Uploaded by
Alexandra Umanzor
RN Medication Study Guide: Cardiac, Respiratory, Mental Health
advertisement

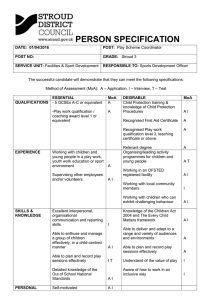
RN STUDY BUDDY MEDICATION MENTAL H E anti-anxiety anti-epileptics anti-depressants anti-psychotics mood stabalizers anti-parkinson spasmolytics substance abuse edication Ca M al antibiotics ories teg egories Cat edication M H ALT adhd Common RESP CORTICOSTEROIDS INHALED ANTICHOLINERGICS LEUKOTRIENE MODIFIERS XANTHINES EXPECTORANTS MUCOLYTICS DECONGESTANTS ANTIHISTAMINES NON-STEROIDAL ANTIALLERGY SUBQ ANTI INFLAMMATORY additio n Common C a ANTI-ARRHYTHMIC ANTI-DYSRHYTHMIC ACE INHIBITORS ANTI-COAGULANTS ANTI-HYPERTENSIVES ANTI-PLATELET ARBS BETA BLOCKERS CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS DIGITALIS DIURETICS or Categ ies on egories Cat edicatio M c a i d r ANTI-ANGINAL n M e d Y icat R O T IRABETA 2 AGONIST i antiviral NSAIDS INSULIN OPIODS emergency meds chemotherapy common antidotes therapeutic levels insulin iv tuberculosis alternative therapies Cardiac MEDICATION Commo nC gories ate d i e c M a t c i o a i n d C r a ACE INHIBITORS ARBS BETA BLOCKERS CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS cardiac glycosides vasodilators DIURETICS ANTI-PLATELET ANTI-COAGULANTS Thrombolytic ANTI-DYSRHYTHMIC hyperlipidemics Cardiac MEDICATION ACE INHIBITORS (-PRIL) & ARB'S (-SARTAN) moa: iNHIBITS THE raas SYSTEM = LOWERS BLOOD PRESSURE BY INHIBITING vasoconstriction and THE KIDNEYS FROM RETAINING NA+/H2O (but retains K+) Ace = -pril Treats: Hypertension, heart failure, post MI, slows diabetic type 2 neuropathy enalapril Notes: ACE cough / angioedema (airway block) k+ circulating in blood (EKG= peak t wave, avoid foods high in K) foods high in K+ (green leafy vegetables, cantaloupe,banana, dried fruits) orthostatic hypotension risk TERATOGENIC! nO PREGNANCY! ↑ → less na+ / less h2o =less fluid = less pressure in system = lower bp lisinopril benazepril Ramipril ARB = sartan losartan irbesartan candesartan olmesartan ACE = Angiotension converting enzyme ACE =It converts the hormone angiotensin I to the active vasoconstrictor angiotensin II angiotensin II is responsible for = ace inhibitors block these from happening increased sympathetic activity increases resorption of salt na+, and retains h20 increases levels of aldosterone (promotes potassium excretion) arteriole vasoconstriction increases (Ad)h anti diuretic hormone = adh prevents h20 from being excreted When ACE inhibitors block the conversion to angiotensin 2 we see the following decreased sypathetic activity excretion of na+,H20 retains k+ (by blocking aldosterones k+ excretion process) arterioles stay relaxed (dilation) decreased levels of adh, (by blocking adh we allow na+ and h20 to be excreted) ARBs inhibit the same thing, they just do it by blocking the receptor site. Cardiac MEDICATION Beta blockers (-olol) MOA: inhibits beta receptors (adrenaline and nor adrenaline) which prevents the heart from speeding up who gets it?: Hypertension, angina pectoris, atrial fibrillation, post MI - hEART FAILURE PATIENTS can only receive (carvedolol, metoprelol succinate) MAY MASK HYPOGLYCEMIA NO beta blockers for Asthma patients *ALWAYS CHECK HR/BP BEFORE ADMINISTRATION / HOLD IF bp <90 /HR <60 EDUCATE/ OBSERVE FOR: ORTHOSTATIC hYPOTENSION, WHEEZING, HR, BP do not stop abruptly = rebound htn and tachycardia ↓ ↓ Heart selective -atenolol -metroprolol -bisoprolol nonselective -propanolol -carvedilol -nadolol Beta Blocker = blocks receptor sites block the receptor site of stress hormones, adrenaline and noradrenaline in certain parts of the body. Epi and nor epi cause vasoconstriction, hr, bronchodilation ↑ Where are these blocked sites? a1= arteries (think 1 main artery) some non selective block a1 so we see vasodilation b1=heart (think 1 heart) by blocking the hormones we see a slower hr b2=lungs (think 2 lungs) by blocking these we see bronchoconstriction (no asthma) ↓ beta blockers cause = vasodilation, hr, Bronchoconstriction This results in a slowing of the heart rate and reduces the force at which blood is pumped around your body. which reduces hypertension, chest pain, atrial fibrillation Cardiac MEDICATION calcium channel blockers - ccbs MOA: blocks calcium movement into heart and arteries which keeps smooth muscle relaxed = Resistance bp ↓ ↓ ↓ bp only -dipine ↓ cAUTIONS: BP/HR NO - 2ND / 3RD DEGREE HEART BLOCKS -ZEM / -AMIL RISK OF - ORTHOSTATIC HYPOTENSION & REFLEX TACHYCARDIA HR/BP ASSESSMENT PRIOR TO ADMIN - HOLD IF BP 90 / HR 60 nO GRAPEFRUIT JUICE* dose dependent peripheral edema - adjust dose, add ace inhibitor, compression socks no heart failure = can worsen edema lowers livers ability to break down drugs = think toxicity = double check other meds ↓ ↓ calcium channel blockers = blocks channels to prevent travel where are they? arteries = calcium causes vasoconstriction (-dipine) heart (sa & av nodes) calcium causes quicker depolarization = faster hr (-zem/-amil) By blocking calcium channels we will see arteries = vasodilation heart (sa/av node) = slower hr ↑ ↓ bp only -dipine Amlodipine nifedipine xl felodipine common uses Angina Pectoris Hypertension zem/amil atrial fibrillation ↓ BP/HR -ZEM / -AMIL verapamil diltiazem Cardiac MEDICATION cardiac glycoside = digoxin moa: slows hr / increases contraction force (slow but strong) nOTES: commonly refered to as a positive ionotropic Caution diuretics (monitor K+ values hypo K = toxicity risk & dysrhythmias) Monitor kidney function - kidney function = toxicity risk hold if hr <60 contact provider / give medication same time every day ↓ therapeutic range=0.5-2 2=toxicity Toxicity s/s vision change, n/v confusion ↑ medications antacids: dig levels ppi: dig levels (ppi = proton pump inhibitor) ↑ ↓ Does not waste potassium - test commonly try to trick you here does not affect blood pressure = no worries for orthostatic hypotension digoxin what it affects? sa/av node= stimulates the vagus nerve = vagus nerve decreases sa/av rate vagus nerve is a parasympathetic nerve and limits the hr hearts na+/K+ pump: blocks na+/K+ pump - increases Calcium levels = stronger contraction Think digoxin = dig = digs low for a slow and strong contraction slow hr strong contraction Cardiac MEDICATION vasodilators moa: relaxes smooth muscles = ↓bp, ↑o2 perfusion nOTES: normal findings = headache, facial flushing, hypotension do not take with sildenafil (erectile dysfunction) hold if bp <90 or hr <60 monitor bp and orthostatic hypotension = dont stand to fast hydralazine = hypertensive emergencies / eclampsia w/ pregnancy may cause tachycardia treats: (acute angina, coronary artery disease, htn emergencies) Acute angina (nitroglycerin) sit down place 1 tablet under tounge let disolve (up to 3 doses) if pain not relieved in 5 min call 911 - continue with next dose vasodilators what it affects? veins= nitros and isosorbide arteries = hydralazine How does it work? releases Nitric oxide (NO) nitric oxide formulates cgmp in the body cgmp causes dilation of smooth muscles vein dilators nitroglycerin nitroprusside isosorbide (last 12 hours) arterial dilator hydralazine Nitro patch instructions do not cut place on hairless area remove each night = 10-12 hours medication free rotate sites to prevent irritation Cardiac MEDICATION diuretics potassium wasting = loop diuretics furosemide, bumetanide, torsemide (also called high ceiling) thiazide diuretics: hydrochlorothiazide, chlorothiazide moa: prevent re-absorption of na+, h2o, K+ use: heart failure, peripheral edema,( pulmonary edema = loops) notes: at risk for K+ = u wave present, st depression, low hr, flat t wave gout = uric acid is blocked from being excreted hyperglycemia = thiazides (thought from lower insulin production= unknown) calcium = (loop = hypocalcemia) (thiazide = hypercalcemia) ototoxicity = tinnitus, hearing changes if given to large a dose renal damage = if given to long, monitor i&os, monitor kidney labs monitor for - dehydration, muscle cramps, orthostatic hypotension, electrolyte imbalance increase K+ consumption: (green leafy vegetables, cantaloupe,banana, dried fruits) ↓ potassium wasting moa: prevent re-absorption of na+, h2o (K+ loops only) by blocking the co transport that would remove them from the urine back into the vascular space. thiazides also waste k+ but not by blocking resorption = the excess na+ exchanges with k+ in the collecting tubule Cardiac MEDICATION diuretics potassium sparing potassium wasting moa: blocks aldosteron in the raas spironolactone use: heart failure, hypertension, edema, notes: at risk for K+ = st elevation, peak t wave decrease K+ consumption: (green leafy vegetables, cantaloupe,banana, dried fruits) avoid salts with k+ additive take in the morning decreases testosterone: gynocomastia (enlarged breast tissue), sexual dysfunction, tender breast, menstrual irregularities monitor for - dehydration, muscle cramps, orthostatic hypotension, electrolyte imbalance ↑ osmotic diuretics mannitol, isosorbide moa: reduces h2o and electrolyte re absorption to decrease plasma volume uses: icp and intraoccular pressure monitor: neuro status, kidney function. typically reserved for emergency or intensive care patients ↓ potassium wasting moa: blocks aldosterone aldosterone: increases na+, h20+ absorption and forces excretion of k+ na+, h20 causes increase in bp aldosterone also causes arterial constriction blocking aldosterone: = this is what spironolactone causes to happen in the body excretes na+ and h20 = this causes client to have lower bp can't constrict the arteries = larger arteries and lower bp because of lower pressure ↑ ↑ Cardiac MEDICATION anti platelets aspirin, clopidogrel, abciximab moa: Blocks enzymes - prevents platelet aggregation use: prevent MI, stroke, tia, coronary syndromes, claudication notes: side effects: mild: dyspepsia (trouble digesting), upper abdominal pain moderate: peptic ulcers: because no protective mucas in stomach severe: gastrointestinal bleeding - dark tarry stools / coffee ground like throw up (emesis) Monitor for: bruising, petechiae, and bleeding gums (test love to ask about these and severe s/e) herbals that increase bleeding (i think G,G,GB,SP) (Garlic, ginger, ginkgo biloba, saw palmetto) [These are important for any meds that affect clotting/bleeding times] ** no aspirin to children = reyes syndrome extreme caution with any other meds that cause bleeding seperate nsaids and aspirin by 2 hours aspirin toxicity - n/v, dizziness, confusion, coma, tinnitus - rare but test still like to ask anti-platelet MOA aspirin moa: platelet aggregation causes a release of txa2 which is regulated by the cox1 enzyme platelet aggregation only is a weak clot, the coagulation cascade adds fibrin to the platelets to strengthen clot aspirin is a cox 1 inhibitor - this inhibits txa2 which inhibits platelet aggregation clopidogrel moa: blocks adp which allows atp to break down into c-amp, c-amp increases the pka enzyme which reduces platelets ability to aggregate. abciximab moa: blocks fibrin receptors so clots cant strengthen Cardiac MEDICATION anti coagulant Warfarin moa: vitamin k antagonist - vitamin k is a natural clotting enzyme Heparin, Enoxaprin moa: stimulates anti-thrombin 3 to reduce the clotting cascade uses: mi, stroke, pe, dvt, post op prevention, atrial fibrillation reversal: Heparin = protamine sulfate warfarin = vitamin k notes: all meds reduce ability to clot = increased risked for bleeds (think thin blood) INR Monitor: normal: 1 heparin = a-ptt (60-80 sec) warfarin 2-3 warfarin inr = 2-3 unusual bleeding: aptt gums, gi, urine, nose, mouth, eyes normal: 30-40 sec no warfarin for pregnancy - heparin and enoxaprin are okay Heparin: 60-80 sec considerations: Warfarin needs about 5 days for full effect - heparin may be given also in the first few days injections are sub-q and must be 2" away from umbilicus (belly button) anti coagulant warfarin moa: blocks vitamin k depenent enzymes which reduces fibrin productions = reduced clots works on both intrinsic (factor 9) and extrinsic pathways (factor 7) both of these combined block factors 10, 2, 1 (fibrin) Heparin moa: stimulates anti-thrombin 3 in the clotting cascade = reduced clotting anti-thrombin 3 is naturally occurring in the body and blocks factor x which inhibits factor 2 and 1 (fibrin) **Fibrin is what strengthens platlet aggregation to form a strong clot** Just good to know info Cardiac MEDICATION thrombolytics - aka clot busters (-ase) thrombolytics moa: breaks down plasminogen and fibrin to dissolve clots use: dvt, stoke, pe, tia, (open iv lines - alteplase only) notes: must be used before 3-4.5 hours of onset (varies by source) thrombolytic alteplase or (tpa) reteplase streptokinase dont use if: recent surgery recent trauma active bleed (to include gi bleeds/ ulcers) av malformations severe hypertension on other blood thinners / anti coagulation use caution in starting new ivs monitor aptt, pt, hgb, hct thrombolytic moa: clots are made up of fibrin, plasminogen, and platelets (to keep things easy) think of plasminogen like a glue holding platelets and and fibrin together clot busters work to convert the plasminogen to plasmin with no plasminogen the clot dissolves and prevents those platelets from aggregating Cardiac MEDICATION anti dysrythmic class 1 - procainamide= class 1a, lidocaine=class 1b propafenone = class 1c moa: block sodium channel, this increases action potential duration use: svt, v-tach, atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation risks: systemic lupus, thombocytopenia, neutropenia, arrhythmia, torsades de pointes class 2 - beta blockers - propranolol moa: blocks beta receptors, slows hr, prevents sympathetic nervous system stimulation use: atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, angina risks: hypotension, seizures, orthostatic hypotension, bradycardia class 3 - amiodarone moa: basically decreases every effect of the heart, channels, strength. (its a huge list) use: svt, v-tach,v-flutter, atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation risks: very long half life (25-60 days), no reversal, side effects in almost every system pulmonary - pul fibrosis, pneumonia, obtain chest xray, monitor pulmonary function gi, cns depressant cardiac - bradycardia, arrhythmia, long qt thyroid issues due to iodine there are more s/e - these are some of the main ones. class 4 - ccb - verapamil, nifedipine, diltiazem moa: block sodium channel, this increases action potential duration use: svt, v-tach, atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation risks: hypotension, edema, bradycardia, arrhythmia Cardiac MEDICATION hyperlipidemics Liver function: ast: 10-40 u/l alt: 7-56 u/l alp: 40-120 u/l bil: <1 mg/dl lipid panel: total cholesterol: <200 triglycerides: <150 LDL: <100 HDL: >60 creatine kinase 22-198 u/l liver toxicity signs jaundice,nausea, vomiting, upper right abdominal pain, decreased appetite, fatigue, rash, fever hmg-coa inhibitors (-statins) moa: block hmg-coa to production of cholesterol in the liver use: high cholesterol, prevention - coronary event, mi, stroke monitor: liver toxicity, myopathy - muscle pain, rhabdomyolysis lft & CK levels, targets liver, but excreted by kidneys avoid alcohol ↓ Cholesterol absorption inhibitors (ezetimibe) moa: lowers ldl by blocking dietary cholesterol absorption in gi tract use: over absorption of cholesterol, monitor/notes take at night nausea / diarrhea / fatigue almost no side effects any-time: atorvastatin rosavastatin bedtime: Lovastatin simvastatin pravastatin ezetimibe Cardiac MEDICATION hyperlipidemics fibrates (fib - is in the name) moa: targets fibrates in dna = breakdown of free fatty acids = less fatty acid being broken down by the liver into triglycerides use: decrease triglycerides, increase hdl monitor/notes muscle pain (typical with statins) monitor ck values liver toxicity cholelithiasis (gall stones) taken with or without food - but same time everyday bile acid sequestrants (cole-) moa: binds to bile in small intestine and prevents absorption cholesterol / fats are attached to bile for reabsorption = fats excreted in stool use: type 2 diabetes to help manage cholesterol and BGL monitor/notes: constipation (very sticky stools) triglyceride levels may be decreases absorption of meds that use fat as transports increase fiber and fluid intake -Fibgemfibrozil fenofibrate colecolesevelam colestipol ↑ Hyperlipidemic meds takeaways all meds affect liver and/or lipid panel test obtain baseline liver function test prior to administration hdl is good cholesterol (holy = hdl / is sometimes used to help remember that its good) ldl is bad cholesterol (lousy / lame = ldl) typically not used during pregnancy caution / avoid with liver / kidney issues a c t i i o d n e M C a l t a antibiotics n antiviral e ies gor addi tio additional MEDICATION nsaid opiods emergency meds chemotherapy common antidotes therapeutic levels insulin iv basics tuberculosis alternative therapies antibiotics targeting the cell wall - no to all 3 if client has penicillin allergies moa: attack and weaken the cell wall (beta-lactams ) (penicillins,cephalosporins, carbapenems) penicillins:caution in kidney impairment clients, effects of oral contraceptives cephalosporins: monitor for thrombus and bleeding carbapenems: may create superinfection = colitis, oral thrush, yeast infection ↓ ↓ targeting protein synthesis - pregnancy risk tetracyclines: effects of oral contraceptives, no children under 8= teeth staining macrolides: -thromyacins, chlamydia treatment, prolonged qt, ototoxic, inhibits warfarin, amnioglycosides: —mycin, ototoxicity, renal toxic, potential neurological issues uti's sulfaonamides and trimethoprim:echoli treatment - blood dyscrasias, crystal aggregates anitseptics: metheNamin - uti’s, chronic uti prophylaxis, monitor for bleeding issues fluoroquinolones: -floxacin, (risk; Achilles’ tendon rupture) photosensitive analgesic: phenazopyridine, local anesthetic, urine is red/orange = expected, bacterial, fungal, parasitic antimycobacterial:tb meds, (isoniazid, rifapentin) hepatotoxic, hyperglycemia, avoid tyramine antimycobacterial: anti tb (rifampin) client secretions turn orange, expected. antiprotozoals: metronidazole (flagyl) no alcohol! Neurotoxic, pseudomembranous colitis antifungals: ketoconazole, nystatin, monitor for thrombus, toxic to kidneys and liver, sexual Dysfunction, gynocomastia additional notes / overall key point effects of oral contraceptives (-cillins, -cyclins) toxic!!! mycin pregnancy risk (-cycline, sulfa, antifungal) ↓ antiviral acyclovir (-clovir) moa: prevent reproduction of the viral dna - interrupts cell replication uses: herpes simplex, varicella-zoster viruses s/e: phlebitis, nephrotoxic, c/i: caution with renal impairment, Notes: does not protect from infecting others with the virus (i.v. given over 1 hour) main types / endings = -clovir / -amivir / -dine moa: all antiviral block replication to kill or suppress by blocking (polymerase enzyme ) uses: smallpox, herpes, flu, rotavirus (gi), warts, aids, hepatitis s/e: gi - N/v/diarrhea (cns) headache, seizures, anxiousness (bones) anemia, marrow suppression (renal) electrolyte imbalance, renal failure c/i: cidofovir - impaired renal function ribavirin - sickle cell amantadine - <1 year old , lactating women nsaid / acetaminophen acetaminophen (tylenol) (not a nsaid) moa: slows the production of prostaglandins in the cns uses: analgesic, antipyretic (does not decrease inflammation) s/e: toxicity, liver damage, (s/e are rare when used appropriately ) c/i: hypersensitivity, kidney impairment, chronic alcohol use, malnutrition Notes: acetyl cysteine is the antidote for overdose aspirin (salicylate acid) ibuprofen ketorolac naproxen moa: inhibits the cox-1 that decreases platelet aggregation (affects clotting) inhibits cox-2 that decreases inflammation, fever, and pain uses: mild to moderate pain, inflammation, fever, (aspirin for platelet aggregation reduction) s/e: GI upset (dyspepsia, abd pain, heartburn, nausea) (take with food or milk) salicylism (asprin toxicity) tinnitus, dizzy, headache, respiratory alkalosis Reyes syndrome (aspirin) c/i: blood thinners (heparin and warfarin) common terms: analgesic: decreases mild to moderate pain anti inflammatory: decreases prostaglandin synthesis anti-platelet: always consider bleeding or reduced clotting with aspirin anti-pyretic: decreases fever or high temperature notes: caution with kidney, liver, heart, and gi system issues or dysfunction ibuprofen: increases risk of htn and stroke ulcers: can be caused if taken without food (unless it is coated, delayed release ) kidneys: can create kidney injury with long term use opiods morphine fentanyl methadone codeine oxycodone hydromorphone moa: act on the mu receptors and kappa receptors. mu receptors produce analgesia, respiratory depression, euphoria and sedation kappa receptors produces analgesia, sedation, and decrease the gi motility uses: moderate to severe pain s/e: respiratory depression, constipation, orthostatic hypotension, urinary retention, sedation, nausea/vomiting, coma c/i: use caution with any respiratory dysfunction, extremely obese patients may accumulate higher doses of narcotic and experience overdose caution with major organ dysfunction, decreased absorption, distribution, embolization, excretion Notes: have naloxone and resuscitation equipment prepared always overdose signs respiratory rate <12, / cold, clammy, skin, / pinpoint pupils / unable to arouse provide naloxone: 1/2 life is 60-90 minutes you may have to give multiple doses before the narcotic wears off. remember abc's support patients with the basics of life support during this time emergency meds (lean) remember the saying (drugs to lean on) lidocaine moa: blocks sodium channels to decrease action potential along nerves (suppresses automaticity of the heart) uses: anti-arrhythmic s/e: edema, flushing, hypo tension, bradycardia, arrhythmia, tinnitus c/i: heart blocks, beta blockers, grapefruit juice, wolff-parkinson white, adam-stokes syndromes hepatic dysfunctions, caution in renal impairment= needs a lower dose Notes: toxicity = confusion, nervousness, tremors, double vision, tinnitus ↑ epinephrine moa: a1=vasoconstriction, b1= contacting strength and speed of heart, b2 = bronchodilation uses: shock, (hr, strength, cardiac output, tissue perfusion ) s/e: hypertensive crisis, cardiac dysrhythmias, necrosis from vasoconstriction, c/i: caution w/ hyperthyroidism, angina, dysrhythmias, hypertension Notes: emergency drugs c/i are typically considered 2nd to the life threat the patient is facing ↑ atropine moa: blocks parasympathetic nervous system - specifically -acetylcholine (think rest and digest) uses: respiratory secretions, bradycardia, low bp, chemical nerve agent poisoning s/e: arrhythmia, chest pain,htn, dry mouth/ eyes, slow gi adsorption, c/i: angle-closure glaucoma nalaxone moa: competes for mu, kappa, and sigma receptors to block opiods uses: opiod overdose s/e: half- life is probably shorter than the opioid the client is on (mey need several doses) c/i: hypersensitivity chemotherapy cyclphosphamide (alkylating agent) moa: kills rapid growing cells by alkalizing the rna synthesis uses: lymphoma related cancers s/e: bone marrow suppression, gi upset, thrombocytopenia, anemia, leukopenia c/i: pregnancy, caution with kidney, liver and blood disorders Notes: may cause Hemorrhagic cystitis** doxorubicin (antitumor antibiotic) moa: binds to dna to alter its structure, this inhibits the synthesis of dna and rna uses: solid tumors, hodgkin and non hodgkin, sarcomas, reproductive carcinomas s/e: bone marrow suppression, gi upset, vesicant = tissue damage, alopecia c/i: pregnancy and myelo suppresion. there is a max lifetime dose of 550mg/m2 Notes: monitor iv site closely, may have delayed cardiac toxicity after completion of treatment interferon alpha - 2b (biologic response modifier) moa: increases the immune response and decreases the production of cancer cells uses: leukemia, melanoma, kaposi sarcoma s/e: flu like symptoms (give acetaminophen) bone marrow suppression, alopecia, neurotoxic w/ prolonged use, thyroid dysfunction, depression, insomnia c/i: suicidal ideation, sever organ dysfunction Notes: (interferes with cancer) may help remember chemotherapy leuprolide (gonadotropin-releasing hormones) moa: prevents the release of luteinizing and follicle stimulating hormones to prevent testosterone production uses: prostate cancer s/e: hot flashes, decrease libido (sex drive), erectile dysfunction and gynecomastia, gi (n/v/d) liver toxic c/i: Notes: increase intake of calcium and vitamin d, monitor testosterone and prostate specific antigen (PSA) tamoxifen (estrogen recepto blocker) moa: stops growth of estrogen dependent cancer cells by blocking the receptor site uses: breast cancer s/e: endometrial cancer, hypercalcemia, thromosis (dvt, pe, strokes) hot flashes, vaginal discharge or bleeding c/i: pregnancy, warfarin use, history of clots Notes: (tami has breast cancer) may help remember, vincristine (anti-miotic) moa: stops cell division during miosis, uses: lymph leukemia, wilms tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, solid tumor, hodgkin and non hodgkin, kaposi s/e: nerve injury, vesicant = tissue damage, alopecia c/i: dont use with radiation, pregnancy Notes: (NOT bone marrow toxic) (given via central line) (anti emetics for nausea) common antidotes acetaminophen anticholinergics benzodiazepines beta-blockers calcium channel blockers warfarin digoxin dopamine heparin iron Magnesium sulfate narcotics potassium tca antidepressants acetylcysteine physostigmine flumazenil epinephrine calcium chloride vitamin k digibind regitine protamine sulfate deferoxamine calcium gluconate narcan kayexalate physostigimine therapeutic levels digoxin lithium phenytoin theophylline amytriptyline cabamazepine gentamicin phenobarbital procainamide salicylate tobramycin 0.6-1.2 ng/ml 0.6-1.2 meq/l 10-20 mcg/ml 10-20 mcg/ml 10-20 mcg/ml 5-12 mcg/ml 0.5-0.8 ng/ml 10-30 mcg/ml 4-8 mcg/ml 100-250 mcg/ml 5-10 mcg/ml insulin rapid-acting onset 15 min peak: 30-120 min aspart: lispro: Gluisine: duration 1-2.5 hours duration: 3-5 hours short-acting onset 30-60 min regular insulin peak: 1.5-4 hours duration: 5-8 hours intermediate-acting onset 1-2 hours nph peak: 6-14 hours duration: 12-24 hours long-acting onset 1-2 hours glargine lantus levemir peak: none diabetes type 1: = none (no insuling produced) type 2: = you lifestyle correction duration: 24 hours pre-mixed just for awareness 70% nph and 30% regular insulin notes: hypoglycemia: cool, clammy, pale, and sweaty = give me candy regular insulin: the only one that can be given by iv nph: mixing = air= cloudy to clear/ withdraw clear to cloudy 1. inject air = cloudy to clear 2. remove med = clear to cloudy think: i never want to cloudy the clear container rotate injection sites increase insulin if sick, septic, stress, on steroids ↑ when to eat? rapid = eat now short= w/i 60 min inter= for 12 hours long = all day long i.v. basics tuberculosis rifampin moa: bactericidal, prevents protein synthesis of TB (broad spectrum antibitotic uses: tb s/e: discoloration (orange/red - sweat, tears, urine = expected finding) hepatotoxic, pseudomembranous colitis. c/i: caution in clients with liver issues Notes: Rifampin is not used alone for tx of tb isoniazid ethmbutol moa: inhibits the growth of mycobacteria by preventing synthesis of mycolic acid. uses: TB - once daily for 9 months (when used alone) s/e: peripheral neuropathy, hepatotoxic, hyperglycemia c/i: liver disease caution with liver disease, diabetes, alcohol abuse Notes: interacts with phenytoin = toxicity ethambutol: routine eye checks, monitor for vision change additional notes Notes: treatment last up to 9 months typically no longer infectious after 3 neg sputum test on 3 different days sputum samplers taken every 2-4 weeks n95 mask worn for isolation precautions family should be tested as well alternative therapies aloe: sooth pain, burns (orally = laxative) black cohosh: estrogen substitute (menopause) Echinacea: immune system stimulant feverfew: blocks platelet aggregation, migraines, decrease number and severity of migraines garlic: blocks ldl , raises hdl cholesterol, suppresses platelet aggregation, vasodialator ginger root: vertigo, nausea, increase gi motility production, anti inflammatory, anti platelet ginkgo biloba: vasodilation, decreased platelet aggregation, decreased bronchospasm, memory support kava: (liver toxic) promotes sleep, lowers anxiety, muscle relaxation St. Johns wart: affects serotonin, used for mild depression, pain reliever, topical for infections saw palmetto: decreases prostate issues from hyperplasia valerian: increases gaba, reduces insomnia, reduces anxiety