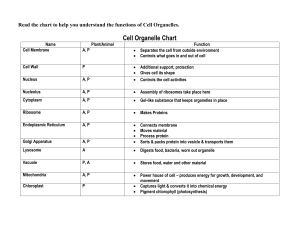
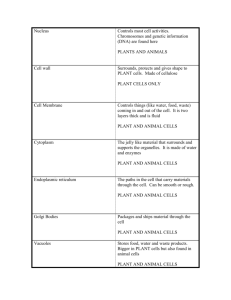
Recognise cell structures under the electron microscope Outline the function of the different cell organelles Cell organelles 1) Nucleus 2) Endoplastic reticulum 3) Golgi apparatus 4) Mitochondria 5) Chloroplasts 6) Lysosomes 7) Ribosomes 8) Centrioles You have 5 minutes to read up on your organelle You must be able to teach everyone else in the group about your organelle Structure Largest organelle Spherical Dark patches=chromatin Surrounded by nuclear envelope Composed of 2 fluid filled membranes Has nuclear poreallows large molecules through Nucleolus inside Function Contains genetic material Chromatin consists of DNA and proteins Contains instructions for making proteins When cells divide, chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes Nucleolus makes RNA and ribosomes. Structure: Consists of flattened membrane-bound sacs cisternae which are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. RER- Ribosomes Smooth ER- no Ribosomes Function: Smooth ER- Involved in making Lipids RER- Transports proteins made on attached ribosomes Golgi Apparatus Structure: Stack of membrane-bound, flattened sacs Function: Receives proteins from the ER Modifies them e.g. adds sugar (Post office) Packages proteins into vesicles to be transported inside cell or to the outside Mitochondria Structure: 2 membranes separated by a fluid filled space Inner membrane is folded to form cristae Central part is the matrix. Function Site where ATP is produced during respiration Chloroplasts Structure: 2 membranes separated by fluid filled space Inner membrane is continuous with a network of thylakoids A stack of thylakoids is called a granum Chlorophyll molecules are present on these membranes. Function: Site of photosynthesis Light energy is used to derive carbohydrate molecules from carbon dioxide. Function: Contain digestive enzymes which break down materials e.g. specialised lysosome (acrosome) in head of sperm cells helps it penetrate the egg. Structure: Spherical sacs surrounded by a single membrane Organelles NOT surrounded by membranes Ribosomes Centrioles Ribosome Structure Very small organelles in the cytoplasm and bound to rough ER Consist of 2 subunits. Function: Site of protein synthesis which acts as an assembly line to use mRNA to assemble proteins. Centrioles Structure Small protein tubes of microtubules. Function: Form fibres in cell division known as spindles which separate chromosomes. Making Cells Make a model of a plant or animal cell out of plastercine You should label the organelles and write a brief function on a cocktail label!! Group Essay In this question, one mark is available for the quality of written communication. Plant cells are also eukaryotic. Outline the function(s) of each part of a plant cell. (Allow one and a half lined pages). [9] Quality of Written Communication [1] [Total 10 marks] nucleus / DNA 1 2 nucleolus 3 4 5 protein synthesis; 6 rough ER transport of proteins; Golgi 7 8 9 processes, molecules / proteins; AW use in secretion; lysosome formation; lysosome 10 11 hydrolytic / digestive, enzymes; breakdown, organelles / cell / ingested material; mitochondria makes / transports, lipids / steroids / hormones; A named plant e.g. rough ER / ribosomes produces, ribosomes / rRNA; smooth ER controls, activities of cell / transcription / named activity / cell division; contains genetic information that can be transmitted to next generation; 12 formation ATP / suitable energy ref.; 13 plasma (cell surface) membrane 14 controls exchange between cell and environment / selectively permeable; R water 15 receptors for, cell recognition / attachment; 16 fluid to allow, endocytosis / exocytosis; cell wall 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 reservoir of, salts / sugars / waste / pigment / other e.g.; ref. to, turgor / support / controlling Ψ; 24 starch grain / amyloplast storage; cytoplasm 25 26 27 site of chemical reaction(s) / correct e.g.; AVP; AVP; photosynthesis; chlorophyll / pigment, absorbs light; vacuole / tonoplast gives, cell shape / strength / support; prevents bursting (when water enters cell by osmosis); fully permeable; chloroplast aerobic respiration; for further detail of function e.g. protein, channels / carriers, to transport, ions / polar substances, phospholipid (bilayer) transports lipid soluble substances ref. waterproofing cell wall (lignin / suberin) mitochondria involved in lipid synthesis addition of carbohydrate to protein to form glycoprotein