Procedure for Calibration of Microscopes Using an Ocular
advertisement

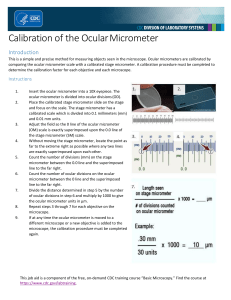
University of Nebraska-Medical Center Clinical Laboratory Science Program CLS 418 & 419 Page 1 of 1 For student use only Procedure for Calibration of Microscopes Using an Ocular Micrometer Place the stage micrometer on the microscope stage and focus on the micrometer scale, until you can distinguish between the large (0.1 mm) and the small (0.01 mm) divisions of the scale. Adjust the stage micrometer so that the "0" line on the ocular micrometer is superimposed with the "0" line on the stage micrometer. Without changing the stage adjustment, find a point as distant as possible from the two superimposed "0" lines where two other lines are also exactly superimposed. Determine the number of ocular micrometer spaces, as well as the number of millimeters on the stage micrometer, between the two points of superimposition. For example: Suppose 48 ocular micrometer spaces (units) equal 0.6 mm. Calculate the number of mm/ocular micrometer space. 0.6 mm x 48 ocular micrometer spaces = 0.0125 mm/ocular micrometer space Since most measurements of microorganisms are given in µm rather than mm, the value calculated above must be converted to µm by multiplying it by 1000 µm/mm. For example: 0.125 mm ocular space x 1000 µm/mm = 12.5 µm/ocular micrometer space Thus in this case, 1 ocular micrometer space (unit) is the equivalent of 12.5 µm. Follow the above steps for each objective. Calibration readings should be posted on each microscope and the microscope should be recalibrated after every cleaning or changing of objectives or oculars.