Uploaded by
Stephanie Trinh [Mojave HS]
Astronomy & Physics Notes: Luminosity, HR Diagram, Big Bang
advertisement

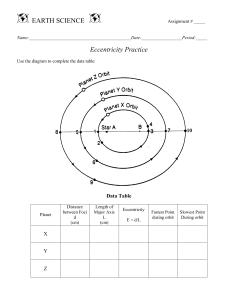
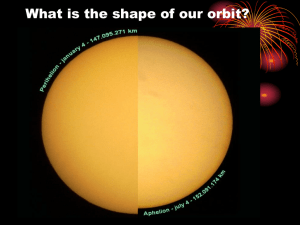
Luis Serrano P2 Notes Luminosity Absolute magnitude - How bright a star actually is. Apparent magnitude - How bright a star appears from Earth. HR Diagram A graph of stars' brightness (luminosity) and temperature. shows color shows the type of stars. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram HR Diagram - Cheat Sheet Luis Serrano P2 Notes Light Energy from stars is transferred in the form of light. And light moves in a wave pattern. Wavelength of a Wave Wavelength - Distance between tips of a wave. (side to side) Measured in nanometers (nm) Frequency: How often the wave goes up and down - # of waves that pass a point during a certain time period - hertz (Hz) =1/s Frequency and wavelength are inversely related. -As frequency goes up wavelength goes down. Frequency and energy are proportional. Higher frequency means higher energy. - Ex: High wavelength = low frequency = low energy Electromagnetic spectrum The entire range of frequencies and wavelengths. The visible spectrum is the only part of the EM s pectrum we can see, and is only one small part. Travel through space at a speed of 300,000,000 m/s. (Speed of Light) Light Year Light year: the distance light travels in one year. Visible Spectrum The part of the spectrum we can see. R O YG. B I V Red Longer wavelengths (~700 nm) Lowest frequency Lowest energy Viole Shorter wavelengths (-400 nm) Highest frequency Highest energy Luis Serrano P2 Notes Spectroscopy Notes The Light of Stars what elements that make it up. Spectroscopy - The study of light given off by elements. -A spectral line is the unique combination of light that is emitted/absorbed by each element. Spectral lines of elements are similar to fingerprints Spectra of Stars Stars emit light across the whole visible spectrum, there is just more light from the area that matches their spectra, or "fingerprint". Each element absorbs part of it creating a “gap" called a spectral line Spectral Lines When the elements absorb the light it makes these black absorption lines By seeing what parts of the spectrum are missing, we can determine what elements are present. Each element has a unique line combination. Spectral Lines and Stars By looking at the spectral lines of a star's light we can tell what elements are in it. -If it has all of the element's lines it has the element Luis Serrano P2 Notes Doppler Effect Doppler Effect: A change in the frequency of a moving wave relative to an observer. -Works for light and sound Diagram: Sketch this Stationary source Moving Source Away: Waves "leaving" A are "expanded" Wavelength long Frequency lower Sound pitch lower Towards you: Waves near B are "compressed" Wavelength short Frequency higher Sound pitch higher Doppler Effect for Light Movement causes the light waves to be bunched up. This causes light to change color. Luis Serrano P2 Notes Big Bang Theory Notes Expanding Universe it has been observed that light from distant galaxies is redshifted, meaning they are moving away from us. Hubble's Law All galaxies are moving away from us! And the farther away they are, the faster their velocity appears to be… Basically the universe is expanding and it's getting faster Big Bang Theory -universe is expanding -trace back in time -13.8 billion years ago everything was in a singularity: A single point that held all of matter -It started expanding and is still expanding today (evidence: red shifted stars and galaxies) -after initial expansion stuff cooled and hydrogen and helium formed. -Once atoms formed, they could give off light and lots of heat! leftover light can still be measured today. Cosmic Background Radiation -Light/Radiation given off by the first atoms created. -Leftover microwave radiation from the Big Bang that can be detected all around us that is still cooling. -This sets the base temperature for space, 2.7 K (37° F) Luis Serrano P2 Notes Kepler's 1st Law -Johannes Kepler made the Three Laws of Planetary motion. -They describe how planets move. -1st Law - Planets move in an elliptical orbit around the sun. Circular Orbit -Circular orbits are based around a single central point (one focus). -No matter where you are on the circle, you're always the same distance from the center. Elliptical Orbit -Elliptical orbits are based around a single, non-central point called a focus. Parts of an Elliptical Orbit -Ellipses have 2 foci that are the same distance from the center on the major axis. -For orbits, one focus is the sun. -Perihelion - Point closest to the sun. -Aphelion - Point farthest from the sun. -An axis is an imaginary line down the center of an ellipse. -Major Axis - The long one. -Minor Axis - The short one. - Semi-Major Axis is from center of the Major axis edge of ellipse. - Semi-Minor Axis is from center of the Minor axis edge of ellipse. Eccentricity how elliptical an orbit is by the eccentricity (e). Eccentricity actually tells us how different from a perfect circle the shape is. -The higher the eccentricity = the more elliptical the orbit -Eccentricity of 0 is a perfect circle (round) -Eccentricity of 1 is a straight line (elliptical). Luis Serrano P2 Notes Kepler's Second Law Part 1: Planets move faster when they are closest to the sun (perihelion point) -due to the greater gravitational force. -slowest at the farthest point from the sun (aphelion point) Part 2: planets will cover the same area in the same given time period. -A and B took the same time to cover -Segment B is equal in area to Segment A Kepler's 2nd Law Luis Serrano P2 Notes Kepler's 3rd Law -Kepler's Third Law - The square of the orbital period of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of its distance to the Sun. -Basically the farther a planet is from the sun (a), the longer it will take to orbit the sun (p). Kepler's 3rd Law Equation pa= a3 p = Orbital Period, time required for the planet to orbit the sun (Earth years) a = Distance to the Sun. The semi-major axis of the elliptical orbit. (AU) Calculating Period (p) calculate how many years it takes something to orbit. 1. Find a 2. Find a? 3. Find Va3 Worked Example A Planet Karl is 0.72 AU from the sun. Find how long it takes the planet to orbit the sun. 1. Find a a = 0.72 2. Find a3 0.72^3 = 0.373248 3. Find Va3 sqrt 0.373248 = 0.6109 years Luis Serrano P2 Notes Gravity Notes Force -Gravity is a kind of force. - Force is a push or a pull -Vectors -they have direction and magnitude. -longer vector = greater force -if all forces are not balanced the object will move. Gravitational Force -Gravitational force is the force that attracts all things with mass toward each other. -Objects in space would move in a line, but gravity makes them curve and orbit around another object. Mass and Distance The gravitational force between objects depends upon their: 1. Masses (greater mass means greater force of gravity) 2. Distance apart (greater distance means less force of gravity) Acceleration due to Gravity All objects fall toward the earth at the same rate of acceleration, regardless of their masses! Weight Vs Mass - Weight is the force caused by gravity Change depending on gravity Mass is the amount of matter (atoms) in an object. Stays the same