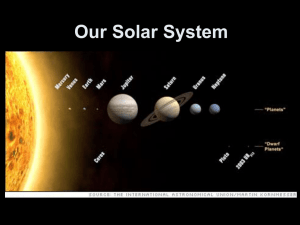
SPACE MODELS OF THE UNIVERSE Earth-centred model In ancient times when there was no technology for looking at the universe, people could only use their eyes to make observations. They saw the Sun rise in the East and set in the West and concluded that the Sun was moving across the sky. Aristotle used his observations of planets and stars in the night sky to propose an Earth-centred model of the universe. In this model, the Earth was the centre with the planets and stars moving in circular orbits around it. Sun-centred model Aristarchus was the first astronomer to suggest that the Sun was at the centre of the universe. He used his observations and estimates of the relative sizes of the Sun, Earth and Moon and their distances from each other to argue that it was more logical to place the largest object, the Sun, at the centre rather than the smaller Earth. He claimed that the apparent motion of the planets and stars was due to the Earth rotating on its axis once per day. With the invention of the telescope, more accurate observations could be made which confirmed the Sun-centred model. Earth-centred model Sun-centred model DAY AND NIGHT Earth has day and night because of Earth’s rotation on its axis. As it spins, one side of the Earth faces the sun and the other side does not. The side facing the sun receives sunlight and so it has day. The other side does not receive sunlight and so it has night. One rotation of the Earth takes 24 hours. ONE YEAR The earth revolves around the sun. One revolution of the Earth around the sun takes one year. SEASONS The Earth has seasons because Earth is tilted on its axis. When a hemisphere is tilted towards the sun it has summer and when it is tilted away from the sun it has winter. In between, it has autumn and spring. GRAVITY Gravity is a force that attracts objects. All bodies in space have gravity that attracts other objects in space towards them. For example, the Sun’s gravity attracts the planets and keeps them in orbit around it. The Earth’s gravity keeps the Moon in orbit around it. It also keeps objects on the surface of the Earth. For an object to leave Earth, it must exert a force greater than the Earth’s gravitational force. TIDES Tides are periodic rises and falls of large bodies of water. They are caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun on the Earth. The diagram above shows high tides on each side of the earth. The gravitational pull of the Moon on the Earth causes the oceans to bulge out in the direction of the Moon. They bulge out on the other side because the Earth is being pulled towards the Moon and the water in the oceans is left behind. The Sun has less effect on the tides but when the Sun and the Moon line up (New Moon and Full Moon), very high tides, called king tides or spring tides, occur. LIGHT AND SOUND Light is a form of energy that does not need a medium (material) to travel through. It travels at 300,000 km/s and it can travel through a vacuum. Light from the Sun travels 150 million kilometres through the vacuum of space to Earth in 8 ½ minutes. Sound is a form of energy that does need a medium to travel through and so it cannot travel through a vacuum. It travels through air at 340 m/s. Because there is no air on the Moon, sound does not travel on the Moon as it does on Earth. SOLAR SYSTEM The solar system is one small part of the universe. The sun is at the centre and the planets orbit it. The eight planets in order from the Sun are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. The Solar System also contains comets, asteroids, meteors and meteorites. A comet is a small mass made of ice mixed with dust, frozen carbon dioxide and organic matter. Comets orbit the Sun in a long, narrow orbit. As a comet approaches the Sun, some of the mass evaporates and forms two tails that point away from the Sun. Asteroids are small rocky objects left over from the formation of the solar system. They orbit the Sun in the asteroid belt which is located between Mars and Jupiter. When a chunk of space rock enters the Earth’s atmosphere the friction between it and the air causes it to burn up. This burning rock is called a meteor. Space rock that lands on the Earth’s surface without completely burning up is called a meteorite. STARS Beyond the solar system are galaxies of stars. A star is a sphere of gas, mainly hydrogen and helium, that produces its own heat and light by nuclear reactions. A galaxy is a group of millions or billions of stars held together by gravity. A nebula is a cloud of gas and dust in space that eventually becomes a star. LIGHT YEAR A light year is equal to the distance travelled by light in one year. Large distances in space are measured in light years rather than kilometres. GLOSSARY axis, rotation, revolution, hydrosphere, solar system, star, galaxy, nebula, light year STUDY QUESTIONS 1. What is the difference between an Earth-centred model of the universe and a Sun-centred model? 2. Describe the observation/s that led Aristotle to propose an Earth-centred model of the universe. 3. Describe the observation/s that led Aristarchus to propose a Sun-centred model of the universe. 4. Which technology provided evidence for the Sun-centred model? 5. Explain why Earth has day and night. 6. What is the name given to the time taken for the earth to revolve once around the sun? 7. Explain why Earth has the seasons. 8. Explain why Earth has tides. 9. Explain why light energy travels on Earth and in space but sound energy only travels on earth and not in space. 10. Name the eight planets in our solar system in order from the sun. 11. What is a a) comet? b) asteroid? c) meteor? d) meteorite? 12.What is the role of gravity in our Solar System? 13. What is a a) galaxy? b) star? c) nebula? 14. What is a light year?