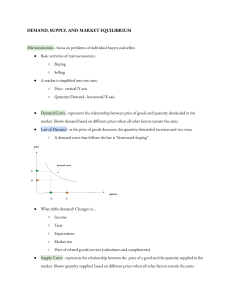
Study Guide: Unit 3 — Demand, Supply, and the Market VOCABULARY For each of the following terms, make a definition card. Use dates/examples where possible. Economics Absolute advantage Comparative advantage Specialization Demand Quantity Demanded Law of de mand Market demand Substitute good (substitute) Complementary good (complement) Supply Quantity Supplied Law of supply Market supply Non price determinants Elasticity Inelastic Unitary elastic Market equilibrium Equilibrium price/market clearing price D isequilibrium Excess demand (shortage) Excess supply (surplus) Price controls Price floor Minimum wage Price ceiling Rent control Rationing Black market QUESTIONS TO CONSIDER Answer each of the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. Use specif ic examples when possible. 1. What’s the difference between the change in quantity demanded and a change in demand? a. What about the change in quantity supplied and a change in supply? 2. Why do price and quantity demanded move in opposite directions? What kind of relationship is this? 3. Why do price and quantity supplied move in the same direction? What kind of relationship is this? 4 . What is the only factor that causes a change in quantity demanded or supplied? 5. What factors cause a change in : a. dema nd b. supply 6 . What factors influence the elasticity of demand and supply ? a. How do you calculate elasticity of demand and supply? 7 . How do you calculate total revenue? 8 . When do people, and economists, know that a “price is right”? Who sets this price? a. When reaching equilibrium, why does time vary in different markets? b. What causes excess demand and excess supply? 9 . What is the relationship between quantity demanded (or quantity supplied) and price in a market? a. What sort of incentives do prices create? b. How do prices allow markets to respond to changing conditions? c. Why do “black markets” exist? Where do they exist? 10 . Explain why it’s so hard to end price controls. 11 . How do price floors and price ceilings affect you as a consumer and as a producer? OVER PRACTICE/REVIEW 1 2 . Be able to graph demand and supply curves using schedules. 13 . Be able to figure out when a curve will shift along the curve or to the right/left and why. a. How does the curve change based on changes in demand only? b. How does the curve change based on changes in supply only? c.How does the curve change based on changes in BOTH demand and supply? 14. Be able to find points of equilibrium, price floors, and price ceilings on a curve.