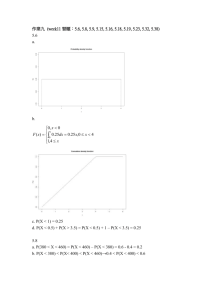
MIDTERM 01 WEEK 01-05 1. Which of the following statements is correct? a. An increase in the leverage ratio leads to a decrease in the insolvency risk. b. None of the other statements is correct. c. An increase in the reserve requirement can lead to a decrease in the contractually promised gross return. d. For an increase in the interest rate, the duration model predicts an increase in the price of a coupon bond. 2. Which of the following statements is correct? a. The loan concentration measure is increasing when the expected returns for the individual loan categories increase. b. In the loan migration matrix, the entries in a column sum up to one. c. None of the other statements is correct d. Diversification reduces the expected return. 3. Consider a loan pool of 100 AUD. In the first period loans of 10 AUD default. In the second period loans of 20 AUD default. Calculate the cumulative probability of default for the second period. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 30% b. 32% c. 26% d. 28% 4. Which of the following statements is correct? a. Regulation tries to increase the negative externalities through a system failure of a financial institution. b. None of the other statements is correct. c. An increase in the interest rate leads to an increase in the interest income and a decrease in the interest expense. d. Lack of confidence in the financial institution can reduce the profitability of the financial institution. 5. Which of the following statements is correct? a. The expected repayment on a loan equals the promised repayment on the loan. b. None of the other statements is correct. c. For an equal interest rate: The duration of a consol bond is equal to the duration of the annuity, when the maturity goes to infinity. d. The modified duration of a consol bond depends on the face value of the payment each period. 6. An annuity pays 100 AUD yearly for the next three years. The market interest rate is 10%. Calculate the Modified Duration. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 2.1 b. 1.8 c. 1.9 d. 2.0 7. Which of the following statements is correct? a. In the first repricing bucket, the GAP is always equal to the CGAP. b. An increase in the spread between the asset rate and the liability rate leads to a decrease in the net interest income. c. One target of regulation is to maximize the net regulatory burden. d. None of the other statements is correct. 8. Which of the following statements is correct? a. Investment in international assets, which are subject to foreign exchange rate risk, can generate additional diversification benefits. b. None of the other statements is correct. c. An increase in the coupon rate leads to a decrease in the Dollar duration of a coupon bond. d. For a coupon bond, the duration can be larger than the maturity. 9. Which of the following statements is correct? a. When a financial institution has only positive CGAPs (and a zero CGAP in the last bucket) it indicates that the assets reprice earlier than the liabilities on average. b. None of the other statements is correct. c. The Altman model is an example of a linear probability model. d. The modified duration of a zero-coupon bond does not depend on the market interest rate. 10. Which of the following statements is correct? a. None of the other statements is correct. b. The spread between the corporate-bond yield and the risk-free yield increases when the probability of default of the corporate bond decreases. c. The weights in the portfolio-duration formula sum up to 1. d. The expected return on a loan is the probability of default multiplied with the promised gross return. 11. Consider a portfolio of two assets. The variance of returns of asset A is 0.01. The variance of returns of asset B is 0.04 The correlation coefficient is 0.8. The portfolio weights of assets A and B are 50% each. Calculate the variance of the portfolio returns. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 0.030 b. 0.015 c. 0.025 d. 0.020 12. A corporation has an asset value of 100 and an equity value of 40. The duration of the assets is 5. For which duration of the liabilities is the leverage adjusted duration gap equal to zero? Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 5 b. 7 c. 8 d. 6 13. Consider a consol bond, which pays 100 AUD every year. The market interest rate is 10%. Calculate the Dollar duration of the consol bond. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 10,000 b. 11,000 c. 15,000 d. 12,000 14. Which of the following statements is correct? a. The cumulative probability of default in a period is always higher than the marginal probability of default in that period. b. None of the other statements is correct. c. The loan migration matrix is a backward-looking approach. d. When the leverage adjusted duration gap is equal to zero, the leverage ratio is immune to changes in the interest rate. 15. The CRSL for the first bucket are 50. The CRSA for the first bucket are 100. The interest rate increases by 10%. Calculate the cumulative change in the net interest income for this bucket. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. -5 b. -1 c. 1 d. 5 16. We have got two zero-coupon bonds available. Zero-Coupon bond A has a maturity of 3 years. Zero Coupon bond B has a maturity of 10 years. We want to achieve a portfolio duration of 5 years. Calculate the weight of Bond A in the portfolio. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 0.5 b. 0.9 c. 0.7 d. 0.3 17. Which of the following statements is correct? a. Syndicated loans are especially suitable for smaller commercial loans. b. Deposits are on the asset side of the balance sheet for a financial institution. c. For a positive leverage adjusted duration gap, an increase in the interest rate leads to an increase in the equity value. d. None of the other statements is correct. 18. The one-year risk-free yield is i_1 = 3%. The two-year risk-free yield is i_2 = 5%. Calculate the forward rate for the second year. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 5% b. 7% c. 9% d. 3% 19. Consider a zero-coupon bond with a maturity of 5 years and a face value of 100 AUD. The current interest rate is 5%. Calculate the price change predicted by the duration when the interest rate increases to 10%. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 10 b. 20 c. -10 d. -20 20. The marginal probability of default in the first year is 20%. The marginal probability in the second year is 10%. Calculate the cumulative probability of default in the second year. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 0.30 b. 0.32 c. 0.02 d. 0.28 MIDTERM 02 WEEK 06-07 1. Which of the following statements is correct? a. When the duration of assets is equal to the duration of liabilities, the leverage adjusted duration gap can be negative. b. None of the other statements is correct. c. For a coupon bond with positive coupon rate: For changes in the interest rate, the new price predicted by the duration model is higher than the true new price. d. When a financial institution invests an equal amount in all loan classes, the loan concentration measure in minimized. 2. Consider the following profit distribution Profit Probability 50 30% 100 60% 200 1% -30 2% -20 3% -40 2,5% -10 1.5% Calculate the value at risk (VaR) for alpha = 2%. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 20 b. 40 c. -200 d. 10 3. Which of the following statements is correct? a. None of the other statements is correct. b. In the Moody's analytics model, an increase in expected default frequency leads to a decrease in the volatility of the loan default rate. c. Consider a zero-coupon bond with maturity 6 and face value 100. When the Dollar duration decreases due to changes in the market condition, the modified duration decreases as well. d. The cumulative probability of default is the multiplication product of the marginal probabilities of default for the individual periods. 4. An Australian financial institution has a USD denominated coupon bond with a coupon rate of 5% and a face value of 100 USD. The maturity is 3 years. The interest rate in the US is 10%. The exchange rate is 1.5 AUD for 1 USD. Calculate the value of the coupon bond in AUD. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 88 b. 132 c. 112 d. 100 5. Which of the following statements is correct? a. Assume the daily value at risk is positive: Under the multiple-day value at risk (VaR) formula, the 3-day value at risk (VaR) can be higher than the 5-day value at risk (VaR). b. When the value at risk (VaR) and the expected shortfall (ES) are positive, the value at risk (VaR) can be higher than the expected shortfall (ES). c. When the expected shortfall (ES) and the value at risk (VaR) are the same for alpha = 2%, there has to be one outcome in the distribution which has an individual probability of more than 1%. d. None of the other statements is correct. 6. The Dollar Duration of a one-year zero-coupon bond with face value 100 is equal to 80. The daily standard deviation in the interest rate is 1%. Calculate the daily earnings at risk for alpha = 1%. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 2 b. 1 c. 10 d. 5 7. Consider a portfolio of the following two assets: 1. Zero-coupon bond with face value 100 and 3-year maturity. 2. Consol bond with annual payment of 10. The market interest rate is 10%. Calculate the DOLLAR duration of the portfolio. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 1700 b. 1500 c. 1300 d. 2000 8. Which of the following statements is correct? a. Under the Risk-Metrics approach and a specific zero-coupon bond: If the Dollar duration decreases and the standard deviation of the market interest rate is constant, the daily earnings at risk have to decrease. b. The modified duration is especially suitable for market risk measurement, because the approximation error is small for large changes in the interest rate. c. If the alpha = 1% expected shortfall ES for an asset is equal to 2, the alpha = 2% expected shortfall can be equal to 4. d. None of the other statements is correct. 9. Which of the following statements is correct? a. None of the other statements is correct. b. On-balance-sheet hedging includes the usage of forward contracts. c. The AUD-return on a USD investment increases, when the USD appreciates over the contract time. d. Investment in a foreign country increases the expected return. 10. An Australian financial institution invests 100 AUD in a USD denominated one-year asset with USD interest rate 10%. The current exchange rate is 1.5 AUD for 1 USD. One year later, the exchange rate is 1.3 AUD for 1 USD. Calculate the AUD return on the asset. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. -20% b. +10% c. -10% d. +20% 11. The spot exchange rate is 0.6 USD for 1 AUD. The yearly interest rate in the US is 20%. The yearly interest rate in Australia is 10%. Calculate the forward exchange rate for an exchange of currencies in TWO years from now. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 0.65 b. 0.50 c. 0.55 d. 0.70 12. Which of the following statements is correct? a. A zero-coupon bond can change repricing buckets over time. b. The price of a consol bond does not depend on the size of the periodical payments. c. Increased competition increases the spread between the asset and liability rate. d. None of the other statements is correct. 13. Which of the following statements is correct? a. Without transaction cost: The X in the quote (USD X) / (AUD 1) and the Y in the quote (AUD Y) / (USD 1) sum up to 1. b. A positive net exposure to a foreign currency is ideal for a financial institution. c. None of the other statements is correct. d. When the X in the quote (USD X) / (AUD 1) increases by 20%, then the Y in the quote (AUD Y) / (USD 1) decreases by 20%. 14. The nominal interest rate in the US is 7% and inflation is 3%. The inflation in Australia is 5%. Calculate the nominal interest rate in Australia under real rate parity. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 9% b. 7% c. 4% d. 5% 15. Consider the following profit distribution Profit Probability 50 30% 100 60% 200 1% -30 2% -20 3% -40 2,5% -10 1.5% Calculate the 5% Expected Shortfall (ES). Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 10 b. 30 c. 40 d. -200 16. Which of the following statements is correct? a. The alpha = 5% value at risk can be equal to the alpha = 10% value at risk for the same asset. b. None of the other statements is correct. c. Consider the profit distribution of an asset and alpha = 1%: The expected shortfall (ES) takes the distribution shape right of the value at risk (VaR) into account. d. The portfolio value at risk (VaR) is always lower than the sum of the values at risk for the assets in the portfolio. 17. For a financial institution, the DEAR for the fixed income is 100. The DEAR for the foreign exchange rate is 150. The correlation is -0.5. Calculate the 5-day value at risk (VaR) for the portfolio. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 290 b. 250 c. 270 d. 230 18. Which of the following statements is correct? a. An increase in the domestic inflation leads to an appreciation of the home currency, according to the purchasing power parity. b. Consider alpha = 1%: When the value at risk (VaR) of asset A is higher than the value at risk (VaR) of asset B, the expected shortfall (ES) of asset A is higher than the expected shortfall (ES) of asset B. c. When the nominal interest rate and the real rate have increased, the inflation rate can have decreased. d. None of the other statements is correct. 19. Which of the following statements is correct? a. None of the other statements is correct. b. The dollar duration is lower than the Macaulay duration for the same asset. c. The over aggregation problem can be reduced by splitting buckets into several different buckets. d. When the real interest rates are the same in two countries, the nominal interest rates in these countries are the same as well. 20. Consider the following term structure: risk-free: i_1 = 3% i_2 = 4% corporate: k_1 = 5% k_2 = 8%. Calculate the cumulative probability of default for the second period implied by the term structure. Which of the following numbers is closest to the solution? a. 14% b. 5% c. 11% d. 8%