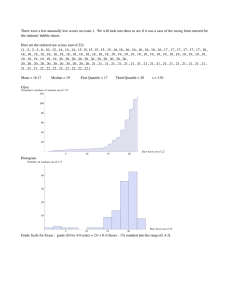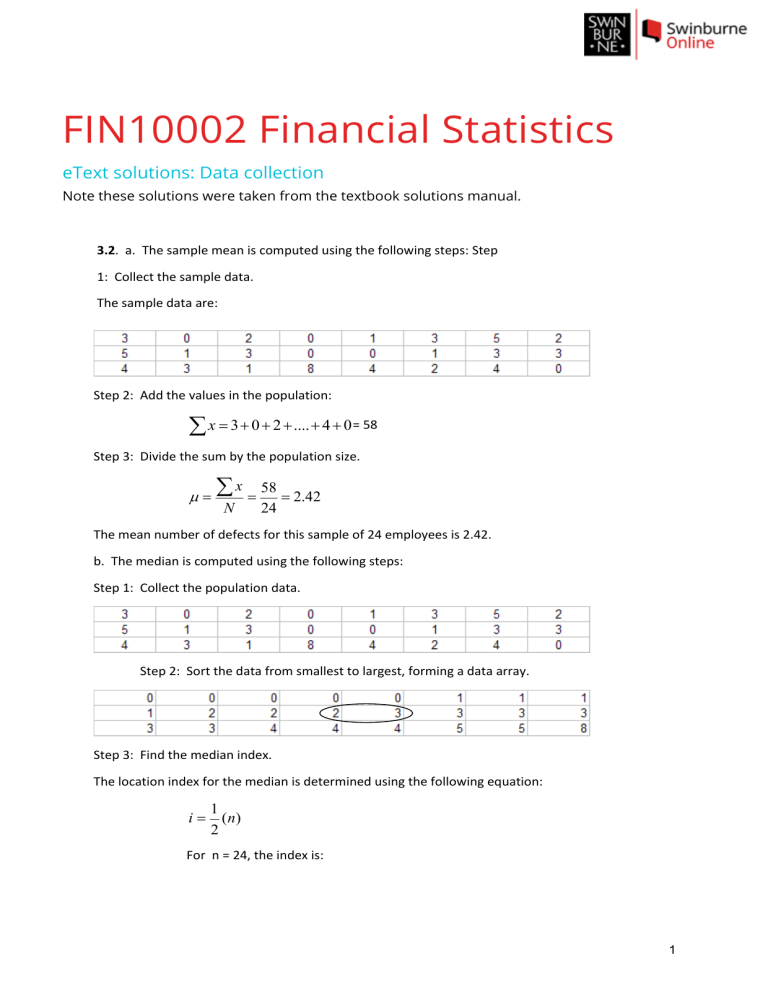
FIN10002 Financial Statistics eText solutions: Data collection Note these solutions were taken from the textbook solutions manual. 3.2. a. The sample mean is computed using the following steps: Step 1: Collect the sample data. The sample data are: Step 2: Add the values in the population: å x = 3 + 0 + 2 + .... + 4 + 0 = 58 Step 3: Divide the sum by the population size. x 58 µ = å = = 2.42 N 24 The mean number of defects for this sample of 24 employees is 2.42. b. The median is computed using the following steps: Step 1: Collect the population data. Step 2: Sort the data from smallest to largest, forming a data array. Step 3: Find the median index. The location index for the median is determined using the following equation: i= 1 ( n) 2 For n = 24, the index is: 1 1 i = (24) = 12 2 Step 4. Find the median Because the index is 12 which is an integer, the median is the average of the 12th and 13th data values going from either end. These two values are 2 and 3. This the median is: Md = 2+3 = 2.5 2 Half the data values fall below 2.5 and half the data values fall above 2.5. c. To determine if there is a mode and what the value of the mode is, we use the following steps: Step 1: Collect the population data. See parts a. or b. Step 2: Organize the data into a frequency distribution. Mode = 3 3 occurs 6 times Step 3: Determine the value that occurs most frequently. The value 3 occurs 6 times which is the most of any value in the sample. 3.3. Step 1: Sort the data from low to high. 11.5 14.4 12.8 14.4 13.1 14.7 13.2 15.1 13.5 15.5 13.6 15.9 13.8 16.2 14.2 16.3 14.2 17.1 14.3 18.7 Step 2: Determine the quartile location index and find the quartile value. To determine the location index for the 1st quartile (p=25) we do the following: i= p 25 ( n) = (20) = 5 100 100 2 Since the index, 5, is an integer, the 1st quartile is determined by finding the average of the 5th and 6th values from the lower end of the sorted data. This is: Q1 = 13.5 + 13.6 = 13.55 2 The location index for the 3rd quartile is: i= p 75 ( n) = (20) = 15 100 100 Since the index, 15, is an integer, the 3rd quartile is determined by finding the average of the 15th and 16th values from the lower end of the sorted data. This is: Q3 = 15.5 + 15.9 = 15.7 2 Thus, the 1st quartile value is 13.55 meaning that 25 percent of the data values fall below 13.55. The third quartile is 15.7 meaning that 75% of the data values fall below 15.7. 3.7. 46 73 Sorted data: 48 73 55 78 58 80 59 81 65 82 66 86 67 88 69 91 70 95 1 (20) = 10; the median is the average of the 10th and 11th values in 2 70 + 73 the data set. So median = = 71.5 2 25 b. 25th percentile (Q1) position = (20) = 5; Q1 is the average of the 5th and 6th values 100 59 + 65 = 62 in the data set. So Q1 = 2 75 (20) = 15; Q3 is the average of the 15th and 16th 75th percentile (Q3) position = 100 81 + 82 = 81.5 values in the data set. So Q3 = 2 60 60th percentile position = (20) = 12; the 60th percentile is the average of the 12th 100 73 + 78 and 13th values in the data set. So the 60th percentile = = 75.5 2 a. Median position = 3 3.11 a. The weighted mean is computed using: xW = åw x åw i i = i (7,400)(123) + (14,400)(402) + (12,300)(256) + (6,200)(109) + (3,100)(67) = 11,213.48 123 + 402 + 256 + 109 + 67 b. It is reasonable that plants with more employees would have more medical issues. The weighted average takes into account the number of employees and is a more reasonable measure of the average payments than would be an unweighted average that treats all plants as equals. 3.16 a. Average = Sxi 4143.6 = = 165.744 n 25 b. The ranked data are 112.6 123.9 131.0 134.0 141.9 145.4 155.2 156.5 159.3 161.3 161.9 162.7 164.9 165.8 168.3 171.2 173.1 177.4 178.8 182.0 185.8 192.0 211.1 213.1 214.4 The median’s index = (p/100)n = (50/100)25 = 12.5. The rule is to round this up to the 13th observation = 164.9. This indicates that the mean is larger than the median. The data’s distribution is slightly right-skewed. c. The first quartile’s index = (25/100)25 = 6.25. The rule is to round this up to the 7th observation = 155.2. The third quartile’s index = (75/100)25 = 18.75. The rule is to round this up to the 19th observation = 178.8. 4 For a Boxplot: Lower limit = Q1 – 1.5(Q3 – Q1) = 155.2 - 1.5(178.8 – 155.2) = 119.8 Upper limit is Q3 + 1.5(Q3 – Q1) = 178.8 + 1.5(178.8 – 155.2) = 214.2. There are no outliers shown in the plot although there are two, 214.4 and 112.6 in the data. 5