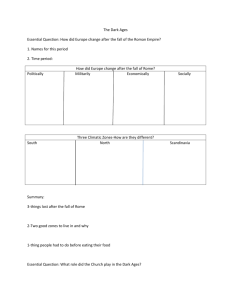
-The Middle Ages(5th – 15th century) After the collapse of Rome, there was a lack of strong central government in Western Europe. Characteristics of the Early Middle Ages 1. Disruption of trade 2. A decline in learning 3. Loss of a common language 4. A general lack of progress Urban centers disappeared as people moved to rural settings. Christianity became the dominant religion in Europe during the Middle Ages. Feudalism A lack of strong leaders led to a new system of government and land holding, know as feudalism. One of the reasons behind the development of feudalism was to provide protection from three groups of invaders. 1. Vikings 2. Magyars 3. Muslims Political characteristics of feudalism included: Decentralized governments A system of local government based on the control of land and mutual obligations. Kings granted land to their nobles in return for their pledge of loyalty and military support. The land kings gave to nobles was called a fief. Local lords made their own laws and controlled their own armies. Social characteristics of feudalism included: The division of society into a rigid class system. Class was determined by birth and there was little social mobility. THE CATHOLIC CHURCH Importance of the Church during the Middle Ages included: 1. Keeping birth, marriage, and death records. 2. Regulating kings’ power through canon law. 3. The Church was the largest land holder in Western Europe. 4. Citizens paid the Church a tithe, which is a 10% income tax. 5. The preservation of learning and education. 6. Establishing the first universities in Europe. The High Middle Ages The development of towns led to the establishment of an influential middle class including merchants and artisans. The growth of towns and cities shifted power from local lords to kings. This period saw a revival of learning, including works by Dante and Chaucer.