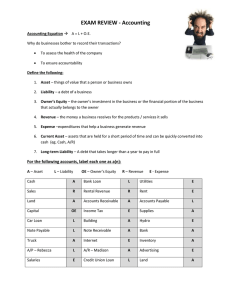
Accounting revision Short answer revision questions 1. What is an asset? Assets are items of value owned or controlled by a business. These include the cash they have in the bank, money owed to them by customers for the supply of goods or services (called accounts receivable or debtors), inventories or stock of goods they own, furniture, vehicles and land. Business try to increase the number and value of assets they have, because it is the assets of a business built up in the past that provide profits and benefits in the future. 2. What is a liability? Liabilities are amounts owed by a business to external parties. A business has liabilities. Typically it will owe money to people because it has bought goods(inventories) or services on credit from them (called accounts payable or creditors). It may have taken out a loan from a finance company. This is also a liability. Similarly, if a business has a loan secured by a mortgage over its property, this is a liability. The business will have to sacrifice benefits and profits to pay these amounts sometime in the future. 3. What is owner’s equity? An owner of a business can calculate what his or her interest or investment in the business is worth by deducting the liabilities from the assets of the business. This is call owner’s equity. Owner’s equity is the difference between the assets and liabilities of a business, and equals the amount of the owner’s interest or investment in the business. 4. What is GST and what does it apply to in Australia? The goods and services tax (GST) is a broad-based tax of 10% on the supply of most goods and services consumed in Australia. It is designed to be collected by enterprises but eventually paid by consumers. 5. What is an accounts receivable? Accounts receivable is the money that a company has a right to receive because it had provided customers with goods or services. Accounts receivable are reported as a current asset on a company’s balance sheet. It’s an asset of the company. 6. What is an accounts payable? When a company orders and receives goods (or services) in advance of paying for them, we say that the company is purchasing the goods on account or on credit. The supplier of the goods on credit is also referred to as a creditor. If the company receiving the goods does not sign a promissory note, the vendor’s bill or invoice will be recorded by the company in its liability account Accounts Payable. 7. In the following scenario identify the accounts receivable and the accounts payable from the point of view of J Jones: H Holmes purchases 4,000 worth of inventories on credit from J Jones. J Jones purchases 2,000 worth of inventories on credit to K Kim 8. State the effect of each of the following transactions on the accounting equation a. 100,000 was borrowed from the bank to purchase new equipment Asset will increase A(increase, equipment)=L(loan increase)+OE b. 6,600(including GST) worth of inventories was purchased on credit from G Good A(inventories, increase)=L(GST Crs Rec decrease)(A/c payable increase)+OE c. 80,000 worth of land was purchased for cash A (land increase) (cash at bank decrease)=L+OE d. The owner commenced business with 20,000 cash, 15,000 motor vehicle and a 10,000 loan from the bank A(cash at bank, motor vehicle increase)= L(loan, increase)+OE(capital, increase 9. Read the following scenario and answer the questions below. Jenny Jones owns a hairdressing salon. She started her business with 50,000 cash, 15,000 worth of furniture and a bank loan of 12,000. She purchased a house for 350,000 and owes 300,000 to the bank. She has a motor vehicle valued at 25,000 which she uses after work hours and on the weekend. She also owns a motor cycle valued at 13,000 which she rides on the weekends with her friends. a. Which assets and liabilities are of a personal nature b. Which assets and liabilities are business related c. Using the businesses assets and liabilities only, find the value of the capital Jenny has contributed to the business 10. What are source documents and what is their function? P39 40 Describe, purpose, why are they important A source document provides details of a transaction and the evidence that the transaction has occurred. Source documents vary in appearance. They may be standard printed or electronic documents (receipts, tax invoices) or less formal documents (properly authorized inter-office memoranda). They may originate in our business organization or in another organization and vary in the way they are generated and transmitted. Source documents are extremely important because they provide evidence for both internal and external auditors as to the validity of transactions. They are used as the basis for entries in the accounting records. They collect and transmit information on transactions that usually occur in a section of the business different from where the accounting entries are made. 11. What is the accounting entity convention? The accounting entity convention is the basic principle that the personal transactions of the owners should be kept separate from those of the business. The business is always viewed as a separate entity, regardless of whether the firm is a sole trader a partnership or a company. The accounting entity convention separates the owner from the business for accounting purposes. 12. What is the double entry principle? Double entry accounting is a record keeping system under which every transaction is recorded in at least two accounts. For every transaction entered in the accounts, total debits equal total credits.