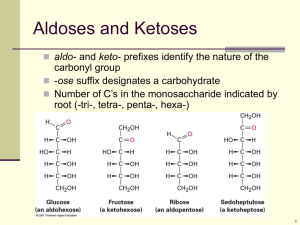
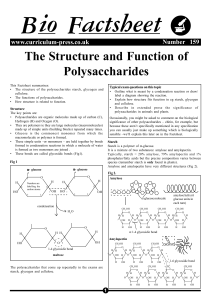
Carbohydrates Wang Xuan Carbohydrates • elements: C H O • general formula: Cx(H2O)y • 3 groups: monosaccharide, disaccharide, polysaccharide Monosaccharides • • • • (CH2O)n triose (3C) : glyceraldehyde pentose (5C) : ribose deoxyribose hexose (6C) : glucose fructose galactose Structures pentoses: glucose hydroxyl group (-OH) α-glucose & β-glucose isomers Functions 1. commonly used as a source of energy in respiration, glucose 2. building blocks for larger molecules, glucose/ribose/deoxyribose Carbohydrates Wang Xuan Disaccharides Structures • glycosidic bond • condesation • hydrolysis Polysacchrides • plants: starch cellulose • animals: glycogen starch glycogen cellulose starch • starch: α-glucose condesations 1. Consists of amylopectin and amylose 2. Amylose forms a stiff helical structure via 1,4-glycosidic bonds 3. Amylopectin is branched via 1,6-glycosidic bonds 4. Both are compact molecules → starch can be stored in small space glycogen 1. Branched, storage, polymer of α-glucose linked via glycosidic bonds 2. Found in skeletal muscle and liver 3. Chains are linked by alpha-1,4-linkage, branches are linked by alpha-1,6-linkages cellulose 1. Polysaccharide consisting of long β-glucose chains 2. Linked together by hydrogen bonds to form microfibrils 3. Structural function is a important component of plant cell walls Homework Draw a mindmap about carbohydrates