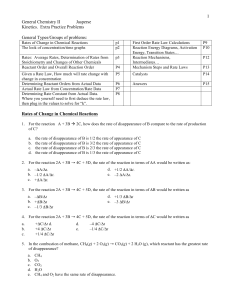
SCH4U Chapter 6: Chemical Kinetics Test Review Before writing the chemical kinetics assessment you should be able to do the following: Determine the rate of reaction from a graph or from given data. Describe how you can measure reaction rate by measuring either reactant consumption or product formation. Understand what has to occur at a molecular level in order for a chemical reaction to take place? Be able to identify the 7 factors that affect reaction rate: ex. concentration, temperature… Understand which of the factors that affect reaction rate cannot be manipulated in order to increase the rate of reaction? Identify the order of reaction for a specific reactant from a graph Be able to determine the rate law and order of a reaction Determine the rate law for a reaction when given either empirical data or a balanced chemical equation Analyze and produce a reaction mechanism. Interpret a rxn mechanism in terms of intermediates, rate determining steps and rate law. Be able to determine the rate law for reactions where the RDS is first and where it is not first. Understand the following terms o activation energy o collision theory o intermediate o rate law o catalyst Test Review Chapter 6 Pg. 396 #1-4, 6-8, 10-14, 16-19, 23, 25, 26, 29, 34, 35, 42, 43, 50, 52, 54, 58, 59, 62, 63, 65, 66, 67, 70, 71 Mixed Questions: 1. Using Figure 9 answer the following for the reaction: A+B C + D a) Determine the enthalpy and overall activation energy. b) What is the RDS? c) Is the reaction endo or exothermic? Explain. d) Which letters represent transition states? e) Which letters represent reaction intermediates? 2. Find the rate law using the data at right. →→→→→→ 3. For the reaction A + B + C → D + E, the rate law is rate = k[A][B][C]. Three possible mechanisms are shown below. Identify whether each one is a likely mechanism for this reaction. If it is not a possible mechanism, explain why not. a. Mechanism 1: Step 1: A + B + C → X + E (slow) Step 2: X → D (fast) Fig. 1 b. Mechanism 2: Step 1 A + B ⇌ X (fast) Step 2 X + C → Y + E (slow) Step 3 Y → D + E (fast) c. Mechanism 3: Step 1 A + B ⇌ X (fast) Step 2 X + C → Y + E (slow) Step 3 Y → D (fast) 4. Which diagram below (if any) would represent the correct energy diagram for the correct mechanism in 3. Above? (C) 5. Use the diagram above (Fig. 1) to generate the reaction mechanism and overall equation. Identify the rate determining step. 6. Consider the following mechanism for a reaction BrCl + H2 ⇌ HBr + HCl fast HCl + BrCl → HBr + Cl2 slow a) Write the chemical equation for the overall reaction b) What is/are the intermediate(s) in the mechanism? c) Write the rate law for the overall reaction. 7. Derive the rate law that is consistent with the proposed mechanism in the formation of phosgene from Cl2 and CO. Note: M is any inert molecule. i. Cl2 + M ⇋ 2 Cl + M (fast equilibrium, K1) ii. Cl + CO + M ⇋ ClCO + M (fast equilibrium, K2) iii. ClCO + Cl2 → Cl2CO + Cl (slow, k3) The overall reaction is Cl2 + CO → Cl2CO