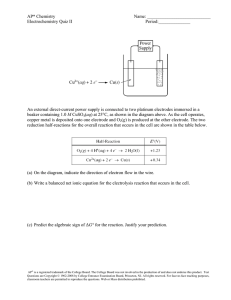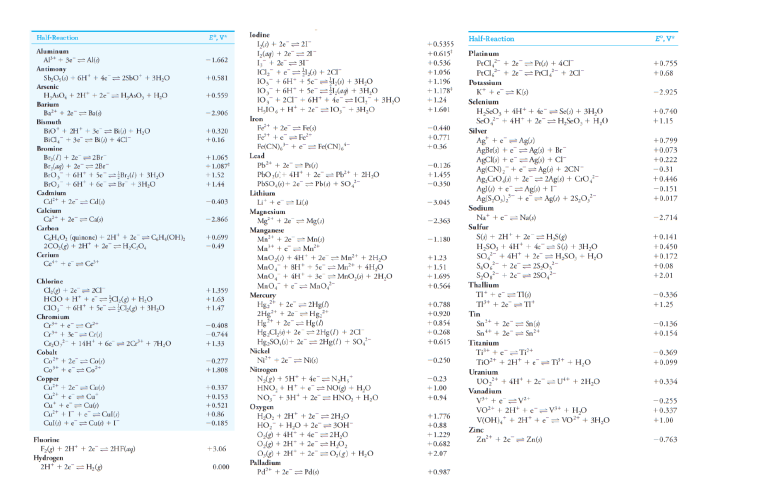
Question 1 In an electrolytic cell, the electrode that acts as a source of electrons to the solution is called the ____; the chemical change that occurs at this electrode is called ____. a. anode, oxidation b. cathode, reduction.. c. Cannot answer unless we know the species being oxidized and reduced. d. cathode, oxidation e. anode, reduction Question 2 In any electrochemical cell, the cathode is always ____. a. the positive electrode. b. the electrode at which oxidation occurs. c. the electrode at which some species gains electrons... d. the electrode at which some species loses electrons. e. the negative electrode. Question 3 At standard conditions, which of the following can oxidize Hg to Hg 2+? a. Zn2+ b. Cl2… c. Cu2+ d. Ag e. Zn Question 4 Standard and Formal Electrode Potentials Half-Reaction E0, V* Formal Potential, V† Aluminum Al3 3e 8 Al(s) 1.662 An aqueous copper(II) sulfate solution is electrolyzed for 45 minutes. A 3.2 ampere current is used. What mass of copper is produced? a. 5.5 g b. 2.8 g… c. 0.95 g d. 4.6 g e. 1.9 g Question 5 Calculate the cell potential of the following voltaic cell at 25°C. Mg|Mg 2+(1.0 10 -6 M)||Ag +(1.0 10 -2 M)|Ag a. +3.23 V b. +3.11 V c. +3.17 V… d. +3.29 V e. +1.63 V Question 6 Calculate the reduction potential of the Cu 2+/Cu electrode when [Cu 2+] = 1.0 10 -8 M. a. +0.37 V b. +0.34 V… c. +0.33 V d. +0.10 V e. +0.35 V Question 7 A voltaic cell is made by placing an iron electrode in a compartment in which the Fe 2+ concentration is 3.0 × 10 –5 M and by placing a Pt electrode in the other compartment, in which the H + concentration is 3.10 M and = 1.00 atm. The Fe 2+/Fe half-cell reduction potential is –0.41 V, and the H +/H 2 half-cell reduction potential is 0.00 V. What is E for the cell at 25 oC? Answer: 0.57 V