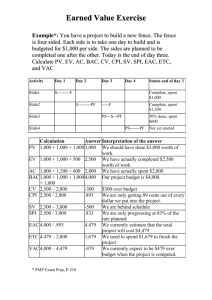
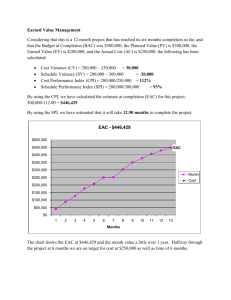
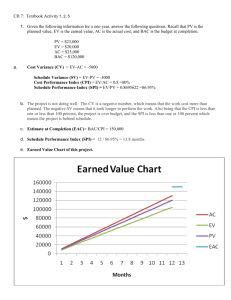
1. If a project has a To Complete Performance Index (TCPI) of 0.80, this means that: a. The project can spend money at a rate 12% higher than planned and still meet the project budget (Correct) b. 90% of the budget planned up to today has been spent c. 90% of the work planned up to today has been completed d. The project can spend money at a rate 8% lower than planned to meet the project budget Solution: 1 Mark. The project can spend money at a rate 12% higher than planned and still meet the project budget. The To Complete Performance Index (TCPI) is the efficiency needed to finish the project on budget. If it is smaller than 1, that means that we have more money left on the budget than the remaining Planned Value (PV) to achieve. Therefore, in theory, we can spend more money yet can still finish the project on budget. (However, in reality, it is generally preferred to finish the project under budget. A TCPI smaller than 1 is a good sign that the project is going healthy.) e. Planned Value (PV) f. Earned Value (EV) g. Estimate at Completion (EAC) Solution: 1 Mark. Estimate to Complete (ETC). By definition, Estimate to Completion (ETC) is the amount of money we need to put into the project from today in order to complete it. Solution: 1 Mark. Planned Value (PV). Planned Value (PV) is how much value of work was scheduled to achieve to date. EVM Estimate At Completion (EAC) Questions. Since there are multiple Estimate at Completion (EAC) formulas, scholars should be able to get clues from the questions on which EAC formula to use (Please write them down somewhere before attempting any questions, in exam however you will be expected to memorize all formulas: EAC = BAC/CPI If we believe the project will continue to spend at the same rate up to now (e.g. the delay is caused by reasons which is likely to continue) EAC = AC + (BAC-EV) If we believe that future expenditures will occur at the original forecasted amount (no more delays of the same kind in future) EAC = AC + [(BAC-EV)/(SPI*CPI)] If we believe that both current cost and current schedule performance will impact future cost performance EAC = AC + New Estimate If we believe the original conditions and assumptions are wrong 2. For the project with original project budget $1000 and both the Cost Performance Index (CPI) and Schedule Performance Index (SPI) equal 1. Assuming the project will continue to spend money at the same rate, what is the Estimate At Completion (EAC) of the project? a. b. c. d. $1,000 $833 $933 $1,033 Solution: 2 Marks. As the project will continue to spend at the same current rate, the formula to be used would be: EAC = BAC/CPI, EAC = $1000 / 1 = $1000 3. For the project with Earned Value (EV) = $360, Actual Cost (AC) = $400 and both Cost Performance Index (CPI) and Schedule Performance Index (SPI) equal 0.90. The original project budget is $1,000. Assuming the remaining work will be impacted by the current cost performance and current schedule performance, what is the Estimate At Completion (EAC) of the project? a. b. c. d. $1,190 $1,390 $1,290 $1,090 Solution: 2 Marks. $1,190. As the project will be impacted by the current cost performance and current schedule performance, the formula would be: EAC = AC + [(BAC-EV)/(SPI*CPI)], EAC = $400 + [($1000 – $360) / (0.9 * 0.9)] = $1190 4. For a project with Estimate at Completion (EAC) = $120,000 and Cost Performance Index (CPI) is 0.90. What is the Budget at Completion (BAC)? a. $108,000 b. $118,000 c. $158,000 d. $208,000 Solution: 1 Mark. $108,000. As no information is given on the future performance of the project, we could safely assume that the project will spend at the same rate. So we will make use of the formula: EAC = BAC / CPI, $120,000 = BAC / 0.90, BAC = $120,000 * 0.90 = $108,000 5. For a project with Earned Value (EV) = $300, Actual Cost (AC) = $350 and Planned Value (PV) = $400. The overall project budget is $1,000. Assume that you will continue to spend at the same rate as you are currently spending. What is the Variance At Completion (VAC)? a. b. c. d. -$167 $167 $150 -$150 Solution: 2 Marks. -$167. As the project will continue to spend at the same current rate, the formula to be used would be: VAC = BAC – EAC, EAC = BAC/CPI, CPI = EV/AC, VAC = BAC – BAC/(EV/AC) = $1000 – $1000/($300/$350) = -$167 6. For the project with Earned Value (EV) = $300, Actual Cost (AC) = $250 and Planned Value (PV) = $300. The original project budget is $1000. Assuming the project will continue to spend money at the same rate, what is the Estimate At Completion (EAC) of the project? a. b. c. d. $833 $933 $1,000 $1,033 Solution: 1 Mark. As the project will continue to spend at the same current rate, the formula to be used would be: EAC = BAC/CPI, CPI = EV/AC, EAC = BAC/(EV/AC) = $1000 / ($300/$250) = $833 7. For the project with Earned Value (EV) = $350, Actual Cost (AC) = $300 and Planned Value (PV) = $400. The original project budget is $1,000. Assuming the remaining work will be impacted by the current cost performance and current schedule performance, what is the Estimate At Completion (EAC) of the project? a. b. c. d. $937 $837 $987 $1,280 Solution: 2 Marks. As the project will be impacted by the current cost performance and current schedule performance, the formula would be: EAC = AC + [(BAC-EV)/(SPI*CPI)], SPI = EV / PV = $350 / $400 = 0.875, CPI = EV / AC = $350 / $300 = 1.167, EAC = BAC/(EV/AC) = $300 + [($1000 – $350) / (0.875 * 1.167)] = $937 8. Your project is scheduled for 2 years. There are six different teams working on five major functional areas. Some teams are ahead of schedule while others are falling behind. There are cost overruns in some areas, but you’ve also saved costs in others. Due to all this, it is difficult to understand whether you are over or under budget. Nine months into the project, while the total project budget is $4,200,000, you’ve already spent $1,650,000. CPI is 0.875. Find out EAC? Solution: 1 Mark. EAC = BAC / CPI = 4,200,000 / 0.875 = $4,800,000 9. Your project is scheduled for 2 years. There are six different teams working on five major functional areas. Some teams are ahead of schedule while others are falling behind. There are cost overruns in some areas, but you’ve also saved costs in others. Due to all this, it is difficult to understand whether you are over or under budget. Nine months into the project, while the total project budget is $4,200,000, you’ve already spent $1,650,000. CPI is 0.875. Find out ETC? Solution: 1 Mark. ETC = EAC – AC = 4,800,000 – 1,650,000 = $3,150,000 10. Your project is scheduled for 2 years. There are six different teams working on five major functional areas. Some teams are ahead of schedule while others are falling behind. There are cost overruns in some areas, but you’ve also saved costs in others. Due to all this, it is difficult to understand whether you are over or under budget. Nine months into the project, while the total project budget is $4,200,000, you’ve already spent $1,650,000. CPI is 0.875. Find out VAC? Solution: 2 Mark. VAC = BAC – EAC, = 4,200,000 – 4,800,000 = $-600,000. Since the Variance At Completion is negative, the project will be over budget at completion by $600,000 11. You are managing a software project with an initial budget estimate of 2 million USD. During interim cost and schedule performance analysis, you figured out that: You should have spent $500,000 till now based on your initial plans and 1,000 man/days of schedule activities. You spent $600,000 till now and completed 1,100 man/days of schedule activities which should have cost $450,000 based on your initial plans. You re-estimated the budget required for the remaining work to be done as $1,500,000. What is the Variance at Completion? a. b. c. d. -$100,000 $100,000 -$50,000 $50000 Solution: 3 Marks VAC (Variance at Completion) = BAC - EAC = 2 million USD - EAC EAC (Estimate at Completion) = AC + ETC = $600,000 + $1,500,000 = $2,100,000 VAC = $2,000,000 - $2,100,000 = -$100,000 12. You are managing a software project with an initial budget estimate of 2 million USD. During interim cost and schedule performance analysis, you figured out that you should have spent $500,000 till now based on your initial plans and 1,000 man/days of schedule activities. You spent $600,000 till now and completed 1,100 man/days of schedule activities which should have cost $450,000 based on your initial plans. You re-estimated the budget required for the remaining work to be done as $1,500,000. What is the TCPI based on your new Estimate at Completion value? a. b. c. d. 1.03 1.11 0.90 0.97 Solution: 1 Mark TCPI based on EAC is calculated as below: TCPI = [BAC-EV] / [EAC-AC] = [$2,000,000-$450,000] / [$2,100,000-$600,000] TCPI (based on EAC) = 1.03 13. You are managing a software project with an initial budget estimate of 2 million USD. During interim cost and schedule performance analysis, you figured out that you should have spent $500,000 till now based on your initial plans and 1,000 man/days of schedule activities. You spent $600,000 till now and completed 1,100 man/days of schedule activities which should have cost $450,000 based on your initial plans. You re-estimated the budget required for the remaining work to be done as $1,500,000. What is the status of your project? a. Project is ahead of schedule, over budget, and it is harder to complete the project on new EAC b. Project is ahead of schedule, over budget, and it is easier to complete the project on new EAC c. Project is behind schedule, over budget, and it is harder to complete the project on new EAC d. Project is ahead of schedule, under budget, and it is easier to complete the project on new EAC Solution: 1 Mark. Project is ahead of schedule, over budget, and it is harder to complete the project on new EAC CPI<1 and CV is negative, therefore project is over budget SPI>1 and SV is positive, therefore project is ahead of schedule TCPI>1, therefore project is harder to complete in new EAC value based on current project performance. 14. When you collect the earned value data for your project, you get the following data: PV = $1,500,000, EV = $ 1,200,000, AC = $1,000,000. You expect the factors for cost variance to continue in the same way in future. The value of the remaining work is $1,000,000. What should be the new EAC for the project? a. b. c. d. $1,833,333 $2,233,333 $2,000,000 $2,400,000 Solution: 3 Marks. Solution: EAC= BAC/CPI, BAC = 1,200,000+1,000,000 =2,200,000. CPI = EV/AC = 1,200,000/1,000,000 = 1.2. EAC = 2,200,000/1.2 = 1,833,333 15. The project is budgeted at $1,000,000. The following earned value figures have been derived. PV=$500,000, EV = $450,000, AC= $550,000. The cost variances in the project are caused by one-time factors which are no more effective. What will be the estimate at completion for the project? a. b. c. d. $1,100,000 $1,000,000 $900,000 $1,222,222 Solution: 1 Mark. Solution: When the cost variance caused is one time and not expected to continue (the future work will be accomplished at the planned rate), EAC= AC+(BAC-EV) EAC = 550000 + 1000000 – 450000 = 1,100,000 16. A software development project that you are managing has budget at completion of $400,000. At month seven, 65% of the work was planned to be complete but stands at 50%. Actual cost is $275,000. What is the project's ETC? a. b. c. d. $275,000 $289,000 $389,855 $55,000 Solution: 2 Marks. Solution: CPI = 50% *400000/ 275000 = 0.72 EAC = BAC/CPI = 400000/0.72 = 550000 ETC = EAC – AC = 550000 - 275000 = 275000 17. During your project analysis, you understand that there is a cost-variance in the project. Further analysis shows that it is a one-time variance caused by an unexpected rework. You do not expect such situation in future. You would like to get the Estimate at completion for your project, so you perform earned value analysis and get the following data: EV = 2,000,000; PV = 1,500,000; AC = 2,500,000; BAC = 4,000,000. What is EAC? a. b. c. d. $4,500,000 $5,000,000 $4,000,000 $5,500,000 Solution: 1 Mark. Solution: When the variations are one-time, then EAC = AC + BAC - EV = 2,500,000 + 4,000,000 – 2,000,000 = 4,500,000 18. Given a project with the following characteristics, answer the following questions: You are the project manager of a project to build fancy birdhouses. You are to build two birdhouses a month for 12 months. Each birdhouse is planned to cost $100. Your project is scheduled to last for 12 months. It is the beginning of month 10. You have built 20 birdhouses and your CPI is .9091. If the variance experienced so far were to stop, what is the project’s estimate at completion? a. b. c. d. $2600 $2440 $2400 $2800 Solution: 1 Mark. $2600. A few of the EMV questions you encounter in the exam will be fairly straightforward. This question is asking you for the EAC if a variance that was encountered on a project is expected to stop, so use EAC = AC + BAC – EV. EAC = 2200 + 2400 – 2000 EAC = $2600 19. Given a project with the following characteristics, answer the following questions: You are the project manager of a project to build fancy birdhouses. You are to build two birdhouses a month for 12 months. Each birdhouse is planned to cost $100. Your project is scheduled to last for 12 months. It is the beginning of month 10. You have built 20 birdhouses and your CPI is .9091. What is the project’s TCPI using the project’s budget at completion? a. b. c. d. 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 Solution: 1 Mark. This one says use BAC, so TCPI = (BAC – EV)/(BAC – AC) = (2400 – 2000) / (2400 – 2200) = 400/200 = 2. 20. Given a project with the following characteristics, answer the following questions: You are the project manager of a project to build fancy birdhouses. You are to build two birdhouses a month for 12 months. Each birdhouse is planned to cost $100. Your project is scheduled to last for 12 months. It is the beginning of month 10. You have built 20 birdhouses and your CPI is .9091. Senior management wants the percentage of the project that is complete. What should you report? a. b. c. d. 75% 83% 92% 95% Solution: 1 Mark. If you can recall the percentage complete formula, then this problem is really easy! Just plug in the values of EV and BAC to formula: (EV / BAC) *100 = 83% 21. An investment of $200,000 is expected to generate the following cash inflows in six years: Year 1: $70,000, Year 2: $60,000, Year 3: $55,000, Year 4: $40,000, Year 5: $30,000, Year 6: $25,000. Required: Compute payback period of the investment. Should the investment be made if management wants to recover the initial investment in 3 years or less? (Simply mention the payback period calculated for this problem and your interpretation with respect to the question asked at the end of this problem). Solution: 2 Marks. Your payback period must equal 3.375 years, or 3.4 years. Even then it is larger than the required period of three years. This implies this project will not be desirable. 22. An initial investment of $8,320 thousand on plant and machinery is expected to generate net cash flows of $3,411 thousand, $4,070 thousand, $5,824 thousand and $2,065 thousand at the end of first, second, third and fourth year respectively. Calculate the net present value of the investment if the discount rate is 18%. Round your answer to nearest thousand dollars. Calculate NPV, PI, IRR and Payback period? (PV Factors: Year 1 = 1 ÷ (1 + 18%)1 = 0.8475; Year 2 = 1 ÷ (1 + 18%)2 = 0.7182; Year 3 = 1 ÷ (1 + 18%)3 = 0.6086; Year 4 = 1 ÷ (1 + 18%)4 = 0.5158), (Write down calculated values of NPV, PI, IRR and Payback period and interpret as to what will be your decision based on each of the answers obtained for NPV, PI, IRR and Payback period, separately/individually) Solution: 6 Marks. Your answers are following: IRR is 29.33% > 18% therefore ACCEPT PI is 1.25 therefore ACCEPT NPV at RRR is $2,103,458.82 therefore ACCEPT Payback Period is 2.14 therefore ACCEPT 4 marks for answers to each criteria and 0.5 mark each for the four interpretations!