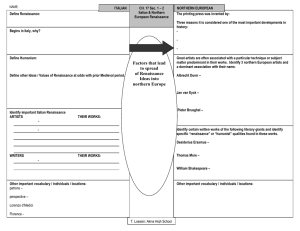
Before 1450, Renaissance humanism had little influence outside Italy; after 1450, these ideas began to spread throughout Europe. The invention of the printing press helped to spread Renaissance ideas throughout Europe. Question: How did Renaissance ideas spread to northern Europe? Growth of Cities • Expanded trade, growth of cities spread Renaissance across Europe • Growing wealthy merchant class eager to support artists Role of Monarchs • Unified governments of England, France supported the arts with money - many rulers viewed artistic achievement as source of national pride Cultural Interaction • In late 1400s, artists fled war in Italy; moved to northern Europe - Italian, northern European artists interacted; shared ideas, styles Question: How did northern Renaissance artwork differ from that of Italian artists? Answer: depicted everyday objects, people as they actually were The Northern Renaissance Main Idea Renaissance ideas soon spread beyond Italy to northern Europe by means of trade, travel, and printed material, influencing the art and ideas of the north Trade, the movement of artists and scholars, and the development of printing helped spread Renaissance ideas north from Italy •Northern scholars traveled to Italy, brought ideas home •Universities started in France, Netherlands, Germany In 1455 Johann Gutenberg printed a complete edition of the Bible using a printing press with movable type. The printing revolution transformed Europe. • Printed books were far easier to produce than hand-copied books. • More people had access to a broad range of learning. • By 1500, the number of books in Europe had risen from a few thousand to between 15 and 20 million. MAJOR WORK OF ARCHITECTURE In Bourges, France the Palais Jacques Coeur 1443 -1451 is a 15th century mansion that marked a turning point in the history of architecture. Built by the rich merchant Jacques Coeur, it will never be inhabited by its owner, who fell into disgrace a few years before the end of the construction. While the 1400’s were a time of peace in Italy, England and France were both fighting each other in the Hundred Years War Flanders was the first place to sponsor artists because it was rich from cloth and trading Italy was divided into city-states, but England and France united under strong monarchs and rulers often sponsored artists Royal courts played a major role in introducing Renaissance styles to northern Europe As ideas spread from Italy, blended with northern traditions= northern renaissance developed its own character In 1494, a French king launched an invasion in through northern Italy Many people (including artists) were forced to flee to a safer life in northern Europe CHARACTERISTICS OF NORTHERN RENAISSANCE ART • Tendency toward realism & naturalism [less emphasis on the “classical ideal”]. • Interest in landscapes. • More emphasis on middle-class and peasant life. • Details of domestic interiors. • Great skill in portraiture. FLEMISH PAINTING (FLANDERS) • First great Flemish Renaissance painter was Jan van Eyck who developed techniques with oil based paints still used today • Oil paintings became popular and spread to Italy • Van Eyck’s paintings display unusually realistic details and reveal the personality of their subjects VAN EYCK -ADORATION OF THE LAMB, GHENT ALTARPIECE, 1432 Inside of St Bravo Cathedral, Ghent Belgium Oil paint on the wood Giovanni Arnolfini and His Wife (Wedding Portrait) Jan Van Eyck 1434 National Gallery, London ROGIER VAN DER WEYDEN (1399-1464) The Deposition 1435 HIERONYMUS BOSCH (1450-1516) • A pessimistic view of human nature. • Had a wild and lurid imagination. • Fanciful monsters & apparitions. • Untouched by the values of the Italian Quattrocento, like mathematical perspective. • His figures are flat. • Perspective is ignored. • More a landscape painter than a portraitist. • Philip II of Spain was an admirer of his work. HIERONYMUS BOSCH THE GARDEN OF EARTHY DELIGHTS 1500 MUSEUM PRADO, MADRID ALBRECHT DÜRER (1471-1528) • The greatest of German artists. • A scholar as well as an artist. • His patron was the Emperor Maximilian I. • Also a scientist • Wrote books on geometry, fortifications, and human proportions. • Self-conscious individualism of the Renaissance is seen in his portraits. • Self-Portrait at 26, 1498. DÜRER – SELF-PORTRAIT IN FURCOLLARED ROBE, 1500 MAJOR WORK - SCULPTURES Claus Sluter Well of Moses 1395 -1406 Limestone, Dijon, France • The Well of Moses (French: Puits de Moïse) is a monumental sculpture recognized as the masterpiece of the Dutch artist Claus Sluter