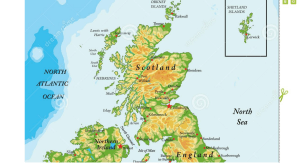
Population Change NGOs Theorists Disease Migration Population Food Topic Overview Specification will give details of topic Population and the Environment Unit is worth 58 marks out of the 120 in Human paper Population and the Environment Lesson 1 Why do people live where they live and why does population size change? Aim Students will be able to distinguish between population density and distribution and be able to describe and explain current global patterns. Students will be able to define the terms over-population, under-population, optimum population. Students will be aware of contemporary concerns regarding population and resources, particularly food supply. Why learn about the population and the environment? • Working with a partner • What do you know about…. the world’s population? where it is distribution? what population density is like across the world? which country is the most densely populated? Current World Population 7, 523, 391, 287 (8 Aug 2017) http://www.worldometers.info/ Population growth https://www .youtube.co m/watch?v= khFjdmp9sZk What does this shows us about population distribution? Look at the map above, it is a choropleth map of the World's population. The darker the red colour the more people live in those regions. Describe population distribution. In your own words, can you explain what has happened to world population growth in the past, and what is predicted to happen in the future? Manipulate the data Describe what you see Give details: use figures. What do the projections tell us about population futures? What environmental factors affect population distribution? Rich in resources Wood / coal / fertile Mountainous Farming / Fertile = $ Good water supply Healthcare Opportunities Employment Equal Rights Stable Governments Good Transport Too Dry Dense Vegetation Too Cold Unstable Govt’s No Opportunity No employment Famine War Environmental Factors affecting distribution of population Sparsely populated areas • Relief • • • • • Climate Vegetation Soils Resources Water supplies Rugged mountains with low temperatures – Andes, Himalayas Active Volcanoes Iceland Low Rainfall – Sahara, Drought – Sahel, Cold – north Canada, north Russia Rainforests - Amazon Frozen soils – permafrost Arctic, Thin soils of mountainous areas, Overgrazed areas Areas lacking in fuel resources, Areas lacking a permanent supply of fresh clean water – Ethiopia, Sudan Densely populated areas • Relief Flat lowland areas – Netherlands, Bangladesh. Stable volcanic areas – Mount Etna • Climate Areas of sunshine • Vegetation Areas of grasslands – Denmark, Argentina • Soils Areas of highly fertile humus (soil) - Ganges • Resources Areas where coal are easily accessible – Rhine, Donbas, Yorkshire • Water supplies Areas of reliable rainfall – North Western Europe Guess the Population and Population Density Country 1. China 2. UK 3. Sweden 4. Ghana 5. Afghanistan 6. The Gambia 7. Nigeria 8. Italy 9. Japan 10. India 11. Bangladesh Population 1. 1.379 billion 2. 65.64 million 3. 9.903 million 4. 28.21 million 5. 34.6 million 6. 63.82 7. 186 million 8. 60.6 million 9. 127 million 10. 1.324billion 11. 163 million Population density per km2 1. 146 2. 263 Why is population 3. 22 density an 4. 126 important statistic 5. 50 6. 176 to consider? 7. 195 8. 201 9. 336 10. 382 11. 1278 • Macao tops the list at 20,204 people per km square. Traffic congestion, bad air quality, and Macao has many social problems. • Monaco is second with 19,250 people per km square. Recently water and drought problems have escalated in Monaco. Where will populations change Where are future populations increasing? Should we worry about where the populations are rising? Implications of population change Try to come up with a definition for the following words: Over Population Under population Optimum Population Overpopulation - when there are too many people in an area relative to the amount of resources and the level of technology available locally to maintain a high standard of living. Overpopulation is characterised by low per capita income, high unemployment and outward migration. Underpopulation This occurs when there are too few people in an area to use the resources efficiently for a given level of technology. An increase in population would mean a more effective use of resources and increased living standards. Optimum Population This is the theoretical population which, working with all the available resources, will produce the highest standard of living for the people of that area. This concept is dynamic, when technology improves, new resources become available which means more people can be supported. Population theories • The world’s population has grown much faster during the last century than it has ever grown before • Many geographers, economists and other academics have tried to work out just how much the world’s population can grow before the planet is overwhelmed • In general the resulting models of development have been classified into 2 groups: optimistic models and pessimistic models The Earth is Full: What are his key arguments? Is he optimistic or pessimistic? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DZT6YpCsapg Malthus, Boserup and Simon may not all agree that we’re full…. Next lesson: Population and resource consumption theories