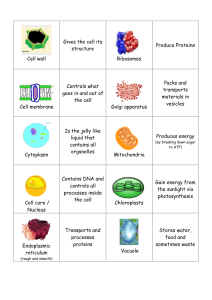
Janae Taylor Function Origin Organelle Name Organelle Function and Origin Plant - Animal - Both Lysosome ★ Lysosomes destroy proteins Both and remove dead cells. ★ Lysosomes are believed to be formed by the joint activity of the endoplasmic reticulum, endosomes and the golgi complex. The precursors are synthesized at the Rough ER then the Golgi complex changes them into enzymes. Vesicles in the Golgi complex are joined by endosomes to form lysosomes. Centriole ★ Centrioles organize microtubules that work as the cell's skeletal system. They help determine the locations of the nucleus and other organelles inside the cell. Centrosome ★ Centrosomes work to direct Animal the movements of microtubules and other cytoskeletal compositions and proteins, eventually allowing large modifications to the shapes of animal cell membranes. ★ Centrosomes are believed to have evolved only in the metazoan (animal) family of eukaryotic cells. Peroxisome ★ Peroxisomes destroy lipids by Both breaking down long chains of fatty acids. ★ The presence of proteins common to many species has been used to suggest an endosymbiotic origin. This means that peroxisomes evolved from bacteria that invaded larger cells as parasites, and slowly evolved Both a symbiotic link. Golgi Appartus ★ The golgi apparatus modifies and packages proteins in vesicles for export. Golgi bodies also synthesize certain polysaccharides and glycolipids. ★ Golgi bodies originated fron the endoplasmic recticulum. The Golgi apparatus receives materials from the cytosol and endoplasmic reticulum in the form of transitional vesicles. The vesicles move to the forming face of the Golgi bodies and fuses there with existing cisternae and support in the maturity of the organelle. (that’s all I could find) Both Secretory Vesicles ★ Secretory vesicles store molecules and proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus until the cell is ready to release them. ★ Secretory vesicles grow from the Trans Golgi network and they release their contents to the cell exterior in response eo extracellular signals. The secreted podut can be either a small molecule or a protein. Animal Mitochondrion ★ The mitochondrion is used for energy production. ★ Mitochondria likely evolved from engulfed prokaryotes that once lived as independent organisms. At some point, a eukaryotic cell engulfed an aerobic prokaryote, which then formed an endosymbiotic relationship with the host eukaryote, steadily developing into a mitochondrion. Both Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum ★ The rough endoplasmic reticulum produces protein. It sends the protein out of the cell. Both ★ The most precise hypothesis is that the endoplasmic reticulum started off from the nuclear envelope. Nuclear Envelope ★ The NE separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells. It also helps in gene regulation. ★ The nuclear envelope is believed to be formed by either a coalescence of vesicles acquired from the endoplasmic rectculum at the surface of the chromosomes or by thin lamellar units of endoplasmic rectculum draping themselves around the chromosomes at the poles in telophase. Animal Nucleoplasm ★ The nucleoplsm stores DNA Animal and promotes an isolated environment where controlled transcriptions and gene regulation is enabled. Nucleolus ★ The nucleous produces and Animal assembles the cell’s ribosomes. ★ The matter from which the nucleous is formed is from a fat-body. It diffuses into the ovarioles, then into the cytolasm and the nuclei of oocytes. It then coalesces to form a single large nucleolus of the Limulus oocyte and the three or four smaller ones of the Tenebrio germ-cell. Nuclear Pore ★ Nuclear pores allows small molecules and ions to diffuse into or out of the nucleus. Nuclear pores also allow proteins to enter the nucleus from the cytoplasm if the proteins have special sequences that showthey belong in the nucleus. Animal Smooth Endoplasmic Recticulum ★ The smooth endoplasmic reticulum produces lipids/fats. It also detoxifies Both poisons and drugs. ★ The most precise hypothesis is that the endoplasmic reticulum started off from the nuclear envelope. Cell Membrane ★ The cell membrane protects Both the cell from damage. It also facilitates communication and signaling between cells. Cilium ★ The cilium keeps the airways Animal clear of mucus and dirt, allowing us to breathe easily and without irritation. ★ The theory suggests that cilium originated from a permanent symbiosis between an ancient Spirochete bacterium (spiral shaped bacteria that can be dangerous to humans) and an Archaebacterium (microorganisms considered to be an ancient form of life that evolved separately from the bacteria and blue-green algae, and they are sometimes labelled as a kingdom). Ribosomes ★ Ribosomes are responsible for bringing amino acids together to make protein. ★ The earliest origins of ribosomes likely lie in the Ribonucleic acid (RNA) world. Studies show that old ribosomes made solely1 of rRNA could have developed the ability to synthesize peptide bonds. Both Central Vacuole ★ The central vacuole stores water. It also pushes the contents of the cell towards the cell membrane, allowing them to take in light energy/maintains turgor pressure against the cell wall. Plant Plasmodesmata ★ The plasmodesmata helps Plant with intercellular communication by allowing molecules to pass directly from cell to cell. ★ The endoplasmic reticulum plays a role in the origin of the plasmodesmata. Plasmodesma originates during cytokinesis when cell plate is created. It is formed at those areas of the cell plate where the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is present and stops the fusion of vesicles. Cell Wall ★ Protecting the cell and giving the cell shape. Plant Chloroplast ★ Chloroplast converts light Plant energy into chemical energy, helping with photosynthesis. ★ Just like the mitochondria, chloroplast likely originated from an ancient symbiosis when a nucleated cell covered a photosynthetic prokaryote. Sources: https://www.khanacademy.org/test-prep/mcat/cells/eukaryotic-cells/a/organelles-article https://www.toppr.com/ask/question/organelle-which-plays-an-important-role-in-detoxification-of-drugs-and-toxins-is/ https://microbenotes.com/plasmodesmata-structure-and-functions/ https://ciliopathyalliance.org/cilia https://biologydictionary.net/centrosome/#:~:text=two%20during%20mitosis.-,Function%20of%20Centrosomes,shapes %20of%20animal%20cell%20membranes https://tardigrade-in.cdn.ampproject.org/v/s/tardigrade.in/question/which-of-the-following-sequence-is-correct-for-theorigin-of-bmlwwclw/amp?amp_gsa=1&amp_js_v=a6&usqp=mq331AQHKAFQArABIA%3D%3D#amp_tf=From%20 %251%24s&aoh=16137083000060&referrer=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.google.com&ampshare=https%3A%2F%2Ftar digrade.in%2Fquestion%2Fwhich-of-the-following-sequence-is-correct-for-the-origin-of-bmlwwclw https://www.nature.com/articles/188239a0 https://www.toppr.com/ask/en-ca/question/golgi-body-originated-from/ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peroxisome#:~:text=The%20protein%20content%20of%20peroxisomes,gradually%20ev olved%20a%20symbiotic%20relationship. https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/plant-cells-chloroplasts-and-cell-walls-14053956/