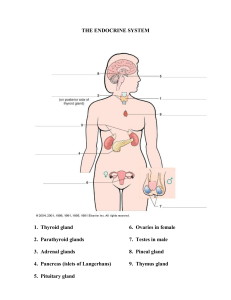
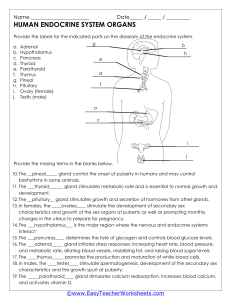
The Endocrine System Lab 1) Label each of the endocrine organs listed below and be able to locate the on appropriate models. Adrenal Gland Hypothalamus Ovary Pancreas Parathyroid Glands Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Testes Thymus Thyroid Gland Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Pineal Gland Thymus Parathyroid Adrenal Gland Pancreas Ovaries Testes 2) Complete the table below. Gland Hormones Produced Main Function of each Hormone 1 Adrenal gland Aldosterone Cortisol Corticosterone Cortisone Epinephrine Norepinephrine Increase blood Na+ levels & increase blood glucose levels Stimulate fight-or-flight response Missing from the cortical section gonadocorticoids Antidiuretic hormone & oxytocin Increases how much water is absorbed into the blood by the kidneys, release of a mother's breast milk, moderating body temp, & regulating sleep cycles. Estrogens & progesterone Stimulate development of female secondary sex characteristics & prepare the body for childbirth. Insulin & glucagon Reduces blood glucose levels & increases blood glucose levels Hypothalamus Ovary Pancreas Parathyroid glands Pineal gland Parathyroid hormone (PTH) Melatonin Increase blood Ca2+ levels Regulates sleep cycle 2 Pituitary Gland Growth hormone (GH) Prolactin (PRL) Thyroid stimulating Hormone (TSH) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Oxytocin Testosterone Stimulate development of male secondary sex characteristics & sperm production Thyroxine (T4) Triiodothyro nine(T3) Calcitonin Stimulate basal metabolic rate, reduces blood Ca2+ levels Testes Thyroid Gland Promotes growth of body tissues Promotes Milk production Stimulates thyroid hormone release Stimulates hormone release by adrenal cortex Stimulates gamete production Stimulates androgen production by gonads Stimulates water reabsorption by kidneys Stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth. 3 3) Endocrine histology. Review the histology micrograph of different endocrine glands provided, and be able to identify the glands on the lab quiz &practical. Adrenal Gland (includin g the medulla, zona reticular is, fascicula ta, glomerul osa) Hypotha lamus 4 Pancrea s (includin g the Islets of Langerh ans) 5 Pituitary Gland (anterior and posterio r) 6 Anterior Pituitary Poterioir pituitatry 7 8 Parathyr oid Gland (be able to different iate from thyroid) 9 Thyroid Gland (includin g follicle, follicular cells “princip al”, colloid, parafolli cular cells “C cells”) 4) Answer the following questions. 1. Gland in the brain that is the control center for all regulatory activities of the body: Hypothalamus 2. Condition in which levels of thyroid hormones in the blood are very low: Hypothyroidism 3. Hormone that helps regulate when you sleep at night and when you wake up in the morning: Melatonin 4. Gland in the brain that makes hormones that control several other endocrine glands: Pituitary Gland 5. Two hormones that reproductive glands produce for females: Estrogen and Progesterone 10 6. Two hormones produced by the pancreas that help regulate blood glucose: Insulin and glucagon 7. Gland which produces hormones that control the rate at which cells produce energy: Thyroid 8. Four tiny glands that function together to regulates calcium levels: Parathyroid glands 9. Adrenal cortex produces this group of hormones: Androgens, Mineralocorticoids, Glucocorticoids 10. The outer part of the Adrenal gland: Adrenal Cortex 11. Main hormone that reproductive glands produce for males: Testosterone 12. Gland that produces melatonin: Pineal Gland 13. Causes milk let-down in nursing mothers and contractions during childbirth: Oxytocin 14. Gland that increases blood pressure and heart rate when the body experiences stress: Adrenal Gland 15. Two hormones that help regulate calcium homeostasis (one to elevate blood calcium and one to lower blood calcium): Calcitonin and parathyroid hormone 16. Adrenal glands are located above this major organ: Kidneys 17. Disease caused by a failure of the body to produce insulin: Diabetes Mellitus 11 18. Produced in the adrenal cortex, keeps blood glucose levels stable: Glucocorticoid: cortisol, corticosterone, cortisone 12 5) Fill out the chart. CHARACTERISTIC Age at onset Onset of symptoms TYPE I DIABETES MELLITUS Early age or adult TYPE II DIABETES MELLITUS Adult, 45-64 Fast Slow 10-15% 85-90% Natural insulin levels at disease onset Below normal Above normal Beta cells of pancreatic islets Damaged/destroyed Not destroyed/present Percentage of diabetics Risk factors for disease Heredity Typical treatments Insulin- subcutaneous Untreated blood glucose Hyperglycemia Overweight 46 yrs old + older Family history Diet, exercise, oral medications Hyperglycemia 13