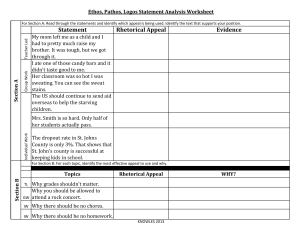
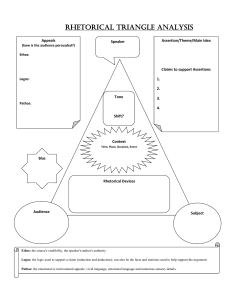
basic rhetorical devices. relevant details from short speeches the main ideas in the speeches inspiration, speech, believe, belief. According to Aristotle, the ability to persuade the audience through one’s speech depends on three : : The moral character of the speaker, which makes him/her and whatever he/she says credible to the audience. : The way the speaker appeals to the emotions of the audience or the frame of mind the speaker puts the audience in. : The logic or convincing facts and evidence put forward by the speaker to convince the audience. : an appeal to credibility or character. An advertisement using ethos will try to convince you that the company is more reliable, honest, and credible; therefore, you should buy its product. Ethos often involves statistics from reliable experts, such as “Nine out of ten dentists agree that Crest is the better than any other brand” or “Americas dieters choose Lean Cuisine”. Often, a celebrity endorses a product to lend it more credibility: Catherine Zeta-Jones makes us want to switch to T-Mobile. : an appeal to emotion. An advertisement using pathos will attempt to evoke an emotional response in the consumer. Sometimes, it is a positive emotion such as happiness: an image of people enjoying themselves while drinking Pepsi. Other times, advertisers will use negative emotions such as pain: a person having back problems after buying the “wrong” mattress. Pathos can also include emotions such as fear and guilt: images of a starving child persuade you to send money. : an appeal to logic or reason. An advertisement using logos will give you the evidence and statistics you need to fully understand what the product does. The logos of an advertisement will be the "straight facts" about the product: One glass of Florida orange juice contains 75% of your daily Vitamin C needs. Rhetorical devices (also known as , , or simply ) are techniques or language used to convey a point or convince an audience; and they are used by everyone: politicians, businesspeople, journalists, novelists, etc. Rhetorical devices add strong appeal to speeches. This is when sounds, words, phrases or clauses are deliberately repeated, to draw readers’ attention to something. Speakers generally use it to appeal to audience’s emotions. Repetition comes in different forms: , and Even though large tracts of Europe and many old and famous States have fallen or may fall into the grip of the Gestapo and all the odious apparatus of Nazi rule, not flag or fail. go on to the end, fight in France, fight on the seas and oceans, fight with growing confidence and growing strength in the air, our Island, whatever the cost may be, fight on the beaches, fight on the landing grounds, fight in the fields and in the streets, fight in the hills; we shall never surrender.“ Winston Churchill This generation of have volunteered the inest ighting our after our of Obama oldiers, ailors, airmen, Marines, and Coast Guardsmen in the time of certain danger. They are part of orce that the world has ever known. They have served uty in istant, ifferent, and ifficult places. Barrack Tod , the d I g ve my daughter’s hand in marriage to D ve, I’d like to s that J ne, my dear daughter, was the reason I bec me a soldier. (the audience laugh). As a soldier, I’ve been ble to scare away from her many men of evil intentions. (audience laugh again). A rhetorical question is a question asked merely for effect, with no answer expected. The answer may be obvious or immediately provided by the questioner. Emotive words/language Use words that appeal to people’s emotion; words capable of arousing people’s feelings Use personal pronouns Use “I’, “we” and most importantly “you” constantly when giving your speech. to make your audience feel included. Are we a nation that tolerates the hypocrisy of a system where workers who pick our fruit and make our beds never have a chance to get right with the law? Are we a nation that accepts the cruelty of ripping children from their parents' arms? Or are we a nation that values families, and works to keep them together?” Barack Obama “Isn’t it shocking to hear of older men having sex with minors or underaged children?” “Isn’t it disgusting having our ears assaulted, everyday, by the unpalatable news of monsters violating unripe kids?” “We need to be mindful of those actions of ours that are capable of damaging our environment.” Simile It’s an indirect comparison between two dissimilar things, using ‘as’ or ‘like’. Similes make writing more appealing. Life is a journey, dear listeners and we all are like travellers on earth. Someday, we all will surely return home. Personification It is a way of animating or giving life to inanimate things; giving animate qualities to inanimate things. In the last one month, the has so many souls. So, for still being alive, we need to be grateful to who made that possible. Metaphor It is a direct comparison between two dissimilar things. Metaphors are meant to create connection between oddly related things. Dear listeners, I urge you to beware of friends in your lives. Beware of the many serpents that wine and dine with you. Hyperbole It is using exaggeration to make a concept seem much more than it really is, so as to draw readers’ attention to whatever is being claimed. - He’s such a gifted runner; runs faster than the wind. - That new apartment costs an arm and a leg A balanced sentence is one where two or more parts which are equal in length, importance, and structure are used to make the sentence. I have met people who are really goodlooking, well-behaved and intelligent. I equally know many who lack beauty, manners and skills. Anecdotes Ten years ago, I met an old man who not only changed my opinion about life but also changed my life. Let me tell you how he did it. are short amusing or interesting stories about real incidents or persons. In your speech, use anecdotes, to make your argument more real and believable Analogy: Analogy is a form of reasoning which compares one thing with another in order to make a particular point. Example: School is like a prison and students are like prisoners. Check the document attached for more persuasive techniques Humor: Humor, such as puns, irony, sarcasm, satire and jokes can be persuasive by dismissing opposing views, providing a more engaging and friendly tone, and sway an audience by having them enter into the joke. Example: 'Totally Artraged' as a pun on 'Totally Outraged' when talking about controversial art. Formal Language: Formal language can make the author sound knowledgeable while removing emotion from the issue. This can make the argument sound reasonable and rational, and the contention seem balanced. For instance, while something like "That totally grassed me out“ will be used in a more relaxed and informal speech, "That really disgusted me.“ will be used in a more formal speech. BREAKOUT SESSION Identify at least FIVE rhetorical devices used in the speech titled “The Metaphor of a Drama Text” Then, explain the intended effect of each of the devices.