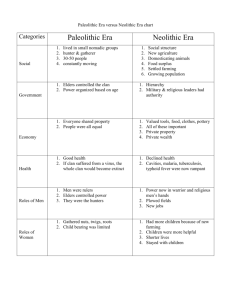
Module 1. Basic Concepts of Agricultural Crop Production Topics Definition and Importance of Agriculture History of Agriculture Branches of Agriculture Plant Parts and their Functions Types of Agricultural Crops and Its Classification Types of Commercial Food Crops in the Philippines OBJECTIVES OF THIS MODULE To describe agriculture, its history and its branches To identify and explain the different parts of the plants and their functions To categorize the types of agricultural crops, the different types of commercial food crops (in the Philippines) and remember each of their common, local and scientific names HISTORY OF AGRICULTURE When it all begun.. Humans invented agriculture during the Neolithic era, or the New Stone Age, which occurred between 7,000 and 10,000 years ago. https://www.crestcapital.com/tax/history_of_agriculture# 5 When it all begun.. Sometime around 12,000 years ago, our huntergatherer ancestors began trying their hand at farming https://www.nationalgeographic.org/article/developm ent-agriculture/ 6 When it all begun.. First evidence of farming in Mideast 23,000 years ago: Evidence of earliest small-scale agricultural cultivation www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2015/07/15072214 4709.htm 7 Birth of agriculture.. The birth of agriculture is often referred to as the Neolithic Revolution since it seems to coincide with the Neolithic period—or new stone age. 8 Neolithic period—or new stone age? For better understanding lets go back in time…. Archeologists have divided the cultures of the past into ages based on materials used for making tools Stone age Old Stone Age - Paleolithic New Stone Age - Neolithic Bronze Age Iron Age Stone Age Periods Paleolithic Period humans existed by foraging Hunting, fishing, gathering wild berries, roots, seeds, etc Number of people restricted by food available in the area Stone Age Periods Neolithic Period people controlled there own food supply by cultivating plants and breeding animals Stone Age Periods Many of the artifacts are stone tools which are believed to have facilitated early agriculture Agricultural tools found in the Iberian settlement Bastida of Alcusses, late 5th century B.C.E. to the 4th century B.C.E. Why did agriculture emerge? The simple answer is that nobody knows. However, legends and theories do exist. Why did agriculture emerge? According to legends among different groups such as Egyptians, Greeks, Aztecs: “Agriculture is a gift from the gods” Why did agriculture emerge? Many theories focus on a wise person or brilliant sage (aka “Genius Theory”) If you sow seeds, a plant will grow Why did agriculture emerge? Scientific theories The fact that agricultural was a gradual cultural evolution not a revolution Why did agriculture emerge? Scientific theories Hunter-gatherers knew the wild plants, knew how they grew, and would incorporate farming along with foraging as part of an overall food collection strategy when necessary Why did agriculture emerge? Scientific theories Environmental change made the difference (archaeologists believe that the climatic dry period around 11,000 years ago brought about a change in the distribution of grains) Why did agriculture emerge? Scientific theories Population pressure - with only hunting and foraging to support growing human populations, people began using their botanical knowledge in cultivation Where did agriculture emerge? It is believed that agriculture emerged independently and spread from places as varied as Mesopotamia, China, South America and sub-Saharan Africa Where did agriculture emerge? Archeological finds dates back approximately 10,000 years in Near East, Far East, and also in the New World Where did agriculture emerge? First evidence of farming in Mideast : New evidence recently published The Zagros Mountain range, which lies at the border between Iran and Iraq, was home to some of the world's earliest farmers. Early Sites of Agriculture Neolithic Agriculture Map Early Sites of Agriculture Neolithic Agriculture Map • Some of the best studied sites of agriculture are in southwestern Asia • In foothills around the Fertile Crescent (Middle East) Early Sites of Agriculture Neolithic Agriculture Map • Area around the Tigris and Euphrates River is a particularly rich area for archeologists especially the foothills of Zagros Mts in Iraq and Iran First crops of agriculture • Neolithic founder crops of agriculture includes emmer wheat, einkorn wheat, hulled barley, peas, lentils, bitter vetch, chickpeas and flax First crops of agriculture • Barley has been found in archeological sites in Levant, and East of the Zagros Mountains in Iran First crops of agriculture • Bitter vetch and lentils along with almonds and pistachios appear in Franchthi Cave Greece simultaneously, about 9,000 BC. First crops of agriculture • From at least 7,000 BC the Indian subcontinent saw farming of wheat and barley, as attested by archaeological excavation at Mehrgarh in Balochistan. First crops of agriculture • About 6,000 BC, agriculture was developed independently in the Far East, with rice as the primary crop. First crops of agriculture • Chinese and Indonesian farmers in 6,000 BC went on to domesticate taro and beans including mung, soy and adzuki. First crops of agriculture • Maize, tapioca, and arrow root were first domesticated in the Americas as far back as 5,200 BC First crops of agriculture • Potato, tomato, pepper, squash, several varieties of bean, tobacco, and several other plants were also developed in the New World Evolution of Agri-technology Ancient era The Fertile Crescent of the Middle East is where the earliest planned sowing and harvesting of plants that had previously been gathered in the wild was initiated. Evolution of Agri-technology Ancient era Independent development of agriculture occurred in northern and southern China, Africa's Sahel, New Guinea and several regions of the Americas. Evolution of Agri-technology Ancient era By 7,000 BC, small-scale agriculture was introduced from Egypt to the Indian subcontinent Evolution of Agri-technology Ancient era By 6,000 BC, mid-scale farming was entrenched on the banks of the Nile river. With abundant source of water, new methods of farming and fishing inaugurated together with human population boom Evolution of Agri-technology Ancient era By 5,000 BC, the Sumerians had developed core agricultural techniques including large scale intensive cultivation of land, monocropping, & organized irrigation. Evolution of Agri-technology Ancient era By 5,200 BC, the Greeks and Romans introduced few fundamentally new advances in agriculture with emphasis on the cultivation of crops for trade. Evolution of Agri-technology Middle Ages Muslim farmers in North Africa and the Near East developed and disseminated agricultural technologies including irrigation systems based on hydraulic and hydrostatic principles. Evolution of Agri-technology Middle Ages Muslim farmers also introduced the use of machines particularly the use of water raising machines, dams, and reservoirs. Evolution of Agri-technology Middle Ages Muslim farmers also invented a three field system of crop rotation during the Middle Ages. Evolution of Agri-technology Middle Ages At the same time, Chinese invention of moldboard plow, vastly improved agricultural efficiency Evolution of Agri-technology Modern Era After 1492, a global exchange of previously local crops and livestock breeds occurred. Evolution of Agri-technology Modern Era Started animal exportations, the most important of which were the horse and dog (breeds suited to farm work). Evolution of Agri-technology Modern Era Rapid rise of mechanization (in the late 1900 to 1920), particularly in the form of the tractor, farming tasks could be done with a speed & on a scale previously impossible Evolution of Agri-technology Modern Era In the 1930 – 1940 the introduction of ammonium nitrate fertilizer saw a major breakthrough that allowed crop yields to overcome previous constraints Evolution of Agri-technology Modern Era In the 1930 – 1940 at the same time, the productivity per hectare of farmland began to rise significantly, as did the use of pesticides and herbicides. Evolution of Agri-technology Modern Era In the 1950 – 1960 (Green Revolution) introduction of highyielding varieties of crops, particularly for grains like wheat and rice. Evolution of Agri-technology Modern Era In the 1950 – 1960 developments in irrigation processes, cultivation methods, and the beginning of selective breeding of plants led to an increase in the amount of food produced around the world. Evolution of Agri-technology Modern Era During the 1970s and 80s, many farmers turned toward no-till farming, a practice that allows farmers to grow crops from year to year without tilling and disturbing the soil. Evolution of Agri-technology Modern Era In the 1990s, the first insect and weed-resistant crops became commercially available and satellite technology became more popular to track and plan farming practices Evolution of Agri-technology Modern Era The introduction of molecular technology enable prediction of offspring of crops and livestock, and identify disease-resistant genes in crops, which lessens the chance of crop loss and future disease Evolution of Agri-technology Modern Era The developments in genetic testing and disease surveillance have increased crop yield and improved animal health, and they also provide solutions to the issues posed by modern agriculture regulations. Evolution of Agri-technology Modern Era The year 2010 to the present – marked major technology innovations focused around on indoor vertical farming, automation and robotics. Evolution of Agri-technology Modern Era At the same time flourished the livestock technology, modern greenhouse practices, precision agriculture, artificial intelligence, and blockchain technology. Evolution of Agri-technology Modern Era Blockchain technology enables the traceability of information in the food supply chain (genetic bar coding) and thus helps improve food safety. Evolution of Agri-technology Modern Era It provides a secure way of storing and managing data, which facilitates the development and use of datadriven innovations for smart farming and smart index-based agriculture insurance. 62 63