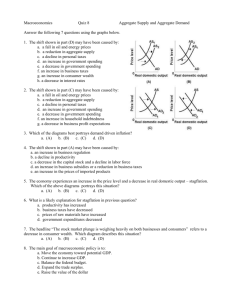
Explain how an increase in the level of taxation can influence the level of aggregate demand in an economy? Aggregate demand is the total demand for a good or service in an economy, at different price levels. The factors that affect aggregate demand are investment spending, consumer spending, government spending, and net exports. In figure 1 the Aggregate demand curve moves from AD1 to AD2 (a leftward shift); or from point A to B, which results in the price decrease from PL1 to PL2, and a decrease in the real GDP from, Y1 to Y2. this causes an increase in unemployment. An increase in Taxation will cause the aggregate demand to shift to the left (decrease). An increase in tax will cause a reduction in their disposable income. This will cause a decrease in consumer spending. Therefore a decline in the purchasing power, hence a decrease in aggregate demand. An increase in corporation taxes will also result in, decrease in the after-tax profits for firms. Hence the firms will reduce their investment spending, which would shift the AD curve to the left. The key concept of change can be linked with business and consumer behavior. As the increased taxes cause a decrease in the consumption of goods and services. Therefore causing a reduction in aggregate demand and a leftward shift of the AD curve.