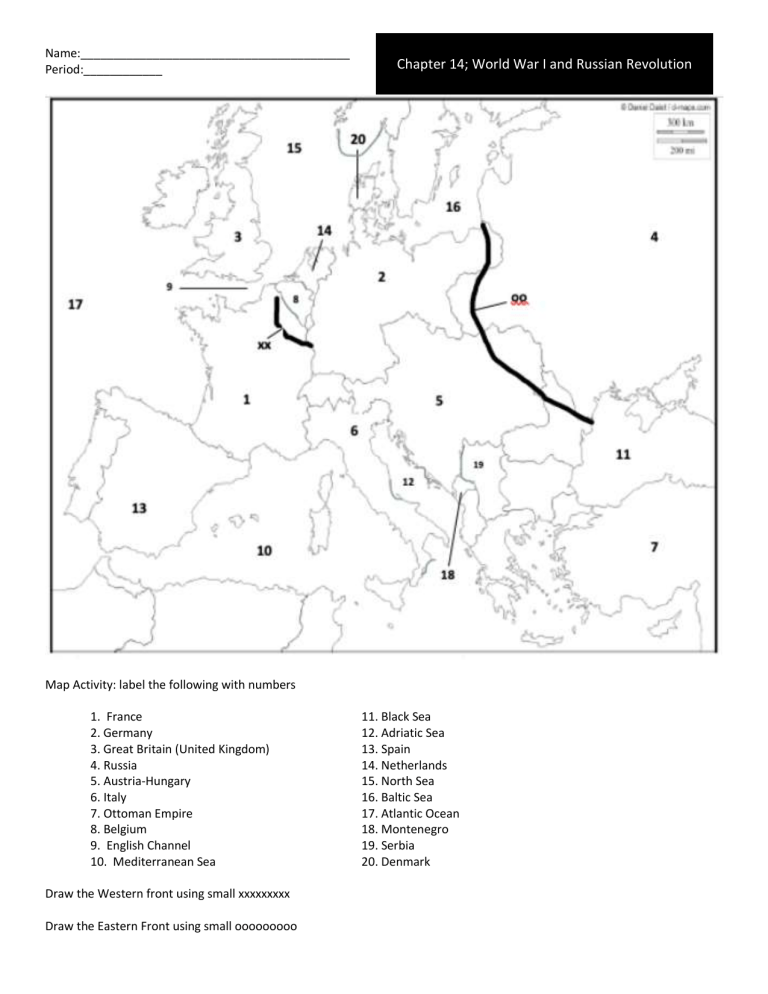
Name:_________________________________________ Period:____________ Chapter 14; World War I and Russian Revolution Map Activity: label the following with numbers 1. France 2. Germany 3. Great Britain (United Kingdom) 4. Russia 5. Austria-Hungary 6. Italy 7. Ottoman Empire 8. Belgium 9. English Channel 10. Mediterranean Sea Draw the Western front using small xxxxxxxxx Draw the Eastern Front using small ooooooooo 11. Black Sea 12. Adriatic Sea 13. Spain 14. Netherlands 15. North Sea 16. Baltic Sea 17. Atlantic Ocean 18. Montenegro 19. Serbia 20. Denmark World War I Vocabulary Central Powers Allied Powers militarism ultimatum mobilize neutrality stalemate total war contraband conscription propaganda atrocities armistice self-determination fourteen points Treaty of Versailles reparations collective security mandates League of Nations radicals Stalemate 1. A deadlock in which neither side is able to defeat the other Mobilize 2. To prepare military forces for war Militarism 3. The glorification of the military Ultimatium 4. Final set of demands Neutrality 5. Policy of supporting neither side in a war Central Powers 6. Alliance of nations; Germany, Austria- Hungary, Ottoman Empire, Japan Allied Powers 7. Alliance of nations; Great Britain (United Kingdom), France, Italy, Russia, Greece, Portugal, Romania Total war 8. Governments take a stronger role in directing the economic and cultural lives of their people Conscription 9. Mandatory military or civilian service that required all young men to be ready for military or other service (often referred to as a draft. Propaganda 10. The spreading of ideas to promote a cause or to damage an opposing cause Atrocities 11. Horrible acts committed against innocent people Armistice 12. An agreement to end fighting fourteen points 13. List of terms for resolving the War to end all Wars, called for freedom of seas, free trade, large scale reduction of arms (weapons), and an end to secret treaties self-determination 14. The right of people to choose their own form of government reparations 15. Payments for war damage collective-security 16. A system in which a group of nations acts as one to preserve the peace of all Treaty of Versailles 17. Ended World War I Radicals 18. People who wanted to make extreme changes League of Nations 19. Group of more than 40 nations that agreed to negotiate disputes rather than resort to war and to take common actions against any aggressor state mandates 20. Territories administered by Western powers contraband 21. raw materials needed to make military supplies, not items such as food or clothing. Chapter 14 Section 1; The Great War Begins What two large alliances took shape before the beginning of World War I? The Triple Alliance; Germany, Italy, Austria-Hungary The Triple Entente; France, Britain, and Russia Why did Germany form alliances with Italy and Austria-Hungary? To protect itself against a potential attack by France and/or Russia How did Germany feel about the other great powers? Germany felt that it was not respected enough by other nations How did other great powers feel about Germany? Britain feared Germany’s economic potential and resented Germany’s challenge towards its navy. France was still angry with Germany after it lost the Franco-Prussian War and the provinces of Alsace and Lorraine How did international competition and nationalism increase tensions in Europe? Economic competition, imperial rivalries, and an arms race created antagonism between great powers. Nationalism contributed to the situation, and it threatened central authority in Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire Why did Austrian leaders send Serbia an ultimatum that they knew Serbian leaders would refuse to honor? They wanted to provoke a war in order to crush Serbia so it could no longer threaten the AustriaHungarian empire. How did Germany encourage Austria’s actions? Germany backed up Austria with a ‘blank check’ giving the Austrian leaders more confidence in their course of action. What happened because of the assassination of Francis Ferdinand and his wife? Austria blamed Serbia for the assassination and took the opportunity to attack Serbia, Germany backed Austria How was France drawn into the war? Why did Britain declare war? France supported its ally Russia and Germany demanded that France keep out of the conflict Britain had an agreement guaranteeing Belgian neutrality. Britain declared war after Germany invaded Belgium on the way to France How did the alliance system deepen the original conflict between Austria-Hungary and Serbia into a general war? Alliances drew more and more countries into what began as a regional conflict. Russia stood by its ally, Serbia. France in turn stood by its ally Russia. Undecided Britain was drawn in when Germany invaded neutral Belgium Why were young men on both sides eager to fight when World War I started? Because of renewed sense of patriotism, people rushed to fight for their homelands. Chapter 14 Section 2; A New Kind of War How did the Allies stop the Germans from executing the Schlieffen Plan? Russian mobilized quickly in the east, causing Germany to divert troops there. The British and French stopped the weakened German advance at the Marne How id the Schlieffen Plan fail? Germany diverted troops from France to the Eastern Front, where Germany fought Russia. French Troops strengthened by British forces, stopped German forces at the first battle of Marne What happened with the Schlieffen Plan failed? Stalemate; Trench Warfare What made World War I much more deadly than pervious wars? New or improved guns and artillery caused more casualties. Poison gas terrified soldiers. Submarines sank many ships. How did the weapons of World War I make trench warfare necessary? Opposing sides dug trenches to protect themselves from the exploding shells and waves of bullets Why would tanks have been useful on the Western Front? How did these weapons make warfare much deadlier than in Napoleon’s day? (when rifles were still hand-loaded) The weapons were able to kill more people quicker Why did tanks fail to break the stalemate? The first tanks did not work properly Tanks would have been able to break through the barbed wire and ride over the uneven terrain of no man’s land. How was the Eastern Front similar to the Western Front? How was the Italian Front similar to the Western Front? From 1915 to 1916 the battle lines did not move Many battles were fought over the same land, with the same results In what ways was the Eastern Front different from the Western Front? The Eastern Front shifted over more area than the Western Front, with less trench warfare and even more casualties How did World War I affect the Ottoman Empire, European Colonies and dominions? The Ottoman Empire joined the Central Powers but eventually lost territory due to an Arab revolt that was supported by the British, British India, French West Africa, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand sent troops to support the Allies Chapter 14 Section 3; Winning the War How did governments manipulate their economies to support the war? Raised taxes, borrowed money, rationed goods, set prices, and forbade strikes How did Britain strike at Germany’s economy? Britain blockaded Germany, so that Germany could not import needed goods. How did Germany strike at Britain’s economy? Germany tried to stop the flow of goods to Britain as well Why was it important for both sides to keep civilian morale high during the war? Total War demanded that civilians work tirelessly to produce and conserve goods needed to keep the war going. If civilians were unhappy, they might not work well or they might create domestic unrest that would upset war plans and demoralize soldiers Why were people tired of war by 1917? There were many casualties, food shortages, and few decisive victories How could low morale hurt a country fighting a war? Troops may refuse to continue fighting or not fight well; civilians may not work hard to contribute materials that supported the war; both troops and civilians may rebel to end the war What happened to Russia, partly because of low morale? The people rebelled and overthrew the government, Russia pulled out of the war. How did Russia’s loss of morale affect the strategic position of the Allies in World War I? Poor morale, among other factors, led to revolution in Russia and Russia’s eventual withdrawal from the war, which weakened the Allies What are the three factors that led to the United States to enter the war? Three of the following; unrestricted submarine war, cultural ties, the Zimmerman Note, US President Wilson’s desire to make the world safe for democracy. How did the Central Powers try to take advantage of the delay in American troops arriving on the battlefield? They pushed to win the war before American troops arrived What was the outcome of the Central Power strategy? The Germans pushed back troops on the Western Front but were unable to win before American reinforcements arrived Why did Germany ask the Allies for an armistice in November 1918? Its las drive failed because the Allies were renewed by American troops and domestic unrest for Germany disrupted the government Chapter 14 Section 4; Making the Peace What were some of the human, economic, and political costs of the war? Due to the war, millions of soldiers and civilians lost their lives, property was destroyed, and several countries experienced political turmoil and unrest How did the goals of the Big Three leaders conflict at the Paris Peace Conference? US President Wilson wanted peace without revenge. Lloyd George wanted to please the British people by punishing Germany and getting money to fulfill his postwar goals. Clemenceau wanted to weaken Germany so that it could never threaten France again. Why were the German delegates surprised when they read the treaty? They believed that the treaty would be based on the more lenient Fourteen Points. Explain the Treaty of Versailles, the parts of the treaty, use detail? Germany assume full blame for the war Huge reparations; paid for the cost of the war, paid pensions for allied soldiers or widows Limited size of German military Returned Alsace and Lorraine to France Removed territory from Western and Eastern Germany Removed German overseas colonies Germans people had to leave homes in Russia, Poland, Alsace-Lorraine Why did the League of Nations fail to accomplish US President Wilsons dreams? The United States did not join the league and so did not have a leading role. The League was too weak to stop new wars from starting.




