enzyme can be affected by + - added [H , OH ], thus reducing their action in high or low pH. •Substrate concentration: As amount of substrate decreases, the rate of enzyme activity will decrease also Background knowledge: the more H+, the more acidic. The more OH-, the more basic. Amylase- an enzyme in saliva that initiates the breakdown of starch into sugar. Pepsin- enzyme that breaks down proteins into smaller proteins in your stomach. Arginase- enzyme that converts toxic ammonia into urea in urinary system.