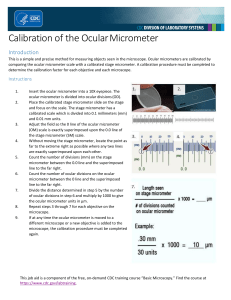
MEASUREMENT OF CELL SIZE: Meaning of Micrometry: • Micrometry is the science in which we have some measurement of the dimensions of an object being observed under the microscope. The method employs some special types of measuring devices which are so oriented that these can well be attached to or put into the microscope and observed. The object, to be measured, is calibrated against these scales. MICROMETER • Once we are observing an object under a microscope by the 5X objective and the 10X eyepiece we say that the image that we are able to perceive is 5 × 10 = 50 times of the object. • We get the magnified view no doubt and also that it is the perfect coordination of the dimensions, but to find out the exact size of the object will need precision and that is achieved through the application of some small scales called micrometers. Types of Micrometry TWO TYPES OF MICROMETERS: 1. stage micrometer 2. ocular meter or ocular micrometer Stage Micrometer • As is clear from its name it is for the measurement on the stage of the microscope where an object is to be kept. This micrometer is of a slide’s shape and size and has a mount of very finely graduated scale. The scale measures only 1 mm and has a least count of 0.01 mm, i.e. 1 mm region is divided into 100 divisions. As 1 mm has 1000µ, one division of stage micrometer is equivalent to 10µ. Ocular Meter • This micrometer is used inside the eyepiece. The upper eye lens is unscrewed and the ocular meter is put into the tube of eyepiece, and the eye lens is again replaced in its original position. There are usually 50 or 100 divisions in the ocular meter which are engraved on the glass. Objective •To measure the dimensions of common microorganisms by calibration and standardization of microscope using stage micrometer and ocular micrometer. Requirements: 1. Microscope 2. stage micrometer 3. ocular meter 4. slide of the microorganism to measured. Procedure • To work out the measurements per ocular divisions the stage micrometer is kept under low power of microscope and is observed through the eyepiece having ocular meter. • Suppose we have 10 X objective and 5 X eyepiece fitted in the microscope with a tube of 170 mm length. Procedure • At this magnification the number of ocular divisions coinciding the stage micrometer are observed and then calculated for microns per ocular divisions • Example: Let us take that 5 ocular divisions coincide with 7 divisions of stage micrometer. • We know 1stage div. =0.01mm or 10μm • So when 5 ocular divisions coincide with 7 divisions of stage micrometer that means 5 ocular div= 7 stage div. or 70 μm Now we have to calibrate 1 ocular div=? μm Procedure • 5 ocular division = 70 μm stage div. (cross multiply) • 1 ocular division= 70/5 ×1= 14 μm • So, 1 ocular div. is equal to14µ where 1stage div.=10 μm Or, it can also be calculated by following formula: • One division of ocular = Number of stage micrometer divisions/Number of ocular meter divisions × 10 • In the case mentioned above it will be = 7 × 10/5µ = 14µ. Procedure In this way the microscope is calibrated for different combinations of eyepieces and objective lenses and is kept for record. It is to note that this calibration will be just only of the tried lenses on this particular microscope. Measurement of the Microorganisms • When the microscope is calibrated, then the object or organism to be measured is kept on the sage of the microscope and is observed through the eyepiece with ocular. The object is measured in the particular magnification by ocular divisions and then is changed into microns by multiplying ocular divisions with calibrated value of one ocular division in that particular magnification. Procedure • Suppose the diameter of an object (Fig. 107) is observed to be equal to 6 divisions of ocular, so the diameter of this object in microns will be: 6 × 14µ = 84µ (where 14µ is the value calculated as 1 ocular division) • In this way the object is measured in different magnifications.