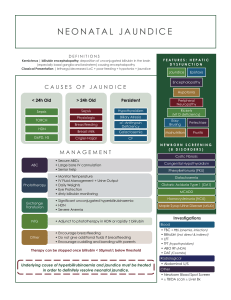
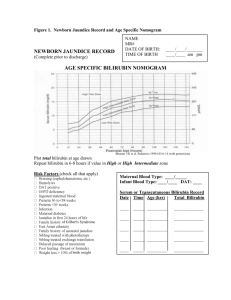
Lesson 6 (II) Сatabolism of complex proteins Variant 1 1. Which one of the following is NOT a heme protein? A. Catalase; B. Cytochrome P450; C. Cytochrome oxidase; D. Phenylalanine hydroxylase. 2. The normal brown color of feces results from the presence of: A. heme; B. biliverdin; C. stercobiline; D. coproporphyrin III. 3. All of the following statements are correct EXCEPT: A. In normal individuals bilirubin is not detectable in urine; B. In hemolytic jaundice excretion of urinary urobilinogen decreases; C. Elevated levels of unconjugated bilirubin in plasma are most often due to increased hemolysis; D. Photoisomers of bilirubin are more water-soluble than natural bilirubin. 4. In cholelithiasis: A. “direct” bilirubin in serum is elevated; B. both may be elevated; C. “indirect” bilirubin in serum is elevated; D. neither is elevated. 5. Products of nucleosides degradation are: A. mononucleotides; B. polynucleotides; C. peptides; D. purine and pyrimidine bases. 6. The patient, 55 years old, is admitted to a hospital with a joint pain syndrome. During examination the contents of uric acid in the blood was 2.1 mmol/l, in the urine 0,066 g/l of protein and blood were found, deposits of lithates in joints and kidney were detected. The cause of such state can be: A. phenylketonuria; B. branched chain aminoaciduria (maple syrup disease); C. alkaptonuria; D. podagra (gout); E. Hartnup’s disease. Lesson 6 (II) Сatabolism of complex proteins Variant 2 1. Unconjugated blirubin is: A. elevated in hemolytic jaundice; B. water-soluble; C. usually found in the bile duct; D. normally excreted in the urine. 2. The enzyme responsible for conjugation of bilirubin, prior to secretion into bile, is A. Alanine synthase; B. Glucuronyl transferase; C. Uroporphyrinogen consynthase; D. Ferrochelatase. 3. Bacteria in the intestine convert bilirubin to: A. urea; B. bilirubin monoglucuronide; C. urobilin; D. bilirubin diglucuronide. 4. In neonatal jaundice: A. "direct" bilirubin in serum is elevated; B. "indirect" bilirubin in serum is elevated; C. both may be elevated; D. neither is elevated. 5. Purine bases are oxidized to: A. urea; B. urine; C. uric acid; D. -alanine. 6. Man, 52 years old, is admitted to a hospital with a joint pain syndrome. During examination the contents of uric acid in the blood was 3.0 mmol/l, in the urine protein and blood were found, deposits in joints were detected. What can be found during X-ray examination (excretory urography) of kidney in this patient? A. Lithates (urates); B. Oxalates; C. Cancer of kidney; D. Absence of kidney; E. Examination of kidney is not necessary in this patient. Lesson 6 (II) Сatabolism of complex proteins Variant 3 1. Urobilinogen can NOT be derived from: A. hemoglobin; B. catalase; C. flavoprotein; D. cytochrome c; E. peroxidase. 2. Bilirubin diglucuronide is: A. elevated in hemolytic jaundice; B. usually found in the bile duct; C. lipid-soluble; D. normally excreted mainly in the urine. 3. After cleavage of hemoglobin iron is released and transported in the blood in: A. transferrin; B. transaminase; C. translocase; D. albumin. 4. In hepatitis: A. "direct" bilirubin in serum is elevated; B. "indirect" bilirubin in serum is elevated; C. both may be elevated; D. neither is elevated. 5. In pyrimidine degradation the nitrogen produce: A. uric acid; B. urine; C. uridine; D. urea. 6. In newborn on the 3rd day of life the skin and mucoses are yellow. Blood level of direct bilirubin is 4.5 mcmol/l, indirect bilirubin – 65.5 mcmol/l. This state is the result of what process? A. Obstruction of bile ways; B. Fructose intolerance; C. Hemolysis of erythrocytes; D. Parenchymatose jaundice; E. Toxic hepatitis. Lesson 6 (II) Сatabolism of complex proteins Variant 4 1. The direct bilirubin is: A. conjugated bilirubin; B. verdoglobin; C. unconjugated bilirubin; D. biliverdin. 2. Urobilinogen is formed in the: A. spleen; B. liver; C. bone marrow; D. bowel; E. kidney. 3. In the liver, the free bilirubin becomes conjugated with: A. glycocholic acid; B. glycosidic bonds; C. glucuronic acid; D. gluconic acid. 4. In cancer of head of pancreas: A. “indirect” bilirubin in serum is elevated; B. “direct” bilirubin in serum is elevated; C. both may be elevated; D. neither is elevated. 5. Purine bases are oxidized to: A. urea; B. urine; C. -alanine; D. uric acid. 6. In infant with neonatal physiological jaundice the blood level of free bilirubin in a considerably exceeds the norm. With lack of what enzyme it is conditioned? A. Biliverdin reductase; B. Xantine oxydase; C. UDP-glucurunyl transferase; D. Adenosine desaminase; E. Hemoglobin oxygenase. Lesson 6 (II) Сatabolism of complex proteins Variant 5 1. Urobilinogen can NOT be derived from: A. hemoglobin; B. catalase; C. flavoprotein; D. cytochrome c; E. peroxidase. 2 At the first step heme is oxidized and cleaved to produce: A. biliverdin; B. bilirubin monoglucuronide; C. bilirubin diglucuronide; D. urobilins. 3. After fomation of biliverdin at the next step it is reduced to: A. bilirubin; B. bilirubin monoglucuronide; C. bilirubin diglucuronide; D. urobilins. 4. Bilirubin diglucuronide is: A. elevated in hemolytic jaundice; B. usually found in the bile duct; C. lipid-soluble; D. normally excreted mainly in the urine. 5. In pyrimidine degradation the nitrogen produce: A. uric acid; B. urine; C. uridine; D. urea. 6. The patient, 55 years old, is admitted to a hospital with a joint pain syndrome. During examination the high contents of uric acid in the blood and deposits of lithates in joints were detected. This state is the result of disorder of what process? A. Disintegration of pyrimidine nucleotides; B. Catabolism of purine nucleotides; C. Catabolism of a hem; D. Proteolysis; E. Reutilization of purine bases.