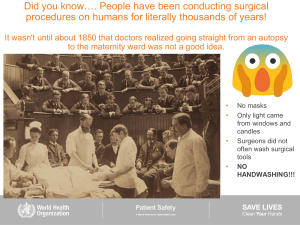
Did you know…. People have been conducting surgical procedures on humans for literally thousands of years! It wasn't until about 1850 that doctors realized going straight from an autopsy to the maternity ward was not a good idea. • • • • No masks Only light came from windows and candles Surgeons did not often wash surgical tools NO HANDWASHING!!! Hand transmission ■ Hands are the most common vehicle to transmit health care-associated pathogens ■ What’s a pathogen? The impact of HCAI - Health Care-associated Infection HCAI can cause: ■ more serious illness ■ prolongation of stay in a health-care facility ■ long-term disability ■ excess deaths ■ high additional financial burden ■ high personal costs on patients and their families A few Types of Bacteria spread by Direct Contact that Cause Illness E. Coli – Escherichia Coli – food poisoning MRSA – Staphylococcus Aureus: Pneumonia, Flesh Eating Disease Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus Pneumoniae, Haemophilus Influenzae, Moraxella Catarrhalis : - Pink Eye - UTI (Urinary Tract Infection) - Meningitis – Swelling of the brain Handwashing vs Hand Sanitizer Hand sanitizer is an alcohol-based substance that does not include water. It only REDUCES the number of microorganisms on your hands. Handwashing, if done properly, can ELIMINATE microorganisms on your hands. Time constraint = major obstacle for hand hygiene Adequate handwashing with water and soap requires 1 – 3 minutes Average time usually adopted by health-care workers: <10 seconds Alcohol-based Hand rubbing: 20–30 seconds Best Practices for Handwashing: 1. 2. 3. 4. Time! Don’t rush!!! (1 – 3 minutes) Warm/hot water Use soap or a liquid antimicrobial agent Use a brush or sponge (See page 213 for specific guidelines) ACTIVITY…. How would you rate your handwashing skills?