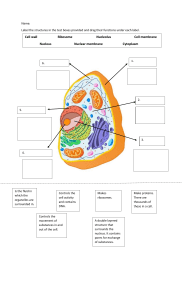
The Ultrastructure of eukaryotic cells: Membrane-Bound organelles Do now: List all of the organelles you can remember Organelles within Eukaryotic cells Within each cell there are tiny structures called organelles. Each organelle has a specific function which allows a cell to carry out its many functions more efficiently due to the labour being divided amongst them. Organelles in Eukaryotic cells • Most of the organelles in Eukaryotic cells are membrane bound • This means they are covered in a membrane which keeps the organelle separate from the rest of the cell Nucleus • A nucleus surrounded by a nuclear envelope and containing DNA organised and wound into linear chromosomes • The nucleolus – an area inside the nucleus containing RNA, where chromosomes unwind. It is also involved in making ribosomes and RNA Rough endoplasmic reticulum • RER is the intracellular transport system: the cisternae form channels for transporting substances from one area of a cell to another • It provides a large surface area for ribosomes, which assemble amino acids into proteins Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum • This is a system of membranes containing cisternae that are continuous with the nuclear membrane • SER contains enzymes that catalyse reactions involved with lipid metabolism e.g. synthesis of cholesterol, lipids/phospholipids and steroid hormones • No ribosomes on its surface unlike the RER Golgi apparatus • This consists of a stack of membrane-bound flattened sacs. • Proteins are modified by adding sugar molecules to make glycoproteins, adding lipids to make lipoproteins, being folded into their 3D shapes • Proteins are packaged into vesicles and then either, stored in the cell, incorporated into the plasma membrane or exported from the cell Mitochondria • Surrounded by two membranes. The inner membrane is highly folded into cristae • Site of ATP production during aerobic respiration • Self-replicating • Abundant in cells where metabolic activity takes place Chloroplasts • • • • Large organelles 4-10 micrometers long Site of photosynthesis Surrounded by a double membrane First stage (when light is trapped by chlorophyll and used to make ATP) occurs in the grana. Water is also split to supply hydrogen ions • Second stage (when hydrogen reduces carbon dioxide to make carbohydrates) occurs in the stroma • Chloroplasts are abundant in the leaf cells (palisade mesophyll layer) Vacuole • Surrounded by a membrane called the tonoplast and contains fluid • Only plant cells have a large permanent vacuole • It is filled with water and solutes and maintains cell stability because when full it pushes the cell wall, making the cell turgid • This helps to support the plant Lysosomes • These are small bags, formed by Golgi • They contain powerful hydrolytic (digestive) enzymes • They are abundant in phagocytic cells • Lysosomes can engulf old cell organelles and foreign matter, digest them and return the digested components to the cell for reuse Cilia and undulipodia • They are protrusions from the cell and are surrounded by the cell surface membrane • Each contains microtubules • They are formed from centrioles • The epithelial cells lining your airways have many hundreds of cilia that waft mucus Questions: Write down 1-7 1. Name one substance that passes out of pores in the nuclear envelope to the cell cytoplasm RNA and Proteins 2. Name one substance that passes into the nucleus via the pores in the nuclear envelope ATP or Nucleic acids or Steroid Hormones 3. Describe the role of the nucleolus Ribosome synthesis and RNA synthesis 4. State two functions of the nucleus Regulate cells activities and carries the genes 5. Name one type of human cell that does not contain a nucleus Red blood cell 6. Suggest why hydrolytic enzymes within cells need to be inside a vesicle Very acidic and can digest the cell from the inside out 7. If you carried out a physical training program, how and why would you expect the number of mitochondria in your muscle cells to change? Increase as more mitochondria are required for aerobic respiration Organelles: - Vacuole - Cell wall - Centrosome - Chloroplast - Peroxisome - Cytoskeleton - Cytoplasm - Cell membrane - Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum - Rough Endoplasmic reticulum - Lysosomes - Nucleus - Nucleolus - Secretory Vesicle - Golgi Apparatus - Mitochondria