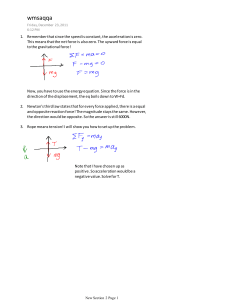
Physics - Forces have strength and direction The forces acting on an object can be balanced or unbalanced Forces are balanced when they are equal in strength but opposite in direction. Balanced forces don’t change the motion of objects. Unbalanced forces cause objects to accelerate. Balanced forces / Unbalanced forces Constant speed + at rest = balanced forces Speeding up (acceleration) + Slowing down (deceleration) = Unbalanced forces Newton’s Law of Motion Newton’s first law of motion is also known as the Law of Inertia. Newtons first law says that an object that IS NOT MOVING or is at rest will stay at rest and an object that IS MOVING will keep moving with constant speed which means at the same strength and in the same direction UNLESS an unbalanced force acts on that object. F=mxa Force = mass x acceleration N (kg) (m/s2) If something is lighter it will need less acceleration to move Measuring acceleration - a = v – u T Newton’s Second Law of Motion Newton’s second law of motion is also known as the Law of Acceleration. It says that when an unbalanced force is applied to a mass, it causes it to accelerate. The greater the force that is applied, the greater the acceleration. The lesser the force that is applied, the lesser the acceleration. If the same force is applied to an object with a large mass, it will have a lesser acceleration. If the same force is applied to an object with a small mass, it will have a greater acceleration. The equation used to solve second law problems is F = m x a Force (N) = mass (kg) x acceleration (m/s2) Newton’s Third Law of Motion Newton’s third law of motion is also known as the Law of Action/Reaction. It says that every time there is an action force, there is also a reaction force that is equal in size and acts in the opposite direction. Newton’s third law states that forces must always occur in pairs. Action forces: your bottom pushing on your desk chair – chair pushing you up. Energy: the capacity to do work. Potential energy: Potential energy is the stored energy an object has because of its position or state. Kinetic energy: kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion. Conservation of energy: Energy transformations Kinetic energy – energy of motion Potential energy – energy of location Energy can be transformed in a variety of years. The Law of Conservation of Energy - The total energy of a closed system is conserved, therefore energy can be transformed, not made or destroyed. Mechanical energy = kinetic energy + potential energy This sum is constant Non-mechanical energy: chemical, thermal, nuclear, electrical, acoustic Energy can be transformed or transferred but the amount of energy in the system must remain the same. Efficiency = Useful energy Total energy input Most energy transfer is inefficient How does the mass of the skater effect the velocity at the bottom of the track? Force = mass x acceleration, this means that the higher the mass, the larger the amount of force exerted on the skateboard. This means that the larger the skater, the higher the velocity will be at the bottom of the track. Mass of Skater (kg) 25 50 75 100 Energy at the bottom of the track (J) 2122.8 4245.6 6368.4 8491.2 As the mass of the skater doubles, the energy at the bottom of the track doubles.