Uploaded by
Ellaine Joy Solis
Cell Biology Study Guide: Membrane, Organelles, Transport
advertisement

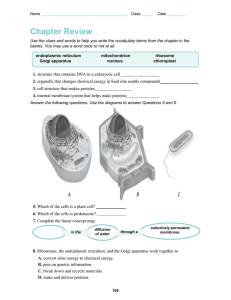
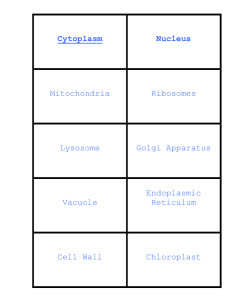
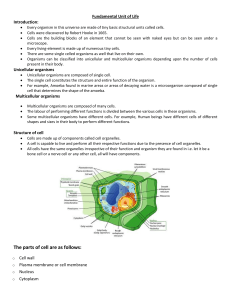
Solis, Elline Joy S. Midwifery 1 CHAPTER 3: CELLS QUESTIONS: 1. State the functions of the organic molecules of cell membranes: cholesterol, proteins, and phospholipids. Cholesterol - decreases the fluidity of the membrane, thus making it more stable. Proteins - Form channels to permit passage of materials such as water or ions. Also, some are carrier enzymes or transporters that also help substances ent erh cell. Phospholipids - They form a bilayer, or double layer, which makes up most of the membrane. They permit lipid-soluble materials to easily enter or leave the cell by diffusion through the cell membrane. 2. Describe the function of each of these cell organelles: mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, and endoplasmic reticulum. Mitochondria (singular mitochondrion) are small organelles responsible for producing considerable amounts of ATP by aerobic (with O2 ) metabolism. Lysosomes - They contain a variety of enzymes that function as intracellular digestive systems. The Golgi apparatus - It collects, modifies, packages, and distributes proteins and lipids manufactured by the ER. Ribosome - Site of protein synthesis The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) - is a series of membranes forming sacs and tubules that extends from the outer nuclear membrane into the cytoplasm 3. Explain why the nucleus is the control center of the cell? Nucleus is the control center of the cell because the nucleus directs all the activities of the cell. It plays a crucial role in determining the way the cell will develop and what form it will exhibit at maturity, by directing the chemical activities of the cell. 4. What part of the cell membrane is necessary for facilitated diffusion? Describe one way this process is important within the body. 5. What provides the energy for active transport? Describe one way this process is important within the body.