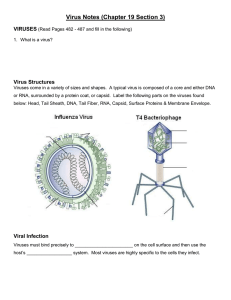
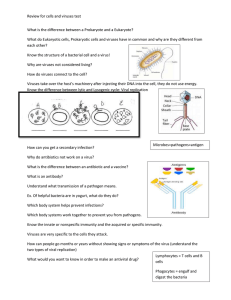
Viral Replication Cycle Worksheet (1) The Lysogenic Cycle occurs when a virus finds matching receptors and then penetrates a host cell and inserts its genetic material. (2) The host cell will then incorporate the genetic material as DNA into its own genome. (3) When the cell replicates its genome before it divides the viral genetic code is copied along with it. (4) The new daughter cells have the viral genetic code in their genome as if it belonged. They may continue to function normally and making more daughter cells or begin the Lytic Cycle to produce viruses. Now that I have outlined the Lysogenic Cycle for you draw an example of it for me. Be sure to label the important parts: virus, cell wall/membrane, viral genetic code, host DNA, daughter cells through out the drawings. (Feel free to use more than one color) 1. 2. 3. 4. The Lytic Cycle is the other cycle used to replicate viral genetic code and it is also used to create new viral particles. Remember that the lytic cycle does not always end with host cell death, some time the viral particles ‘bud’ out of the cell wall or membrane leaving the host cell intact to produce more viruses. On the next page you will find the steps outlined and room for you to draw an example of the cycle. Using the steps described below draw the lytic cycle in the boxes provided, Be sure to label each step in your drawings. (1) The Lytic Cycle begins with the virus finding matching receptors on the host cell wall or membrane. (2) The host cell will engulf the virus in an endosome or the virus will fuse with the cell membrane. (bacteriaphages will dock with the tail fibers, weakening the host cell wall and inserting the viral DNA or RNA) (3) Once the virus has penetrated the host cell the viral genetic material is transcribed then translated using the host cell’s machinery. (4) The host cell will create proteins and genetic material needed to make new virus particles. (5) New viruses will be constructed with the new particles made by the host cell. (6) Viruses lyse the cell to release lots of newly made viruses or viruses ‘bud’ out of the cell wall/membrane to infect other cells. SEE NEXT PAGE FOR TABLE