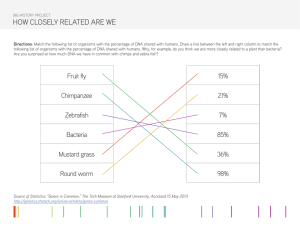
Biology End of Course Review Experimental Design Experimental Group: receives element being tested Control Group: does NOT receive the element being tested; used for comparison Constants: factors that remain the same in every group Bias:a personal belief that may affect the results Dependent Variable: the Data collected(results) Independent Variable: what I change or test DRY MIX Dependent Responding Y- axis of graph Manipulated Independent X- axis of graph BAR GRAPH Used for comparison LINE GRAPH Used to show change over time (trends) PIE/CIRCLE GRAPH Used to show parts of a Whole (percentages) Biological Molecules Carbohydrates-CHO in a 1:2:1 ratio “-OSE” Sugars called “–saccharides” Monosaccharide examples: Glucose, Galactose, Fructose Polysaccharide Examples: Cellulose, Chitin, Glycogen. Starch SHORT TERM ENERGY Lipids-CHO more C’s and H’s, very few O’s Monomers: Fatty Acids and Glycerol Examples: Fats, Oils, Waxes, Steroids, Phospholipids LONG TERM ENERGY Proteins- CHON Monomer: made up of amino acids Function: act as ENZYMES to speed up chem. reactions by lowering activation energy (catalysts) Examples: Hair, Skin, Muscles, enzymes end in “-ASE” Eukaryotes-(DO) has a nucleus and membrane bound organelles “You”- are Eukaryotic PLANT ANIMAL FUNGUS Nucleic Acids- CHONP Monomer: made up of nucleotides Examples: DNA, RNA, ATP Optimum: produces the best results Nucleotide: Pool, House, Garage Fungal cell walls= Chitin Septa- partial divisions between cells in a fungi ATP: Adenine Ribose 3 Phosphates Cell Organelles Cell membrane- Phospholipid bilayer-selectively permeable (Controls what enters and leaves) Nucleus- contain the DNA (genetic information) Nucleolus- makes ribosomes Rough ER-has ribosomes attached to it; passageway for proteins “highway” inside cell Smooth ER- no ribosomes- lipid production Vacuole- storage Golgi- packaging of proteins “Post Office” ships outside of cell in a vesicle Mitochondria- site of cellular respiration, make ATP “powerhouse” Ribosome- makes (synthesizes) protein Cell transport PASSIVE - no energy ; moves high to low; with the gradient Diffusion- movement of particles from an area of high to low concentration; wants to reach equilibrium Osmosis- diffusion of water from high to low concentration Facilitated diffusion- large molecules move through a protein channel PLANT ONLY Chloroplasts- green organelle where photosynthesis takes place Large central vacuole-water storage Cell wall- rigid, gives structure, made of cellulose Exocytosis- getting rid of material from the cell Sodium Potassium Pump: kicks 3 Na out Lets 2 K in ANIMAL ONLY Lysosome-digestive enzymes, cleans “slice” Centrioles-help in cell division “go to the poles” Centrosome-centrioles lined up perpendicular to each other; they serve as anchors during mitosis. Cytoskeleton: aids in cell structure (made of microtubules and microfilaments) PROTISTS ONLY Contractile Vacuole: pumps water out of the cell Virus LIVING characteristics -can reproduce (but needs a host) - contains genetic code (DNA or RNA) - Responds to the environment via mutations - change over time or evolve NON-LIVING characteristics - not made of cells - cannot reproduce on its own - does not grow or develop - does not obtain material for energy - does not maintain homeostasis Bacteriophage: (bacteria eater) DNA inside of CAPSID head Cells: Robert Hooke- first to observe cells in cork; Came up with the term “cell” Van Leeuwenhoke- first to see living cells, perfected the microscope Cell theory Men Schleiden: All Plants are made of cells Schwann: All Animals are made of cells Virchow: Cells come from other cells 3 Tenets of the Cell Theory: 1.Cell are the basic unit of life (Schwann) 2.All living things are made of cells (Schleiden) 3.Cells come from pre-existing cells (Virchow) Prokaryotes-(NO) - no nucleus or organelles Examples: Bacteria C 3 Dr Plasmid: circular DNA REACTANTS PRODUCTS Photosynthesis Converting light energy into chemical energy 6CO2 + 6H2O + light→C6H12O6 + 6O2 Location: Chloroplast 2 parts of photosynthesis Light Dependent Water + sunlight 🡪 Oxygen Location: thylakoids (pancakes) Light Independent aka “Calvin Cycle” Carbon Dioxide 🡪 Glucose Location: stroma (syrup) ACTIVE: requires energy(ATP); moves low to high; against the gradient Endocytosis-bringing bulk materials into the cell Pinocytosis-liquid Phagocytosis-Solid Osmolarity-Tonicity Solute (salt) + Solvent (water) = Solution (Saltwater) Remember: “Solute Sucks” ; water moves to where there is more solute HYPOtonic- water moves into the cell; cell swells and could burst Hypo= grow HYPERtonic- water moves out of cell; cell shrinks Hyper= smaller ISOtonic - water moves in and out, cell in equilibrium; NO NET movement Iso= same Cell cycle: Asexual reproduction- involves one parent (identical to parent) Budding (hydra) Binary fission (bacteria) G1-growth Interphase 90% S phase-DNA synthesized. G2- growth, prepare for mitosis M phase10% Mitosis (PMAT)- Nucleus divides Cytokinesis – cytoplasm divides Purpose of Mitosis: growth, repair, development Stages: Prophase-chromosomes visible, nucleus disappears Metaphase-chromosomes line up at equator Anaphase-chromatids pull apart to the poles Telophase-nuclear membrane reappears End Result: 2 -Identical daughter cells, both diploid Cellular Respiration Converting glucose into ATP C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 +6 H2O + ATP Always starts with GLYCOLYSIS: Location: Cytoplasm Breaking 1 Glucose into 2 Pyruvates AEROBIC ANAEROBIC requires oxygen no oxygen Location: Mitochondria Location: Cytoplasm Step 1: glycolysis (2 ATP) Step 1: glycolysis (2ATP) Step 2: Krebs Cycle (2 ATP) Step 2: FERMENTATION Step 3: ETC (32-34 ATP) Plants = Ethanol (alcohol) Animals = Lactic Acid Vegetative propagation (plants) My Toes are made by Mitosis Toe=Body cell Regeneration (growing new parts) Fragmentation Meiosis “makes ME” “ME Ovaries” “ME Testes” Purpose: Forms gametes (eggs, sperm) PMAT x 2 Replicate DNA only once! But divide twice! CROSSING OVER: occurs in Prophase 1 between non-sister chromatids Allows for genetic variation Spermatogenesis: 4 different sperm Oogenesis: 1 ovum and 3 polar bodies Sexual reproduction- Involves 2 parents, fertilization produces a zygote. Pollination- transfer of pollen from male reproductive organ to female reproductive organ in plants Independent Assortment: inheriting one trait doesn’t affect the inheritance of another trait. Example: having brown eyes has nothing to do with having freckles Allows for genetic diversity with different combinations of traits! Karyotype: picture of chromosomes Genetics Genetics: Study of heredity Heredity: the passing of traits from one generation to the next Gregor Mendel: “father of genetics” studied pea plants and the concept of complete dominance (a dominant will completely cover a recessive allele) Genotype: Letters Phenotype: Physical appearance Monohybrid-1 trait is crossed (4 squares) Dihybrid-2 traits are crossed (16 square) Allele: alternate version of a gene Homozygous = Same Heterozygous = Different Homozygous Recessive = tt True Breeding Homozygous Dominant = TT “Purebred” Heterozygous = Tt “Hybrid or Carrier” Test cross-using a recessive plant (tt) to find out if one parent Is heterozygous or homozygous dominant Codominance-both phenotypes appear CO = SHOW Black(BB) X White (WW)= Spotted Black & White(BW) Blood- AB blood type Roan- Spotted cow or horse Sex linked: Trait carried on the X chromosome Seen mostly in males because they only have one X Only females can be carriers in sex-linked! Genotype must include XX for females and XY for males Examples: color blindness Hemophilia, Duchene’s How to FOIL in dihybrids: Muscular dystrophy, baldness Blood Types: Multiple Alleles Type A IAIA or IAi Type B IBIB or IBi Type AB (Codominant) IAIB Type O (recessive) ii Sex linked: mostly males affected Autosomal: males & females equal AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE Disorders to recognize: KLEINFELTERS: XXY DOWN SYNDROME : 3 of #21 “trisomy 21” TURNERS: only 1 X chromosome (XO) EDWARDS: trisomy 18 PATAU: trisomy 13 Incomplete dominance- blending of alleles, phenotype completely different than either parent. IN = BLEND Example: Red (RR) X White (R’R’)= Pink (RR’) Shaded skipped a generation Males and females are affected Dominant: in every generation Recessive: skips a generation Cell Differentiation- embryonic stem cells turn into specific cell types when certain genes are turned on in the cell AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT Shaded in every generation Males and females are affected SEX-LINKED RECESSIVE (X-LINKED) SEX-LINKED (Y-LINKED) All caused by: Nondisjunction: - when chromosomes do not separate during anaphase in meiosis resulting in too many or not enough chromosomes Stem Cell: an undifferentiated cell that can become multiple cell types *cells can differentiate based on what genes they activate. Not all cells activate all genes! Levels of Organization Cell: basic unit of life Tissue: a group of cells working together Organ: group of tissues with a similar function Organ system: group of organs with similar function Organism: group of organ systems working together Pedigrees: show patterns of inheritance Shaded skipped a generation. Passes from Mother to Son! Mostly males are affected Simplest →→→→→→→→→→→→ →→→→→ Most Complex Factors that Affect Populations Density Dependent Factors- affect crowded/large populations. EX: availability of food, predation, disease, and migration. Density Independent Factors- affect all population sizes the same. EX: weather and Climate Limiting factor- whatever resource that keeps the population from growing larger. EX: Limiting factor in a desert is rainfall. Cancer: uncontrolled cell growth Characteristics of Life “DOG RACE” D O G R A C E - Example of how enzymes lower the activation energy DNA or genetic material for heredity Obtain and use materials for energy (metabolism) Grow and Develop Reproduce Adapt to environment or stimulus Made of Cells Evolution Cell Respiration Diagram Why do cells need energy? “AMNOP” 1. Active transport 2. Muscle contraction 3. Nerve Impulses 4. Organelle movement in cell 5. Photosynthesis in plants Types of Energy in Livign Systems: Chemical: energy contained in bonds of molecules and released by chemical reactions Light: from the sun (photons) Thermal (Heat): measured by temperature Biology End of Course Review Page 3 DNA/RNA/PRotein Synthesis DNA- Deoxyribonucleic Acid “At The Gulf Coast” “Apples in Trees/Cars in the Garage” A-T & G-C double stranded double helix built of nucleotides stores genetic information codes for traits/proteins RNA- Ribonucleic Acid “U R Single” “Aliens in the Universe/Craters in the Galaxy” A-U & G-C Single stranded built of nucleotides used to build proteins 3 types of RNA rRNA- ribosomes mRNA-message “instructions” tRNA- brings amino acids Replication= DNA to DNA- copying the DNA A-T & G-C happens in the nucleus happens during S-phase of Mitosis History of Life & Evolution Organic Evolution- organisms become better suited to their environment over time. Chemical Evolution- chemicals combined over time to form the first cells. Endosymbiotic Theory- Because mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA, scientists believe that they were once their own organisms. This explains how cells evolved to have chloroplasts and mitochondria through a symbiotic relationship with cells. Pathway that led to eukaryotic cells: “AH-PA-AHH” Anaerobic Heterotrophs→Photosynthetic Autotrophs→ Aerobic Autotrophs & Heterotrophs Evidence of Evolution: Fossils- preserved remains of past life Biogeography- distribution of organisms/fossils on the planet Embryology- comparison of the embryonic stage of organisms shows evidence of common ancestry. Comparative Anatomy(body structures) *Homologous Structures- same structure but different function *Analogous Structure- same function but different structure “Does not show common ancestry” Ecology- relationships between organisms, and organisms with their environment. 1. Biotic- living 2.Abiotic-nonliving 3. Organism- one living thing 4. Population- one species of organisms living in the same place 5. Community- several species living in the same place 6. Ecosystem- living and nonliving things in the same location. 7. Biome- a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar communities. 8. Biosphere- the portion of the planet where life exists. 9.Autotroph (producer)- makes its own food through photosynthesis (sunlight) or chemosynthesis (chemicals) 10. Heterotroph (Consumer)- gets energy by consuming (eating) others Herbivore- plant eater Carnivore- meat eater Omnivore- eats both (meat & plant) Scavenger- only eats things that are already dead “does not kill its own food” Decomposer- breaks down dead organisms and returns nutrients to the ecosystem 11. Habitat- place where an organism lives 12. Niche- role organism has within its habitat “everything it does” Energy Flow Sun→Plant→herbivore→carnivore only 10% of energy moves up each level & 90% ● is lost or used Food Chain Food Web Transcription= DNA to RNA- making mRNA A-U & G-C happens in the nucleus (DNA is in Nucleus) creates a strand of mRNA which travels out of the nucleus - - Translation= mRNA to Protein A-U & G-C happens on a ribosome (rRNA) Ribosomes read directions from mRNA to build a protein using amino acids. The amino acids are carried to the ribosome by tRNA Central Dogma = “Don’t Ride A Pony Today” DNA→RNA→Amino Acid→Protein=Trait(Gene Vestigial Structure- remains of structures that were used by ancestors. ex wisdom teeth Biochemical Evidence- similarities in sequences of DNA, RNA, or Protein- This is the best evidence. Concepts of Evolution- (Differential Success): organisms are born with differences; some differences make survival easier; organisms that have them will survive and produce offspring. Speciation- formation of a new species due to evolution. Geographic Isolation- physical barrier separates organisms (Mountains or Canyon) Reproductive Isolation- species develop different reproductive cycles and can no longer mate Behavioral Isolation-species develop different courtship behaviors and can no longer interbreed. Adaptation- anything that helps a species survive Mimicry- copy the appearance of another Camouflage- blending in with environment Physiological- metabolic activity that aids survival. Ex: bacteria becoming resistant to an antibiotic Cladogram- diagram used to show evolutionary relationships -shows traits (derived characteristics) at the bottom organisms on the right/above have the trait Phylogenetic tree- shows relationships NO TRAITS SHOWN Ecological Succession process where ecosystems undergo natural changes Primary Succession- begins on bare rock. Lichens and mosses are pioneer species: lava cools to form rocks Secondary Succession- when one type of living community changes into another type ex: grass is replaced by shrubs Climax Community- stable community that will remain unchanged unless it is damaged by humans or natural disaster. EX: Hardwood forest Symbiosis-when organisms live in close association with another organism Mutualism= both benefit Commensalism=one organism benefits Parasitism= one organism benefits and one is harmed. Expression) Biology End of Course Review Page 4 Genetic Technology manipulation of the genetic code in order to: produce things people want/need treat genetic disorders Gel Electrophoresis used to solve criminal and paternity cases DNA is cut by a restriction enzyme and is separated in a gel by its size. creates DNA Fingerprints Transformation (Bacterial Transformation) DNA is moved from one organism and placed into another. organisms that have been transformed are called GMO-genetically modified organism or transgenic organisms gene of interest- gene that is moved into other organisms vector- agent used to carry the gene of interest. (plasmid, yeast, virus) Human Impact Extinction- caused by habitat destruction. Production of non biodegradable products such as plastics Pollution- of bodies of water by dumping waste and creation of landfills Production-of harmful chemicals including DDT and CFC’s Ozone Depletion- caused by the use of CFC’s Biological Magnification- pollutants increase in concentration as they travel through trophic levels. The top predator will be most affected by pollution. Ex: DDT & Mercury - Unsustainable- use of nonrenewable resources (Fossil Fuels, metal, topsoil) Deficient- use of renewable resources (wind, water, solar) Algal Blooms- (overabundance of algae in water) is caused by the use of fertilizers in farming. Eutrophication Applications of Genetic Technology Agriculture- creates crops and livestock for human consumption plants that resist freezing cows that are double muscled for beef Industry- creating bacteria that can help break down pollutants like oil and plastic Medicalvaccines, interferon, insulin, human growth hormone Cell Membraneis made of phospholipids and embedded proteins also called plasma membrane or lipid bilayer maintains homeostasis by allowing certain molecules into or out of the cell is selectively permeable Phosphorus Cycle Only cycle that the element does not pass through the atmosphere. We remove phosphorus from the earth to make fertilizers. Phosphorous leeches from the soil when we clear forests. Phosphorous travels into bodies of water in runoff from animal waste and from fertilizers used by farming. Natural Selection Organisms who are the best suited to their environment will survive to produce offspring. is the driving force for evolution (change over time) Concepts of Natural Selection Genetic Variation- organisms are born with genetic variation These variations are inheritable Overproduction- Organisms produce more offspring than necessary, not all will survive Struggle for Survival- Organisms struggle for resources & only the best suited survive Descent with Modification- New species arise from common ancestors and replace less fit Mutations- any change in the DNA point mutation- one letter in the code changes deletion- genetic information is missing duplication- information is copied twice inversion- genes are put on in the reverse “backwards” order translocation- genes have moved to a new location. Ex: gene from chromosome 5 moves to chromosome 12 Mutations cause proteins to be formed incorrectly because the genetic code is altered and will code for a different amino acid sequence. Shape = function; if the protein is shaped differently after a Biogeochemical Cycles Bio- Life * Geo- Earth * Chemical- Elements ● Water Cycle Evaporation- water changes from liquid to gas Condensation- water changes from gas to liquid, forming droplets Transpiration- Water evaporates from plants Respiration- living things release water as a by product of cellular respiration Runoff- rainwater washes into bodies of water Groundwater- water that seeps underground Carbon-Oxygen Cycle Volcanic Activity - releases CO2 Combustion- Burning fossil fuels releases CO2 Decomposition- dead organisms break down and release CO2 Cellular Respiration- living things take in O2 and release CO2 Photosynthesis- plants take in CO2 and release O2 Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen Fixation- N2 is converted into a usable form by combining it with Hydrogen creating ammonia (NH3). Nitrogen is fixed by lightning, Bacteria, and Volcanic Activity. NH3 is then converted into nitrates and nitrites by bacteria in a process called nitrification. Plants use nitrates and nitrites to make proteins. Consumers get nitrogen by eating plants Nitrogen is returned to the ecosystem in animal waste Waste and dead organisms are broken down by decomposers and bacteria to return nitrogen to the atmosphere in the process of denitrification. ones. mutation, it can not perform its intended job.