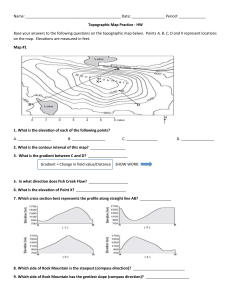
Field Maps Topic 4 Field Maps Field maps show a certain value over a given space. Examples of field include temperature, pollution, noise, elevation, etc. Isolines are lines drawn to connect values that are the same. Isotherms – equal temperature Isobars – equal atmospheric pressure Contour lines – equal elevation Drawing Isolines Connect equal values Infer where values may be. 10 would be between 5 and 15. The interval is the difference in value between lines. This value must remain constant. Isotherms connect equal temperature. Isolines Notes Isolines “never” cross If isolines are closer together, rate of change will be greater If isolines are further apart, rate of change will be less. Gradient = Change in value Distance Topographic Maps Contour maps are field maps where elevation is the value measured. Contour lines only cross if there is a cliff Contour lines bend upstream when there is a river. V’s point upstream Closer contour lines – steeper gradient Maximum elevation is one less than next contour line. The V’s are due to erosion by the river. The V’s point upstream. Depressions Depressions are indicated with hatchur marks on the contour lines. First hatchur line and last elevation line must be equal. The interval remains the same. Minimum elevation is one more than next lower hatchur line. Topographic Profiles A profile is a side view of a topographic map. How to Make a Profile 1. 2. 3. Write values for each isoline that crosses the profile line. Place a piece of scrap paper from point to point. Mark the paper and include the values.