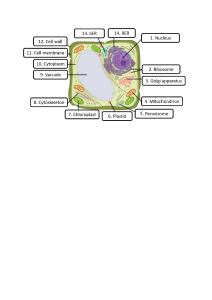
Fundamental Unit of Life Introduction: Every organism in this universe are made of tiny basic structural units called cells. Cells were discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665. Cells are the building blocks of an element that cannot be seen with naked eyes but can be seen under a microscope. Every living-element is made up of numerous tiny cells. There are some single celled organisms as well that live on their own. Organisms can be classified into unicellular and multicellular organisms depending upon the number of cells present in their body. Unicellular organisms Unicellular organisms are composed of single cell. The single cell constitutes the structure and entire function of the organism. For example, Amoeba found in marine areas or areas of decaying water is a microorganism composed of single cell that determines the shape of the amoeba. Multicellular organisms Multicellular organisms are composed of many cells. The labour of performing different functions is divided between the various cells in these organisms. Some multicellular organisms have different cells. For example, Human beings have different cells of different shapes and sizes in their body to perform different functions. Structure of cell Cells are made up of components called cell organelles. A cell is capable to live and perform all their respective functions due to the presence of cell organelles. All cells have the same organelles irrespective of their function and organism they are found in i.e. let it be a bone cell or a nerve cell or any other cell, all will have components. The parts of cell are as follows: o Cell wall o Plasma membrane or cell membrane o Nucleus o Cytoplasm o Endoplasmic Reticulum o Golgi Apparatus o Lysosomes o Mitochondria o Plastids o Vacuole Plasma membrane o o o o o o Plasma membrane is the outermost layer in cells. It separates the content of cell from their external environment. It allows the materials from surrounding to enter and exit the cell. It also allows the materials from cell to exit outside. It controls the entry and exit of materials in nd out of cell and hence it is called selectively permeable membrane. Gases like carbon-dioxide or oxygen can also move in or out from high concentration to low concentration in a cell through the cell membrane by the process of diffusion. It also allows the movement of water in and out of the cell depending upon the concentration outside the cell by the process of osmosis. Cell wall o Cell Wall is found in plant cells outside the plasma membrane. o It is a rigid covering made up of cellulose which a complex substance is providing structural support to the plants. Cytoplasm o A thick solution composed of water, salts, and proteins that fills the cell is called cytoplasm. o It is surrounded by cell membrane. Nucleus o o o o o o The nucleus is small, round and membrane bound structure found in cell. The fluid inside the nucleus surrounded by nuclear membrane is called nucleoplasm. It controls the cell’s growth and reproduction because it contains cell's hereditary information. It is covered by dual layer called nuclear membrane. The nuclear membrane contains pores due to which materials can travel both inside the nucleus from its outer surrounding i.e. cytoplasm. The nucleus contains some thread like structures called chromatin. It exists during the resting stage of cell. o o o o o o o o o The chromatin contains DNA (Deoxy-ribo nucleic acid), RNA (Ribo Nucleic acid) and proteins. The nucleus contains some rod shaped structures in a cell that contains the hereditary information. They are called chromosome. They are formed when the chromatin condenses together when the cell is about to divide. Chromosomes contain DNA and nuclear proteins. They contain the hereditary information for inheritance of features from the parents to the offspring as DNA. The DNA molecules contain the information for construction and organization of cells. Genes are the functional segments of DNA. Human body has 23 pairs of sex chromosomes. A boy has one X chromosome and one Y chromosome whereas a girl has two X chromosomes. The nucleus of cell divides itself to give rise to new offsprings. Genes present in the chromosomes decide the hereditary characters. Endoplasmic reticulum The large network of membranous sheets and tubes is called endoplasmic reticulum. They are filled with fluids and carries materials throughout the cell due to which it is also called transport system of the cell. It transports materials between the regions of cytoplasm or between the cytoplasm and nucleus. It also provides a surface for some biochemical activities of cell. It can be classified into two types: RER (Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum) : The RER appears rough under a microscope as it is lined with ribosomes. SER (Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum): The SER appears smooth under microscope due to absence of ribosomes. It also manufactures fat molecules or lipids that are important for proper functioning of cell. Ribosome: The ribosomes manufacture the proteins which are then transported throughout the cell by the Endoplasmic Reticulum. It is also called as a “Protein Factory of the cell” Golgi apparatus: The stacks of flattened membranous vesicles are called Golgi apparatus. It basically stores, packs and modifies the products in vesicles. It temporarily stores protein that moves out of the cell through the vesicles of the Golgi apparatus. It packs and transports the materials synthesised in Endoplasmic Reticulum to different targets inside and outside the cell. Fig. Golgi Apparatus in Plant cell Lysosomes: The sac-like structures in a cell surrounded by membrane are called lysosomes. They keep the cells clean by digesting and breaking the outside materials like bacteria, food entering the cell or worn-out cell organelles into small pieces. They can digest these organic materials due to the presence of strong digestive enzymes that can break down organic compounds. Therefore, lysosome is also known as a “suicidal bag of the cell”. Mitochondria Mitochondria are round "tube-like" organelles that provide energy to a cell in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) for performing different chemical activities for the sustainance of life. The mitochondria is also called “powerhouse of the cell”. It is surrounded by two membranes. The outer membrane is porous whereas the inner membrane has deep folds that provide a large surface to perform the chemical reactions required for the generation of ATP. The Jelly like substance present in the space enclosed by inner membrane is called matrix. Mitochondria have their own DNA and ribosomes and are hence capable to produce some of their required proteins all by themselves. Plastids Plastids refer to the double membrane bound organelles found in plant cells. They are found in the cytoplasm. Plants make and store food in plastids. They have their own DNA and Ribosomes. They can be classified into three types: Chloroplast: Chloroplasts are the plastids containing the green pigment called chlorophyll. They are necessary to carry the process of photosynthesis. Leucoplast : Leucoplast stores starch, oils and protein granules Prokaryotes and eukaryotes: Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Nuclear Membrane is absent. Nuclear Membrane is present. Membrane-bound cell organelles are absent. Membrane-bound cell organelles are present. Mitochondria are absent. Mitochondria are present. Golgi apparatus is absent. Golgi apparatus is absent. Region bounded by nuclear membrane contains DNA and Proteins. Undefined region with nucleic acid is called nucleoid. The concentration of DNA is low. DNA is found in nucleus, plastids, and mitochondria. Sexual reproduction is absent. Sexual reproduction is generally present. Animal Cell Plant Cell Vacuoles in Plant vs. Animal cell Vacuoles are fluid filled organelles surrounded by a membrane. Animal cells have small sized vacuoles whereas plant cells have large vacuoles. It provides turbidity and rigidity to the plant cell. It acts as storage sacs of cell and stores food, water, sugar, minerals and waste products of the cell.