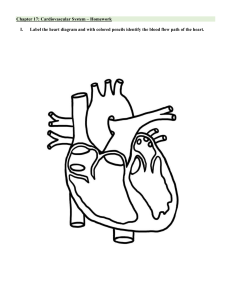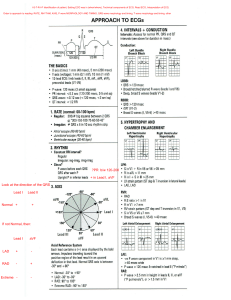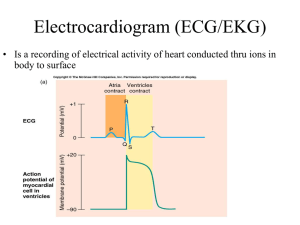
Dysrhythmias – Part 1 Chapter 35 Content Objectives • Review the heart and cardiovascular system, electrical and mechanical components of the cardiac cycle, and cardiac output. • Describe the cardiovascular diagnostics. • Apply nursing considerations for diagnostics relevant to cardiovascular function. • Examine the nursing care of patients needing continuous electrocardiographic (ECG) monitoring including rhythm interpretation. Nervous System Control of Heart • Autonomic Nervous System • Parasympathetic Nervous System – vagus nerve fibers (rest & digest) • ↓ rate of SA node • Slows impulse conduction of AV node • Sympathetic Nervous System –nerve fibers (flight & fight) • ↑ rate of SA node • ↑ impulse conduction of AV node • ↑ cardiac contractility Conduction System of the Heart Dysrhythmias Disorder of impulse formation, conduction of impulses, or both SA node normal pacemaker of heart (60–100 beats/minute) AV node (40–60 beats/minute) Secondary pacemakers His-Purkinje fibers (20–40 beats/minute) Electrocardiogram Monitoring • Graphic tracing of electrical impulses produced by heart • Waveforms of ECG/EKG represent activity of charged ions across membranes of myocardial cells Electrocardiogram Monitoring 12-Lead ECG Clip excessive hair on chest Patient Preparation for Lead Placement Rub skin with dry gauze May need to use alcohol for oily skin Apply electrode pad 12 –EKG Lead Placement 5-Lead Placement Resting ECG Monitoring • Observation of HR & rhythm at a distant site Ambulatory ECG Monitoring • Event monitor • Loop recorder • Holter monitoring Artifact ECG Time and Voltage ECG • Three Principal Waveforms • • • • P Wave QRS Complex T Wave U Wave-advanced interpretation • Segments & Intervals • PR interval • ST segment • QT interval Assessment of Heart Rhythm • Interpret the rhythm AND assess the clinical status of the patient • Is the patient hemodynamically stable? • Determine cause of dysrhythmia • Assess & treat the patient, not the monitor! 5-Step Method to ECG/EKG Interpretation • Step One –regular or not/irregular • Start with measuring the first two RR intervals then measure across the tracing • If the shortest and longest vary by more than 0.12 (3 squares) then irregular • Step Two • Step Three • Step Four • Step Five 5-Step Method to ECG/EKG Interpretation • Step One • Step Two – determine the rate • First Method • Count the number of R waves in a 6-second strip and multiple by 10 • Step Three • Step Four • Step Five • Step Two – determine the rate • Second Method 5-Step Method to ECG/EKG Interpretation • Find an R wave that falls on a thick vertical line • • • • • • 1 Box = 300 beats per minute (bpm) 2 Boxes = 150 beats per minute (bpm) 3 Boxes = 100 beats per minute (bpm) 4 Boxes = 75 beats per minute (bpm) 5 Boxes = 60 beats per minute (bpm) 6 Boxes = 50 beats per minute (bpm) • The rate becomes a guestimate of whatever 2 numbers the R wave falls between • What is the approximate rate? 5-Step Method to ECG/EKG Interpretation Regular/irregular? What is the rate? 5-Step Method to ECG/EKG Interpretation • Step Three – identify the P wave • Should be near identical, one P to one QRS • Normal P wave is indicated as Sinus aka sinus rhythm • As long as there is a normal or biphasic appearance and the rate is 60-100 it is normal sinus rhythm • If the P wave is normal and the rate is above 100 then sinus tachycardia; below 60 sinus bradycardia • In the second example, the P wave is inverted which is not a normal biphasic appearance • The P wave that is inverted, or not normal in shape, is coming from somewhere else besides the SA node so it is not a sinus rhythm • This is considered an ectopic morphology • Hint: atrial rate = count the # of P waves 5-Step Method to ECG/EKG Interpretation • Step One • Step Two • Step Three • Step Four – measure the PR interval • Count the number of small squares and multiple by 0.04 • Is it normal duration or longer or shorter • Normal PR interval=0.12 to 0.20 sec • Step Five 5-Step Method to ECG/EKG Interpretation • Step One • Step Two • Step Three • Step Four • Step Five – evaluate the ventricular rhythm • Measure the QRS Complex • Count the small squares and times by 0.04 • Normal QRS Complex < 0.12 sec Other questions to ask….. • Assess the ST segment • Is it isoelectric (flat), elevated, or depressed? • This may indicate electrolyte issues, ischemia, or infarction Other questions to ask….. • Measure the duration of the QT interval • Is it normal duration or prolonged? • 0.34-0.43 • Certain medications impact the QT as well as electrolytes • Note the T wave • Is it upright or inverted? • This may indicate electrolyte issues • What is the dominant or underlying rhythm and/or dysrhythmia? • What is the clinical significance of your findings? • What is the treatment for that rhythm? Copyright © 2017, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. Hot-Spot Answer Options: • Apex • Atrioventricular (AV) bundle/Bundle of HIS • Atrioventricular (AV) node • Left and right bundle branches • Left atrium • Left ventricle • Purkinje fibers • Sinoatrial (SA) node Hot-Spot Copyright © 2017, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. Hot-Spot • HESI NCLEX book – p. 45 – incorrect rate • Steps: • #1 – Regular/irregular? • #2 – Rate? • #3 – P-wave? • #4 – PR interval? • #5 – QRS interval? Steps: • • • • • #1 – Regular/irregular? #2 – Rate? #3 – P-wave? #4 – PR interval? #5 – QRS interval?