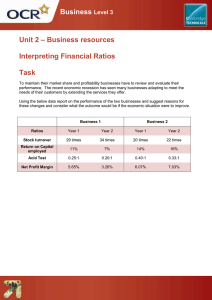
1. BUSINESS STRATEGY ANALYSIS 1.1. 1.1.1. Industry Analysis Actual and potential competition a) Rivalry among existing firms Profitability is low if competition for market share is strong: - Low industry concentration (number of firms & their relative sizes): industry is fragmented price competition is severe. - Low product differentiation: similar products. - Low switching costs: customers easy to change products. - Low industry growth - Large economy of scale - Steep learning curve - High portion of fixed costs - Excess capacity (capacity > demand), high exit costs. b) Threat of new entrants Profitability is low if threat of new entrants is high: - Small economies of scale: - Less first mover advantages: low brand loyalty… - Easy to access channels of distribution and relationships: many existing channels or low cost of developing new channels - Low legal barriers: patents, copyrights, licensing regulation… - Less requirements of expertise/specialized knowledge c) Threat of Substitute products Profitability is low if threat of substitute products is high: - Price and performance function are similar Low price & high performance: high threat - Customers are willing to switch Products are similar or seen as being substitutes Low brand allegiance 1.1.2. Products are replaceable Bargaining power in Input and output market d) Bargaining power of Buyers Low profitability if power is Strong: - More sensitive to price: Products are similar Low switching costs Unimportant products (relative cost and quality) - Higher bargaining power: Fewer buyers High volume per buyer Low switching costs More substitute products High threat of backward integration by the buyers e) Bargaining power of Suppliers Low profitability if power is Strong: - Few suppliers - High volume per supplier - High switching costs - High product differentiation - Importance of products in terms of cost and quality 1.2. Competitive Strategy Analysis 1.2.1. Cost leadership Same product at lower price because of: 1.2.2. - Economies of scale, scopes, and learning - Efficient production - Simpler product designs - Efficient organization processes - Lower costs of inputs and distribution - Little R&D or brand advertising required - Tight cost control Differentiation Unique product at a lower price than the price customers willing to pay: - Superior product quality - Superior product variety - Superior customer services - More flexible delivery - Investment in brand images - Investment in R&D and marketing Organizational and control system must foster on creativity and innovation. 1.2.3. 1.3. Mixture of Cost Leadership and Differentiation Corporate Strategy Analysis 2. ACCOUNTING ANALYSIS Degree accounting captures underlying business reality. Appropriateness of policies and estimates. Distortions: identify and undo. Improve reliability of FS. Annual reports: + Management Discussion and Analysis (MD&A): trends in sales, expenses, cash flow… + Financial statements: IS, SFP, CFS, SE + Notes. 6 STEPS: Identify key policies and estimates: to measure critical factors and risks Assess flexibility: allocation methods, estimate bad debts, inventory methods. Flexibility // Informative // Distortion Evaluate Accounting Strategy: Evaluate Quality of Disclosure: adequate? Informative Explanation? UpToDate?... Identify potential red flags: unusual transactions, unusual changes… Undo distortions: make adjustments … 3. FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 3.1. Return ROE = Net income/Equity ROA 3.2. Profitability Net margin Gross margin Operating margin 3.3. Efficiency Asset turnover = Sales/Total assets Fixed asset turnover = Sales/Fixed assets 3.4. Working capital Working capital turnover Working capital = current assets (cash, AR, inv…) + current liabilities (AP, short-term debts, current portion of unearned rev…) Inventories turnover, Days of inv on hand Receivable turnover, Days of sales outstanding Payable turnover, Number of days of payables 3.5. Leverage Leverage = Total assets / Equity 3.6. Credit Risk Liquidity ratios Current ratio = CA/CL Quick ratio (acid ratio) = (CA – Inv)/CL Cash ratio = (CA – marketable securities)/CL Solvency ratios Debt ratios Debt-to-Equity = Total debts / Total equity Long term debt to equity Total debts ratio = Total debts/ Total assets Leverage Coverage ratio Interest coverage = EBIT/interest expense