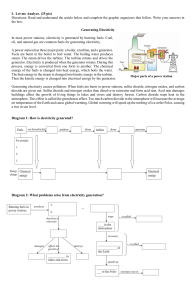
Energy & Usage Fossil Fuels • A fossil fuel is a nonrenewable energy resource formed from the remains of organic life that release CO2 when combusted • Issues with fossil fuels include: • Releasing CO2 and greenhouse gases when burned • They’re used up faster than they’re replaced (supply is limited) • Use has environmental consequences Fuels for Purpose • We have four main uses for fuel: • • • • Transportation Manufacturing Heating and cooling buildings Generating electricity to run machines and appliances • Fuels are used for different purposes based on their energy content, availability, safety, and byproducts Power on “Demand” • Electricity is more convenient because the energy in fuel is converted before its used and can be transported quickly across distances • Disadvantages are that it is difficult to store and other energy sources have to be used to generate it How Electricity is Generated Generating Electricity • A generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by moving an electrically conductive material within a magnetic field • Commercial generators convert the movement of a turbine into electrical energy. A turbine is a wheel that changes the force of moving gas into energy that can do work and spins the generator to produce electricity • These can be spun by steam released from boiling water heated by using a coal or gas fired plant, or from the fission of uranium in nuclear plants World Energy Use • The difference in energy use among developed countries depends on how energy is generated and used in those countries Energy Use in the United States • The US uses more energy per person than most other countries • Residents of the United States and Canada have some of the lowest gas taxes in the world • Countries with limited fossil fuel resources supplement their energy needs with other sources Energy Security • Energy security is the ability to have sufficient, reliable, and affordable energy supplies for the needs of a country • Factors that can affect energy security: • Physical availability or exhaustion of natural resources • Political relationships with energy secure countries • Economic cost of imported supplies