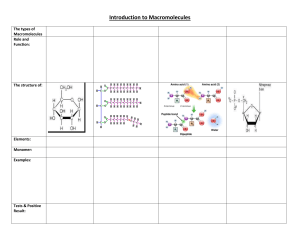
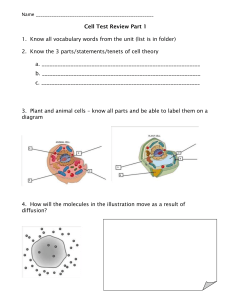
MIDTERM 1 STUDY GUIDE FORMAT AND LOGISTICS Weighting: 10% of final grade Timing: ONE attempt, 90 minutes (1 ½ hours) allowed*** Total Points: 70 Format: o 30 multiple choice questions (1 point each) o 1 matching question (10 points) o 10 fill in the blanks questions with a provided word bank (1 point each) o 5 multi-select questions (4 points each) *** If you have an accommodation from CAL and require extra time, DO NOT START THE TEST and contact your instructor first to set up your test with the appropriate time allotment.*** CONTENT STUDY TIPS: Module 1: Intro and Scientific Method - Identify/list the characteristics of life Given an example, identify independent and dependent variables Definition and limits of a scientific theory Nature of scientific experimentation and conclusions; overview scientific method Module 2: Chemistry of Life and Macromolecules - What chemical bonds are and how they are formed; types of bonds and their characteristics Define isotope, matter, ion, atom, proton, neutron, electron Special properties of water and their consequences (ice floating; painful belly flops, etc) Understanding of pH scale (what is acidic, basic, neutral) Define and apply hydrophilic; hydrophobic How macromolecules are formed and broken down For each macromolecule, know what the monomer is called (and for lipids: what are the main components) Different classes of lipids and their properties; saturated vs. unsaturated vs. trans fats Different types of carbohydrates and their functions in plant or animal cells Levels of protein structure: what each looks like, what kinds of forces/bonds hold together EACH level Compare and contrast RNA and DNA; overall DNA structure Module 3: Cell Structure and Function - Cell organelles/parts and their functions Compare and contrast: eukaryotic vs. prokaryotic cells; animal vs. plant cells Explain how enzymes work (use terms like active site, substrate, competitive and noncompetitive inhibitor); label a diagram of an enzyme Understand the fluid mosaic model of membranes; what are the functions of the proteins; what substances can cross freely vs. not Definitions of kinetic energy, potential energy, entropy - Compare and contrast types of transport across cell membranes (facilitated diffusion vs. active transport, etc) Apply principles of osmosis to a situation (hyper, hypo and isotonic environments) Different types of cell junctions: where they are found and what the main function is for each Module 4: Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis - Inputs and outputs for each stage of respiration: glycolysis, citric acid cycle, electron transport chain Consequences and purposes of fermentation Inputs and outputs for each stage of photosynthesis: Light reactions and Calvin cycle Define heterotroph, autotroph Parts of a leaf and chloroplast