toaz.info-oral-comm-11-quarter-1-module-2-week-2-pr e08f5d0bad994a5f9cea58f45c084774
advertisement

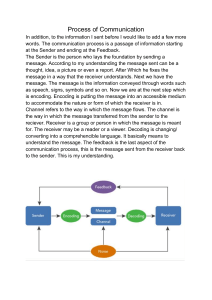
MODULE 1 LESSON 2 THE COMMUNICATION PROCESS ORAL COMMUNICATION IN CONTEXT GRADE 11 LEARNING OUTCOMES At the end of this lesson, students are able to: Familiarize the process of communication Construct a communication process based on the situations in real-life context and; Show appreciation on the process of communication through an activity. Lesson 1: Overview As a future professional, you will engage in both formal and informal interactions with various people. In each of these interactions, you will have to skills that will enable you to build rapport and connections with all sorts of people. Communication is a complex process, and it is difficult to determine where or when a communication starts and ends. It is simply the act of transferring information from one place, person or group to another. To have a better understanding, answer the following activities and study the information in this module for you to understand the communication process. DEFINITION OF TERMS Communication Process – is the guide toward realizing effective communication. Barriers/Noise – these refer to specific items that can distort or prevent communication within an organization. Feedback - is the response of a receiver to a message. WHAT DO YOU ALREADY KNOW? Read the following statements and choose the letter of the correct answer. PRE-TEST. 1. The sender of the message is officially called: a. The sender c. The originator b. The inceptor d. The receiver 2. The message being sent is officially called: a. The message c. The sent b. The idea d. The package 3. The receiver of the message is officially called: a. The receiver c. The receptionist b. The terminus d. The terminator 4. Which of these is the biggest hurdle to communication that exists before a message is even sent? a. Interference c. Feedback b. Sender d. Context 5. The person who starts a conversation is called: a. Receiver b. Messenger c. Sender d. Inceptor 6. A response from a receiver is called: a. Feedback c. Communication b. Medium (Channel) d. Context 7. The location in which communication takes place. a. Noise/Communication Barrier c. Feedback b. Context d. Channel 8. Communication between two people. a. Interpersonal c. Intrapersonal b. Interference d. Context 9. Noise barrier/Interference. a. A conflict with another person. b. Blockage of communication. c. The way a message is transmitted. d. Sending message with words. 10. Communication within oneself. a. Interpersonal b. Group c. Intrapersonal d. None of the above. WHAT DO YOU NEED TO KNOW? Communication is reciprocal. It is a dynamic, ongoing, and non-static activity. Again, it is a two-way process. Here are the elements of the communication process: 1. SENDER – this represents the source, the speaker, or the person who creates, encodes, and transmits the message. 2. MESSAGE – this refers to the ideas, feelings, perceptions, values, beliefs, or opinions conveyed by the speaker to the receiver. Messages can be transmitted verbally or non-verbally. 3. CHANNEL – this serves as the vehicle or medium used in transmitting messages, or ideas. a. Written Media – this includes memos, letters, reports, bulletin boards, handbooks, newsletters, and the like. b. Verbal Media – this includes face-to-face conversation, telephone, mobile phone, computer, television, radio, tape-recorded messages, emails, slide shows, and many more. c. Non-verbal – this refers to simple gestures, facial expressions, body position, and clothing can transmit an idea or message to the receiver. 4. NOISE or BARRIERS – this pertains to something that can distort the sending and receiving of messages. There are so many factors that can block effective communication process: a. Physical Barrier – refers to conspicuous disruptions in the environment that make it difficult to hear or listen. This includes the environment noise, or background noise. b. Psychological Barrier – refers to emotions, mood, knowledge, or other mechanisms within the speaker that can impede the speaker’s or receiver’s ability to express and to understand the message clearly. c. Semantic Barrier – refers to the ability of the receiver to understand the meaning of the words. It is very important to use appropriate words and phrases the receiver will surely understand. d. Psychosocial Barrier – this is related to the receiver’s background, perception values, biases, needs, and expectations. Here are the few areas that may affect communication: a. Sincerity – it is the foundation of all communication. Without sincerity and honesty, all attempts at communication well will surely fail. b. Empathy – you can put oneself into some one’s shoes. If you can see the world through the eyes of the others, you will surely be a good conversationalist. c. Self-perception – how we see ourselves affects our ability to communicate effectively. d. Role Perception – it is very important for us to know our role, and the importance of our role as a person, as a student, as a daughter/son. This will guide us when to communicate, whom to communicate with, and what to communicate. e. Listening ability – you will not fail to understand the message of the sender when you know how to listen attentively. 6. RECEIVER – is the individual or individuals to whom the message is directed. The receiver will understand the message depending on his/her experiences, attitudes, knowledge, skills, perceptions, and culture. 5. FEEDBACK/RESPONSE – is considered as the key component in the communication process. It allows the sender to evaluate and to respond to the message, whether the feedback is positive or negative. HOW DO YOU EXTEND YOUR LEARNING? 1. Cite situations and examples of NOISE and BARRIERS inside the classroom. COMPREHENSION CHECK! (1) Physical Noise Psychological 2. What could be the appropriate FEEDBACK on the following situation? a. You saw a burglar in your neighbor’s house. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ b. While you were inside the jeep, you saw a pickpocket burglar trying to slash the bag of a woman beside you. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ c. While watching the television, you learn about the suspension of classes due to heavy rain. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ d. You were a manager of a food chain and you received a letter of complaint from your customer due to poor service. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ HOW DO YOU EXTEND YOUR LEARNING? COMPREHENSION CHECK! Communication Situation Watch and listen to different communication situations on the television or video from the internet and determine the verbal and non-verbal cues employed by each speaker to achieve his/her purpose. Write your answer in the table below. Verbal Cue Non-Verbal Cue Functions of Communication HOW DO YOU APPLY WHAT YOU HAVE LEARNED? In the box below, show how the communication process works by citing a situation in real-life. Label it with the components of communication and other essential variables that you think are very important in the process. REFERENCES Dalumay, M., Suan, J., Quintero, G. (2016). Oral Communication in Context – Grade 11. Chancery Compound Rizal St., Tagum City, Davao del Norte, Philippines. Diocesan Printing Press and Publishing, Inc. https://oralcom.wordpress.com/2016/10/14/communication/