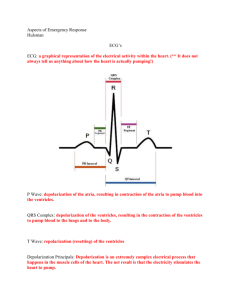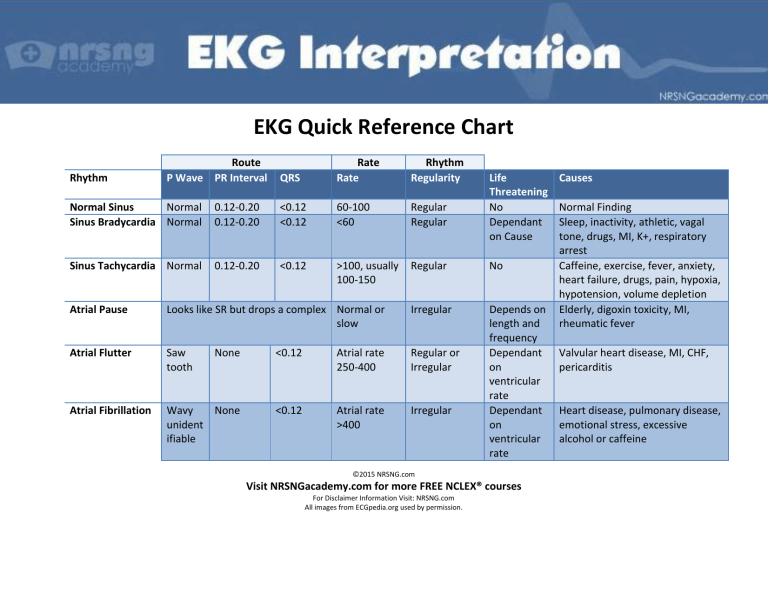
EKG Quick Reference Chart Rhythm Route P Wave PR Interval QRS Rate Rate Rhythm Regularity Life Threatening No Dependant on Cause Normal Sinus Normal Sinus Bradycardia Normal 0.12-0.20 0.12-0.20 <0.12 <0.12 60-100 <60 Regular Regular Sinus Tachycardia Normal 0.12-0.20 <0.12 >100, usually 100-150 Regular No Depends on length and frequency Dependant on ventricular rate Dependant on ventricular rate Atrial Pause Looks like SR but drops a complex Normal or slow Irregular Atrial Flutter Saw tooth None <0.12 Atrial rate 250-400 Regular or Irregular Atrial Fibrillation Wavy None unident ifiable <0.12 Atrial rate >400 Irregular ©2015 NRSNG.com Visit NRSNGacademy.com for more FREE NCLEX® courses For Disclaimer Information Visit: NRSNG.com All images from ECGpedia.org used by permission. Causes Normal Finding Sleep, inactivity, athletic, vagal tone, drugs, MI, K+, respiratory arrest Caffeine, exercise, fever, anxiety, heart failure, drugs, pain, hypoxia, hypotension, volume depletion Elderly, digoxin toxicity, MI, rheumatic fever Valvular heart disease, MI, CHF, pericarditis Heart disease, pulmonary disease, emotional stress, excessive alcohol or caffeine Junctional Rhythm Accelerated Junctional Rhythm Junctional Tachycardia Supraventricular Tachycardia INVERT ED before or after QRS or absent INVERT ED before or after QRS or absent INVERT ED before or after QRS or absent Pointed or hidden in T <0.12 <0.12 40-60 Regular Dependant on ventricular rate Electrical impulse not arriving from SA node, AV node fires at inherent rate <0.12 <0.12 60-100 Regular Dependant on ventricular rate Digoxin toxicity, damage to AV node <0.12 <0.12 >100 Regular Dependant on ventricular rate Same as SVT Immeasur able <0.12 150-250 Regular Dependant on rate and patient ability to tolerate Caffeine, CHF, fatigue, hypoxia, mitral valve disease, altered pacemaker in heart ©2015 NRSNG.com Visit NRSNGacademy.com for more FREE NCLEX® courses For Disclaimer Information Visit: NRSNG.com All images from ECGpedia.org used by permission. Idioventricular Rhythm None None 20-40 Regular Yes Digoxin toxicity, acute MI 150-250 Regular Yes, may have pulse MI, ischemia, digoxin toxicity, hypoxia, acidosis, ↓K+, ↓BP None >0.11 wide and bizarre >0.11 wide and bizarre None Ventricular Tachycardia None None Ventricular Fibrillation None None Yes, no pulse Follow PVC, VT, most common cause of sudden death Possibl e Normal None None None Irregular, vary in size, shape and height No QRS Asystole Yes >0.20 <0.12 Varies Usually Not 2° AV Block Type I Normal Varies: progressiv ely prolonged <0.12 Varies 2° AV Block Type II Normal Consistent Normal or normal or wide prolonged Regular or irregular Regularly irregular: QRS dropped after progressively prolonged PRI Regular or irregular; occasionally dropped QRS Follows VT/VFib, acidosis, hypoxia, ↓K+, hypothermia, drug overdose First sign of increasing AV block 1° AV Block Usually slow Usually Not Acute inferior MI, digoxin toxicity, vagal stimulation, conduction system disease Dependant on overall ventricular rate, may progress to 3° AV Block BBB, anterior MI, lesions of conduction system ©2015 NRSNG.com Visit NRSNGacademy.com for more FREE NCLEX® courses For Disclaimer Information Visit: NRSNG.com All images from ECGpedia.org used by permission. 3° AV Block Normal Premature Atrial Contractions Yes, PAC P wave shaped differe nt Inverte d before or after QRS or absent None Premature Junctional Contractions Premature Ventricular Contractions No Wide relationshi p between PR & QRS May differ <0.12 from underlying rhythm Slow Regular Yes: pacemaker needed Rate of underlying rhythm PAC complexes come early No <0.12 <0.12 Rate of underlying rhythm PJC make it irregular No Vagal tone, stress, caffeine, alcohol, heart failure, digoxin toxicity, ↓K+ N/A >0.11 wide and bizarre Dependant on underlying rhythm Irregular due to premature beat Depends on frequency and how close to T wave Ventricular irritability, hypoxia, ↓K+, Ca, MI, digoxin toxicity, anxiety ©2015 NRSNG.com Visit NRSNGacademy.com for more FREE NCLEX® courses For Disclaimer Information Visit: NRSNG.com All images from ECGpedia.org used by permission. Atria and ventricles beat independently, digoxin or K+ toxicity, acute MI, ischemic heart disease Coffee, tea, alcohol, CHF, emotions, fatigue, fever, hypoxia, mitral valve disease