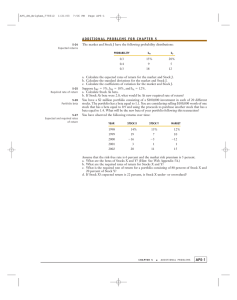
It can be observed that as the number of stocks increases the diversify and effect of each additional stock on unsystematic risk diminishes. Stocks included in portfolio are carefully selected rather than adding them randomly the graph would change. if you choose tax correlations within another and with lost and alone risk the portfolio whatsoever decline faster than if random stocks were added. the rivers would hold if we added stocks with high correlations and high standard deviation of expected returns most investors are rational in the sense that they dislike risk other things held constant. Why would an investor hold one or only few stocks? why not hold a market portfolio consisting of all stocks? there are several answers to the second question. 1. Administrative costs and commission would more than offset the income for individual investors. 2. Index fund can be used by investors for diversification and many individuals can and do get broad diversification thru these funds. 3. To believe that they can pick stocks that will be the market so they buy them rather than the broad market. 4. Superior analysis get the market should i find and buy undervalued stocks and sell overvalued ones. In the process most tax become proper in baguio with their expected returns consistent with the risks. Capital asset pricing model illustrated If we know the risk as measured by beta of a particular share we can use the capital asset pricing model to determine that securities required rate f return. The capital asset pricing model known as CAPM is a model developed to help determine a shares required rate of return for a given level of risk. If an individual chooses to invest her money then she must approve phone consumption. What rate of return would our investor in demand just to postpone her consumption? we implicitly assume the investor takes on no risks whatsoever but merely postpones consumption. she will want compensation for the wait plus an additional returned for any inflationary pressures an inflation premium. Investor demands at 3% return to postpone consumption and another 2% to cover the expected rate of inflation 5% rate of return. that is a the risk-free rate of return is 5%. for now let us put her funds into a riskless security that pays a 5% rate of return. We tend to think of treasury securities as a good proxy for a riskless asset there is no default risk. The beta coefficient concept When a stock is held by itself it's rest can be the standard deviation of its expected returns never the standard deviation is difficult to use when the stock is held in a portfolio as stocks a general are. systemic risk is measured by a stocks a beta coefficient (b) Beta is a measure of the sensitivity of a securities return relative to the returns of a broad-based market portfolio securities. later is a defined mathematically as the ratio of the covariance aphro terms of security (i) and market portfolio (m) variance of returns of the market portfolio. covariance is an absolute statistical measure of the extent of two variables securities move together beta measures to the comovement between a stock and the market portfolio. the tendency of a stock to move with the market is reflected in its beta coefficient which is a measure of the stocks of volatility relative to that of an average stock. Beta is a key element of the CAPM. The succeeding analysis of risks in a portfolio setting as part of the capital asset pricing model. An average risk stock is defined as one that tends to move up and down in step for the general market as measured by some index such as the dow jones industrials, s & p 500, for the new york stock exchange index. Such a stockwell by definition have a beta of 1.0 watch it's about in general if you the market moves up by 10% the structure also move up by 10% one of the market falls by 10% the stock will likewise fall by 10%.